體檢人群幽門螺桿菌感染與血清胃蛋白酶原的關系研究
張 群,蔣葉華,董 連,李曉娜
(1.南京醫科大學第一附屬醫院健康管理中心,江蘇 南京 210029;2.江蘇省原子醫學研究所,江蘇 無錫 214063)
體檢人群幽門螺桿菌感染與血清胃蛋白酶原的關系研究
張群1,蔣葉華2,董連1,李曉娜1
(1.南京醫科大學第一附屬醫院健康管理中心,江蘇南京210029;2.江蘇省原子醫學研究所,江蘇無錫214063)
[摘要]目的:通過篩查體檢人群幽門螺桿菌(Hp)感染情況,并檢測其血清胃蛋白酶原(PG)的含量,探討Hp感染與血清PG的關系。方法:選取2013年4月~2014年6月間在江蘇省人民醫院體檢的735名受檢者,采用HG-IRIS13C紅外光譜儀測定Hp感染情況,時間分辨熒光免疫法(TRFIA)檢測血清中PG I和PGⅡ水平。結果:血清PG I水平異常組(高于正常組、低于正常組)的Hp陽性率明顯高于PG I水平正常組,差異有統計學意義(P<0.05);血清PG II水平高于正常組的Hp陽性率明顯高于PG II水平正常組,差異有統計學意義(P<0.05);PG I/II比值低于正常組的Hp陽性率明顯高于正常組,差異有統計學意義(P<0.05)。Hp陽性組的血清PG I、PG II水平顯著高于陰性組,差異有統計學意義(P<0.05),PG I/Ⅱ比值則顯著低于陰性組(P<0.05)。Hp感染與血清PG I、PG II水平呈正相關,與血清PGI/II比值呈負相關。結論:血清PG水平的變化與Hp感染相關。血清PGI、PGII水平升高,PG I/PG II比值下降提示HP感染的可能。
[關鍵詞]幽門螺桿菌;胃蛋白酶原;體檢
Abstract:ObjectiveTo screen the situation of Helicobacter pylori(Hp) infections and detect the level of serum pepsinogen(PG)in physical examination people.Then to study the relation between Hp infections and the level of serum PG.MethodA total of 735 subjects who had physical examination in Jiangsu Province Hospital from April 2013 to June 2014 were recruited.The Hp infections were determined by HG - IRIS13C infrared spectrometer.Fasting serum samples for PG Ⅰ and PGⅡ determination were analyzed by time-resolved fluoroimmunoassay (TRFIA ).ResultsThe positivity rate of Hp infection were significantly higher in abnormal PG Ⅰ level group (higher than normal group,lower than normal group) than that innormal PG Ⅰ level group(P<0.05).The positivity rate of Hp infection was obviously higher in raised PG Ⅱ level group than that in normal PG Ⅱ level group(P<0.05).In reduced PG Ⅰ/Ⅱ ratio group,the positivity rate of Hp infection was obviously higher than that in normal PG Ⅰ/Ⅱ ratio group(P<0.05).The PG Ⅰ,PG Ⅱ level of HP-positive group were significantly higher than Hp-negative group(P<0.05).PG Ⅱ/Ⅱ ratio were significantly lower than Hp-negative group (P<0.05).Hp infection was positively related to serum PG Ⅰ,PG Ⅱ level and negatively related to PGⅠ/Ⅱ ratio.ConclusionHp infection is related tothe change of PG level.Increased serum PG Ⅰ,PG Ⅱ level and decreased serum PGⅠ/Ⅱ ratio suggest Hp infection.
基金項目:江蘇省衛生廳科技項目課題[項目編號:H201335]
Doi[15]Lorente S,z O,Trinidad Semno M,et al.Helicobacter pylori stimulates pepsinogen secretion from isolated human peptic cells[J].Gut,2002,50(1):13.
