家族聚集性慢性乙型肝炎病毒感染者自然病程與相關因素的研究
郭素娟,李 娟,李智偉
1.寶雞市中心醫院感染科,陜西 寶雞 721008;2.中國醫科大學附屬盛京醫院感染科
家族聚集性慢性乙型肝炎病毒感染者自然病程與相關因素的研究
郭素娟1,李 娟1,李智偉2
1.寶雞市中心醫院感染科,陜西 寶雞 721008;2.中國醫科大學附屬盛京醫院感染科
目的 明確慢性乙型肝炎病毒(hepatitis B virus,HBV)感染者自然病程進展規律與感染持續時間、年齡、性別、血清ALT水平及肝組織病理學的關系。方法 收集2007年1月-2010年8月就診于中國醫科大學附屬盛京醫院感染科的家族聚集性慢性HBV感染患者,排除其他肝臟疾病,未應用干擾素或核苷類似物抗病毒治療,肝臟組織病理切片采用Knodell評分系統讀取,統計學方法采用描述統計學評價,卡方檢驗及線性回歸分析,只有與單變量分析(P<0.05)密切相關的因素才進入多因素分析模式。結果 132例患者中年齡>30歲組炎癥評分≥5分及纖維化評分≥3分所占頻率明顯高于年齡≤30歲組(P<0.05);肝功正常組肝組織炎癥評分≤4分及纖維化評分≤2分所占頻率高于肝功異常組(P<0.05);肝功反復異常>1年組肝組織炎癥評分≥5分及纖維化評分≥3分所占頻率高于肝功反復異常≤1年組(P<0.05)。血清ALT水平正常組肝組織炎癥評分≤4分及纖維化評分≤2分所占頻率高于ALT水平異常組(P<0.05);ALT>2×ULN組肝組織炎癥評分≥5分及纖維化評分≥3分所占頻率高于ALT≤2×ULN組(P<0.05)。結論 家族聚集性慢性HBV感染者肝組織炎癥及纖維化程度與感染持續時間呈正相關;尤其年齡>30歲時更易出現肝臟疾病的進展;持續肝功異常時間越長肝臟炎癥及纖維化改變越顯著;血清ALT異常的慢性HBV感染者肝組織炎癥及纖維化程度較血清ALT正常者重,而血清ALT異常者血清ALT水平越高,肝組織炎癥及纖維化改變越顯著。
慢性乙型肝炎病毒感染;炎癥;纖維化
目前慢性乙型肝炎病毒(heptatitis B virus,HBV)感染仍然是世界公共衛生所面臨的一個嚴峻問題[1-3]。慢性HBV感染的病程進展復雜多變,同樣是慢性HBV感染者,其臨床結局卻往往不同,有的可表現為終身攜帶狀態,有的卻表現出慢性肝炎,甚至進展為肝硬化或肝癌[4-6]。慢性HBV感染的病程進展與多種因素有關,目前關于慢性HBV感染病程進展的研究很多,但多數是與某種單一因素之間的關系,而在臨床上影響病程進展的因素往往很多。
1 資料與方法
1.1 一般資料 選取2007年1月-2010年8月就診于中國醫科大學盛京醫院感染科家族聚集性的慢性HBV感染者132例。男83例(62.9%),女49例(37.1%),年齡8~62歲,平均年齡(33.81±11.61)歲。入選標準:(1)有乙肝家族聚集史,即:有1位以上家庭成員為慢性HBV感染者;(2)HBsAg陽性>6個月,肝功能異常或正常;(3)已行肝穿組織活檢病理檢查;(4)除外合并有甲丙戊型肝炎病毒重疊感染和其他肝臟疾病,如自身免疫性肝病、肝豆狀核變性、酒精或藥物性肝損傷等。
1.2 數據收集及整理 回顧性分析患者資料包括年齡、性別、飲酒史、吸煙史。臨床數據包括ALT、反復肝功能異常時間、HBV DNA載量、HBeAg、HBsAg、HBeAb、脾臟厚度及肝組織炎癥及纖維化評分,收集的ALT為已知最高值,其他數據為最新的實驗室檢測數據。相關檢測方法:肝功能采用雅培全自動生化分析儀ARCIECT Ci8000,HBV血清學指標應用雅培ARCHITECT Ci8000,化學發光法進行定量檢測,部分應用上海科華生物公司試劑盒,通過酶聯免疫吸附法(ELISA)監測,監測項目包括:乙肝表面抗原、乙肝e抗原、乙肝e抗體,HBV DNA定量采用BIOER Line-gene Ⅱ熒光定量PCR檢測系統,ABI 7300 Real Time PCR系統,應用深圳凱杰生物工程公司的(HBV)核酸擴增(PCR)熒光定量檢測試劑盒。ALT水平的上限值定義為40 U/L。脾臟厚度由空腹超聲檢查測量所得;肝臟組織病理是在超聲引導下用14 G肝穿針穿刺取2個位點的肝組織,由同一名資深病理專家統一用1995年版的Knodell評分系統進行肝組織炎癥及纖維化評分[7]。肝臟疾病狀態由肝穿組織炎癥及纖維化程度來評價。
1.3 統計學處理 采用SPSS 17.0軟件進行分析。數據的誤差及常態用描述統計學評價,χ2檢驗用于決定變量的比較,多因素分析用線性回歸分析,與單變量分析密切相關的因素進入多因素分析。P<0.05為差異有統計學意義。
2 結果