[收稿日期:2015-04-07編校:王麗娜]
The study on the relationship between Helicobacter pylori infections and serum pepsinogen in physical examination peopleZHANGQun1,JIANGYe-hua2,DONGLian1,etal(1.Departmentofhealthmanagementcenter,theFirstAffiliatedHospitalofNanjingMedicalUniversity,Nanjing210029,China;2.JiangsuInstituteofNuclearMedicine,Wuxi214063,China)
Key Words:Helicobacter pylori;Pepsinogen;Physical examination
目前幽門螺桿菌(Helicobacter pylori,Hp)感染已被國際癌癥研究中心列為I類致癌因子,被證實與多種胃良惡性疾病的發生發展密切相關[1]。胃蛋白酶原(pepsinogen,PG)是胃蛋白酶的無活性前體,可分成PGI、PGII 兩個亞群。血清PG的水平可反映胃中PG的分泌及胃黏膜的狀態和功能情況。關于Hp感染與血清PG水平的變化關系目前已有一些文獻報道,但結論不一,且在體檢人群中研究Hp感染與血清PG水平相關情況的報道較少,故本文擬通過篩查體檢人群Hp感染情況,并檢測其血清PG的含量,探討Hp感染與血清PG的關系。
1資料與方法
1.1研究對象:選擇2013年4月~2014年6月間在江蘇省人民醫院進行體檢的735名受檢者,其中男429例,女306例,年齡17~87歲。
1.2Hp測定:受檢者空腹8 h以上,收集呼出氣體10 ml,口服13C標記液體后保持安靜坐姿30 min,再收集另外10 ml呼出氣體,一并送檢。采用HG-IRIS13C紅外光譜儀(北京華亙安邦科技有限公司產品)測定Hp感染情況,測定值<4.0‰為Hp感染陰性,≥4.0‰為Hp感染陽性。
1.3PG測定:受檢者抽取空腹靜脈血,分離出血清后置于-4℃冷凍保存。采用夾心法PGI和PGII時間分辨熒光免疫分析(time-resolved fluoroimmunoassay,TRFIA)試劑盒(無錫市江原實業技貿總公司產品)測定血清中PG I和PGⅡ水平,檢測儀器為美國PE公司Auto DELFLA 1235全自動TRFIA檢測儀。PG I正常參考值范圍為60~240 g/L,PGⅡ正常參考值范圍為<27 μg/L,PG I/II正常參考范圍為>6。
1.4統計學處理:采用STATA7.0軟件進行統計學分析。分類變量采用χ2檢驗,連續變量采用t檢驗,相關影響因素采用logistic回歸分析,P<0.05為差異有統計學意義。
2結果
2.1不同血清PG水平組Hp感染情況:血清PG I水平異常組(高于正常組、低于正常組)的Hp陽性率明顯高于正常組;血清PG II水平高于正常組的Hp陽性率明顯高于PG II水平正常組;PG I/II比值低于正常組的Hp陽性率明顯高于PG I/II比值正常組。見表1。
2.2不同Hp感染組血清PG情況:Hp陽性組的血清PG I、PG II水平均顯著高于陰性組,PG I/II比值則顯著低于陰性組。見表2。
2.3Hp感染與血清PG水平相關性:Hp感染與血清PG I、PG II水平呈正相關,與血清PGI/II比值呈負相關。見表3。
表1不同血清PG組Hp感染情況比較(例)