2.1 研究資料描述性評價 132例患者中,19.7%(26/132)有長期吸煙史,25.0%(33/132)有長期飲酒史。68.2%(90/132)出現ALT升高。入選病例中肝組織活檢炎癥評分≤4分者98例(74.2%),5~10分者29例(22.0%),>10分者5例(3.8%);肝組織活檢病理纖維化程度評分≤2者94例(71.2%),3~4分者21例(15.9%),≥5分者17例(12.9%)。所有入選病例HBV DNA載量、血清HBeAg狀態、肝功能情況、ALT水平等指標的分布情況如表1所示。

表1 研究資料的描述性評價[例數(%)]Tab 1 Descriptive evaluation of research data [n(%)]
2.2 單因素分析
2.2.1 宿主因素:將132例患者按年齡分為>30歲組及≤30歲組,>30歲組炎癥評分≥5分及纖維化評分≥3分所占頻率分別為33.3%和38.4%;年齡≤30歲組炎癥評分≥5分及纖維化評分≥3分所占頻率分別為14.9%和14.8%。慢性HBV感染者的性別、飲酒史及吸煙史對肝組織炎癥及纖維化的影響相比,差異無統計學意義(P>0.05,見表2~3)。
2.2.2 生化指標:肝功能正常組肝組織炎癥評分≤4分及纖維化評分≤2分所占頻率明顯高于肝功異常組;肝功反復異常>1年組肝組織炎癥評分≥5分及纖維化評分≥3分所占頻率高于肝功反復異常≤1年組;血清ALT水平正常組肝組織炎癥評分≤4分及纖維化評分≤2分所占頻率高于血清ALT水平異常組;ALT>2×ULN組肝組織炎癥評分≥5分及纖維化評分≥3分所占頻率高于ALT≤2×ULN組(見表2、4)。
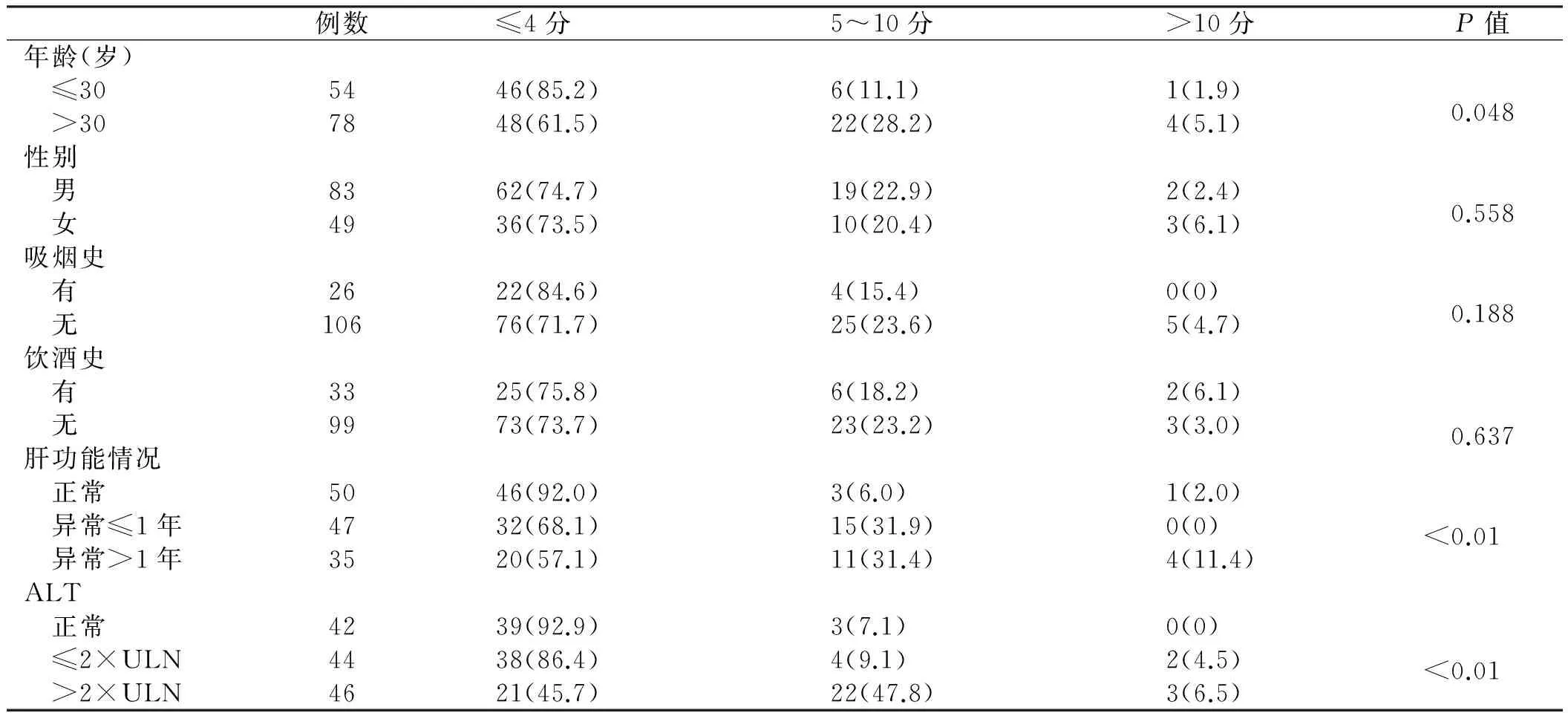
表2 肝組織炎癥與各因素之間單變量分析[例數(%)]Tab 2 Univariate analysis between liver inflammation and different factors [n(%)]
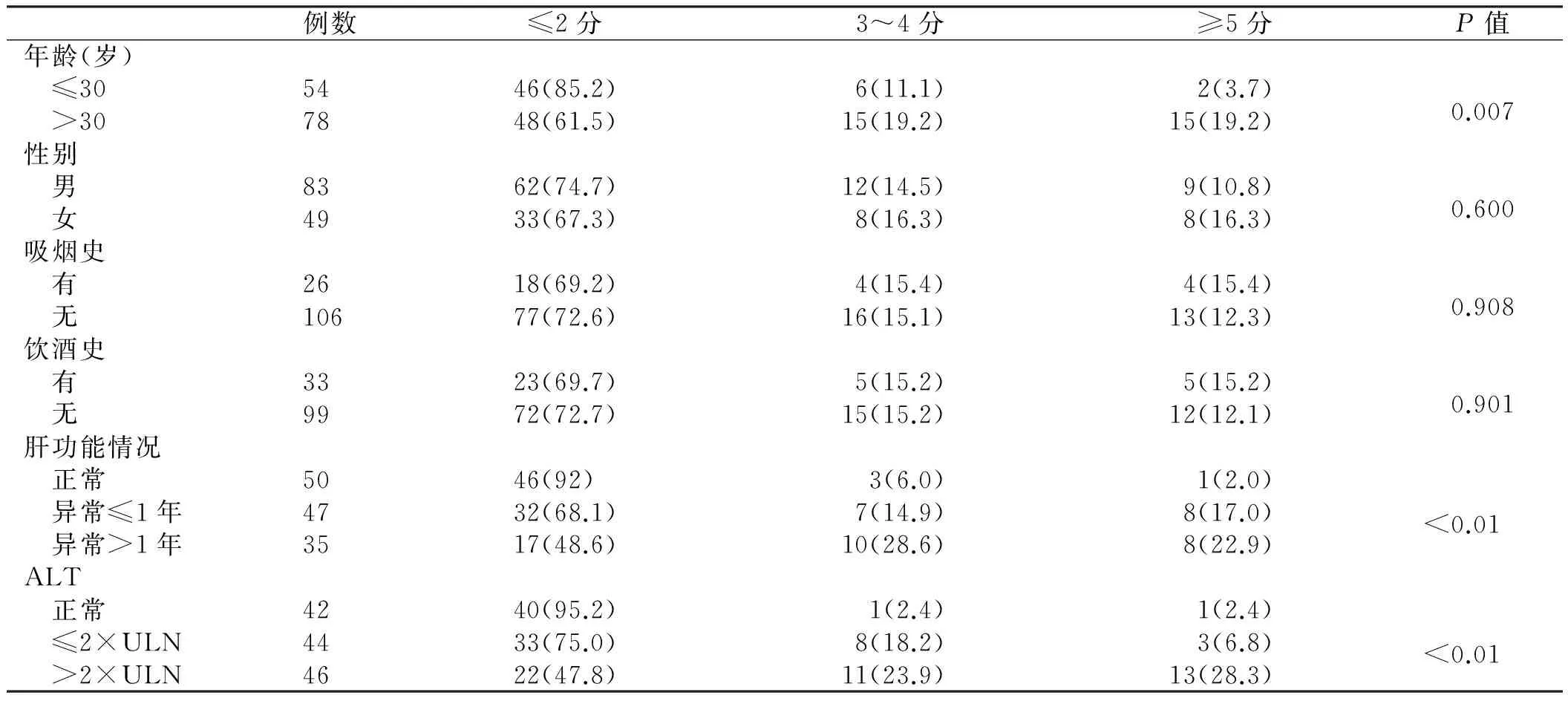
表3 肝組織纖維化程度與各因素之間單變量分析[例數(%)]Tab 3 Univariate analysis between liver fibrosis and different factors[n(%)]
2.3 多因素分析 將以上單因素分析中差異有統計學意義因素進行多因素分析。ALT水平與肝組織炎癥及纖維化程度呈顯著獨立正相關性。而肝功能情況及感染者的年齡對肝組織炎癥及纖維化的影響則無獨立相關性(P>0.05,見表4~5)。
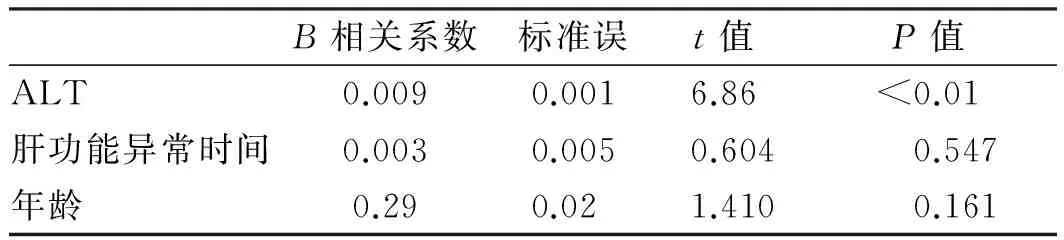
表4 與肝組織炎癥程度相關因素的多因素分析Tab 4 Multivariate analysis of factors related to the degree of liver inflammation

表5 與肝組織纖維化程度相關因素的多因素分析Tab 5 Multivariate analysis of factors related to the degree of liver fibrosis
3 討論
肝組織炎癥及纖維化改變與機體的免疫狀態及病毒自身的狀態密切相關,并可引起ALT、病毒狀態等一系列的改變[8-9]。本研究單因素分析結果表明,肝組織炎癥及纖維化程度與感染持續時間呈正相關:此132例者中有78例年齡>30歲,其中有33.3%肝組織炎癥評分>5分,38.4%肝組織纖維化評分>3分,相對于年齡≤30歲患者頻率顯著增加。ALT水平是反映肝細胞損傷的靈敏指標,有研究表明ALT水平越高,其發生肝硬化或肝細胞癌的可能性越高[10]。本研究中,ALT正常組在肝組織炎癥評分≥5分及纖維化評分≥3分所占頻率依次遞減,這也證實了以上結論。這一規律也適用于持續肝功能異常時間與肝組織炎癥及纖維化改變之間的關系,即肝功持續異常時間越長,肝臟疾病進展的可能性越高[11-12]。另外,在本研究的單一因素分析中,肝臟炎癥及纖維化程度與患者吸煙史、飲酒史及性別均無明顯相關性。
進一步的多因素分析結果表明,ALT水平與肝組織炎癥及纖維化程度獨立正相關性,而其他因素如年齡、肝功情況對肝組織炎癥及纖維化程度的影響則是與其他因素共同作用的結果。
[1]National Center for HIV/AIDs,Viral Hepatitis,STD & TB Prevention. Viral hepatitis surveillance [C].United States,2010.
[2]Mitchell AE,Colvin HM,Palmer Beasley R. Institute of medicine recommendations for the prevention and control of hepatitis B and C [J]. Hepatology,2010,51(3): 729-733.