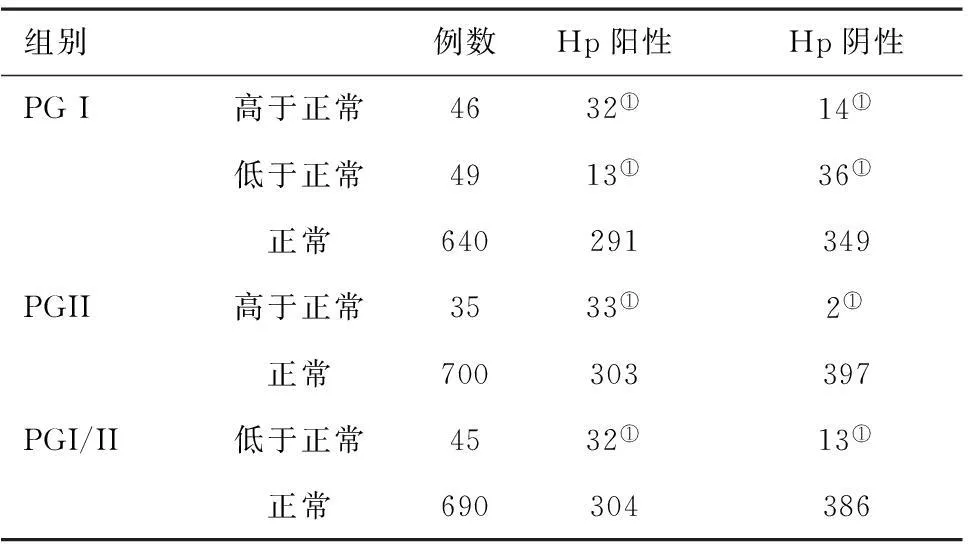
組別例數Hp陽性Hp陰性PGI高于正常4632①14①低于正常4913①36①正常640291349PGII高于正常3533①2①正常700303397PGI/II低于正常4532①13①正常690304386
注:與正常相比,①P<0.05
表2不同Hp感染組血清PGI、PGII水平及PGI/Ⅱ比值情況比較


Hp例數PGI(g/L)PGII(g/L)PGI/II陽性組336155.33±69.1617.38±10.629.95±3.72陰性組399116.66±55.928.59±5.9015.09±7.36
注:與陰性組相比,tPGI=-8.38,tPGII=-14.15,tPGI/II=11.61,①P<0.05
表3Hp感染與血清PGI、PGII水平及PGI/Ⅱ相關性分析
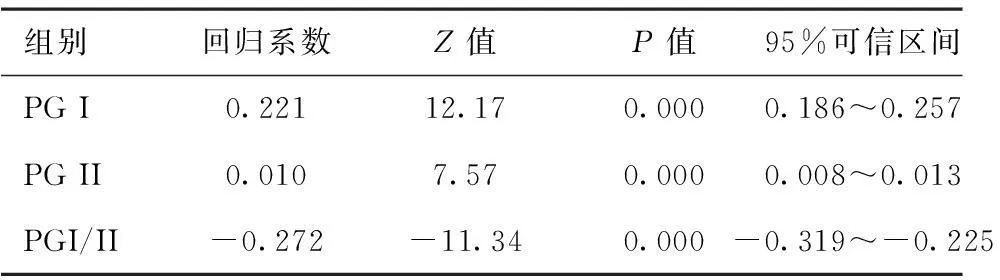
組別回歸系數Z值P值95%可信區間PGI0.22112.170.0000.186~0.257PGII0.0107.570.0000.008~0.013PGI/II-0.272-11.340.000-0.319~-0.225
注:PGI、PGII、PGI/II三組logic回歸方程χ2=255.43、67.5、196.7,P<0.01
3討論
近年來,研究顯示發展中國家的人群Hp感染率高達50%~80%[2-3]。Hp感染不僅是慢性活動性胃炎、消化性潰瘍、胃黏膜相關淋巴瘤和胃癌主要致病因素,還可導致心血管系統、血液系統、免疫系統、皮疹等多種全身性疾病的發生,嚴重損害人類的健康[4-8]。目前,關于HP感染的檢測方法很多,包括有細菌學、病理學、血清學、同位素示蹤、分子生物學等[9-10]。
其中組織病理是診斷Hp感染的金標準。此外,國內外多篇大型流行病學研究還提示,Hp感染與血清PGI,特別是PG II升高相關,與PG I/II比值的降低相關[11-13],可能對Hp感染的診斷具有一定的價值。本研究通過logistic回歸分析分析血清PG水平和Hp感染的相關性,也提示兩者間存在一定的依存關系。
Hp感染通過刺激主細胞,增加主細胞內鈣離子流、cAMP和磷酸肌醇濃度,從而刺激主細胞合成和分泌PG(主要是PG II)[14-15]。這可能也是本研究中Hp陽性組PGI、PGII水平升高,尤其是PGII升高明顯,PG I/PG II比值下降的機制之一。另一項在日本和德國人群中開展的研究中也發現Hp感染致PG I明顯增高的現象,且Hp陽性受試者PG I水平和PG I/PG II比值與胃酸分泌量相關[16]。
由于PG I主要存在于胃體,而PG II除胃體外,也可見于胃竇、十二指腸近端和十二指腸腺(Brunner腺)。因此,胃黏膜不同部位的病變及程度可導致PG I、PGII水平及PG I/PG II比值產生不同的變化。本研究中部分Hp陽性受檢者血清PG I、PGII水平在正常范圍,可能即與PG反映胃部病變的這種局限性有關。至于少量Hp陰性受檢者血清PG I、PG II水平不在正常范圍,則可能與消化道病變不一定都伴有Hp感染有關。
總之,血清PG水平和Hp感染相關,血清PGI、PGII水平升高,PG I/PG II比值下降提示HP感染存在的可能,在體檢中適當開展血清PG檢測或可提高HP感染篩查的有效性及準確性。
參考文獻4
[1]Suerbaum S,Michetti P.Helicobacter pylori infection[J]. Springer Netherlands,2005,35(13):37.