[3]Chen CJ,Yang HI,Su J,et al. Risk of hepatocellular carcinoma across a biological gradient of serum hepatitis B virus DNA level [J]. JAMA,2006,295(1): 65-73.
[4]Yuen MF,Tanaka Y,Mizokami M,et al. Role of hepatitis B virus genotypes Ba and C,core promoter and precore mutations on hepatocellular carcinoma: a case control study [J]. Carcinogenesis,2004,25(9): 153-159.
[5]The Chinese National Workshop on Fatty Liver and Alcoholic Liver Disease for the Chinese Liver Disease Association. Guidelines for management of alcoholic liver disease: an updated and revised edition [J]. Chin J Hepatol,2010,18(3): 167-170. 中華醫學會肝病學分會脂肪肝和酒精性肝病學組. 酒精性肝病診療指南(2010年修訂版)[J]. 中華肝臟病雜志,2010,18(3): 167-170.
[6]Manno M,Cammà C,Schepis F,et al. Natural history of chronic HBV carriers in northern Italy: morbidity and mortality after 30 years [J]. Gastroenterology,2004,127(3): 756-763.
[7]Ishak K,Baptista A,Bianchi L,et al. Histological grading and staging of chronic hepatitis [J]. J Hepatol,1995,22(6): 696-699.
[8]Anna SF,Lok Brian J. McMahon. Chronic Hepatitis B: Update 2009. AASLD practice guidelines [J]. Hepatology,2009,9(50): 1-36.
[9]European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL clinical practice guidelines: management of chronic hepatitis B [J]. J Hepatol,2009,50(2): 227-242.
[10]Yuen MF,Yuan HJ,Wong DK,et al. Prognostic determinants for chronic hepatitis B in Asians: therapeutic implications [J]. Gut,2005,54(11): 1610-1614.
[11]Thompson AJ,Nguyen T,Iser D,et al. Serum hepatitis B surface antigen and hepatitis B e antigen titers: disease phase influences correlation with viral load and intrahepatic hepatitis B virus markers [J]. Hepatology,2010,51(6): 1933-1944.
[12]Kim HC,Nam CM,Jee SH,et al. Normal serum aminotransferase concentration and risk of mortality from liver diseases: prospective cohort study [J]. BMJ,2004,328(7446): 983.
(責任編輯:王全楚)
Study on natural progressive course and relative factors of chronic hepatitis B virus infection with family cluster
GUO Sujuan1,LI Juan1,LI Zhiwei2
1.Department of Infectious Diseases,Baoji Municipal Center Hospital,Baoji 721008; 2.Department of Infectious Diseases,Shengjing Hospital of China Medical University,China
Objective To investigate the relationship between natural progressive course of chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection and the factors such as the time length of infection,age,sex,ALT level and liver biopsy.Methods Chronic HBV infection with family cluster who were treated in Shengjing Hospital of China Medical University from Jan. 2007 to Aug. 2010. without other liver diseases,without treatment of interferon or analogues antiretroviral were collected. Liver tissue pathological slices were read with Knodell score system; statistical methods were descriptive statistics,Chi-square test and linear regression analysis,only univariate analysis (P<0.05) closely related factors could enter multiple factors analysis model.Results Among the 132 patients,the frequencies of group in the inflammation score≥5 and fibrosis score ≥3 when age>30 years old,which was higher than the group of age≤30 years old. The frequencies in inflammation score≤4 and fibrosis score≤2 in liver function normal group,which was higher than the liver function abnormal group. The liver function kept on abnormal>1 year had higher frequencies than the liver function kept on abnormal≤1 year,in the inflammation score≥5 and fibrosis score≥3 group. The frequencies in inflammation score≤4 and fibrosis score≤2 in serum ALT normal group,which was higher than that in serum ALT abnormal group. And the frequencies in the group inflammation score≥5 and fibrosis score≥3 when serum ALT>2×ULN,which was higher than the group of ALT≤2×ULN.Conclusion The time length of infection have positive correlation to the severity of liver inflammation and fibrosis of chronic HBV infection with family cluster. It shows that progress of liver disease appear easily when age>30 years old. The longer of liver function abnormal,the liver inflammation and fibrosis are more serious.
Chronic hepatitis B virus infection; Inflammation; Fibrosis
郭素娟,碩士,主治醫師,研究方向:感染性疾病。E-mail:22255467@qq.com
李智偉,教授,主任醫師,研究方向:感染性疾病。E-mail:lizw@sjhospital.org
10.3969/j.issn.1006-5709.2016.04.015
R512.6+2
A
1006-5709(2016)04-0419-04
2015-05-12