[2]劉泉,竇丹波.幽門螺桿菌感染與治療現狀[J].中華實用中西醫雜志,2010,23(1):15.
[3]童能勝,史瑞燕.2239例體檢者幽門螺桿菌感染監測結果分析[J].標記免疫分析與臨床,2010,17(4):267-268.記免疫分析與臨床,2010,17(4):267.
[4]Chaabane NB,Mansour IB,Hellara O,et al.Role of Helicobacter,pylori infection in iron deficiency anemia[J].Presse Med,2011,40(3):239.
[5]Enomoto S,Maekita T,Ohata H,et al.Novel risk markers for gastric cancer screening:Present status and future prospects[J].World.J Gastrointest Endosc,2010,2(12):381.
[6]Hybenova M,Hrda P,Potuznikova B,et al.Lymphocyte proliferative response to Helicobacter pylori antigens in H.pylori-infectedpatients[J].Folia Microbiol(Praha),2010,55(6):649.
[7]Tan VP,Wong BC.Helicobacter pylori and gastritis:Untangling acomplex relationship 27 years on[J].J Gastroenterol Hepatol,2011,26(Suppl 1):42.
[8]高歌,周長玉,林種玉,等.Hp感染與胃癌及癌前病變中p53、bcl-2、c-myc基因表達關系的研究[J].中國腫瘤臨床,2002,29(5):325.
[9]管彩霞,劉鴻燕,楊秀清.淺析幽門螺桿菌的臨床實驗室檢測[J].臨床醫藥實踐,2010,19(6):443.
[10]Kokkola A,Rautelin H,Puolakkainen P,et al.Diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori infection in patients with atrophic gastritis:comparison of histology,13C-urea breath test,and serology[J]. Scand J Gastroenterol,2000,35(2):138.
[11]楊勝茹.胃蛋白酶原的研究現狀及應用[J].醫學綜述,2009,15(4):605.
[12]Ohkusa T,Miwa H,Nomura T,et al.Improvement in serum pepsinogens and gastrin in long-term monitoring after eradication of Helicobacter pylori:comparison with H.pylori-negative patients[J].Aliment Pharmaclo Ther,2004,20(Suppl 1):25.
[13]李曉慶,鄭奎城,林曙光,等.福建省胃癌高中發區居民血清PG和幽門螺桿菌感染調查[J].中國熱帶醫學,2012,2(2):226.
[14]Di Mario F,Carallaro LG,Moussa AM,et al.Usefulness of serum pepsinogens in Helicobacter pylori chronic gastritis:relationship with inflammation,activity,and density of the bacterium[J].Dig Dis Sci,2006,51(10):1791.
[16]Ito M,Haruma K,Kaya S,et al.Serological comparison serum pepsinogen and anti-parietal cell antibody levels between Japanese and German patients[J].Eur J Gastroenterology Hepatol,2002,14(2):123.

