長鏈非編碼RNA與胃癌相關性的研究進展
黃艷霞 張 靖 王 歌 朱金水
?
長鏈非編碼RNA與胃癌相關性的研究進展
黃艷霞張靖王歌朱金水
200233上海交通大學附屬第六人民醫院消化內科
摘要:長鏈非編碼RNA(lncRNA)因其長度大于200個核苷酸,缺乏編碼蛋白能力而得名。在表觀遺傳學控制、轉錄和轉錄后調控等多個層面,lncRNA參與了機體多種生理及病理過程的調節。研究已經證明,lncRNA在胃癌生物學的調節過程中起關鍵的作用,lncRNA與胃癌的發生、發展、侵襲、轉移及預后密切相關。該文對lncRNA在胃癌中的研究進展作一綜述。
關鍵詞:lncRNA;胃癌;轉移
長鏈非編碼RNA(lncRNA)因其長度大于200個核苷酸,缺乏編碼蛋白能力而得名。lncRNA Xist 為哺乳動物中首先被發現的lncRNA,可導致染色質結構與組成的重塑。盡管lncRNA發揮了重要的生物學功能,但多數情況下仍被認為是轉錄中的“噪音”。其后發現lncRNA HOTAIR可與多梳蛋白復合體相互作用,參與機體生長、發育過程的調節。隨著高通量測序等生物信息學技術的快速發展,已發現lncRNA在表觀遺傳學控制、轉錄和轉錄后調控等多個層面參與了機體多種生理及病理過程的調節。
1lncRNA的結構、分類及功能
lncRNA可位于細胞核和細胞質中,多由RNA聚合酶Ⅱ轉錄。其長度變異性較大,部分可延長至100 kb。人類基因組約有15 000種lncRNA,其轉錄水平遠低于蛋白編碼基因,且具有組織特異性。目前分子結構明確的lncRNA所占比例甚少,Niazi等[1]對204種功能性lncRNA進行分析后發現,內含子數量少、鳥嘌呤(G)和胞嘧啶(C)含量低、起始密碼子和開放閱讀框架的缺乏可能是lncRNA的一些結構特征。根據lncRNA基因與編碼基因間的位置關系,可以將其分為正義lncRNA、反義lncRNA、雙向lncRNA、內含子lncRNA和基因間lncRNA五類[2]。lncRNA的異常表達與人類疾病密切相關,如老化相關的阿爾茨海默病及認知障礙相關疾病都被認為與lncRNA的異常表達有關;其在心血管疾病、內分泌疾病(如糖尿病)中亦發揮了作用[3]。值得關注的是,lncRNA與腫瘤的發生發展密切相關,lncRNA在前列腺癌、結直腸癌、乳腺癌、膀胱癌、肝細胞癌及胃癌等多種惡性腫瘤中均有異常表達,可作為致癌或抑癌因子參與腫瘤細胞轉錄、染色質重塑、微血管侵襲等過程的調控。
2lncRNA與胃癌
lncRNA AC096655首先被發現與胃癌相關,并被命名為GACAT1[4]。2012年Yang等[5]發現lncRNA H19表達上調可促進胃癌細胞增殖。其后lncRNA在胃癌中的重要性得到越來越多的關注,它們幾乎參與胃癌發生發展的全過程,包括腫瘤細胞增殖、凋亡、侵襲、轉移、預后及耐藥性等多個方面。此外,lncRNA對胃癌的診斷也有幫助,可能是胃癌診斷的潛在分子標志物。
2.1lncRNA在胃癌中的生物學功能
lncRNA在胃癌的發生發展中具有促癌或抑癌雙重作用。如lncRNA H19、HULC、Linc00152、HOTAIR、PVT1、HIF1A-AS2、LINC00982、MALAT1及SPRY4-IT1等具有促進腫瘤細胞增殖、入侵及轉移的作用[6-14],而lncRNA MEG3、GAS5、FENDRR、LEIGC、FER1L4及WT1-AS等具有抑制腫瘤細胞增殖、促進腫瘤細胞凋亡的作用[15-20]。此外,lncRNA在胃癌組織中的表達水平也不一致,lncRNA的表達水平與胃癌臨床病理特征的關系見表1。
2.2lncRNA在胃癌耐藥中的作用
腫瘤細胞耐藥是化學治療失敗的重要原因之一,越來越多的研究發現lncRNA參與腫瘤細胞耐藥的調節,如Zhang等[29]的研究發現lncRNA PVT1在對順鉑耐藥患者的胃癌組織及胃癌細胞中高表達,過表達lncRNA PVT1促進了胃癌細胞耐藥。Ding等[30]亦證實lncRNA PVT1表達升高能促進胃癌細胞對紫杉醇的耐藥。此外,癌細胞中高表達的lncRNA MRUL促進了胃癌耐藥細胞中ABCB1的表達,從而促進了胃癌細胞對藥物的耐藥性[31]。然而,一些lncRNA卻具有提高腫瘤細胞對化學治療藥物敏感性的作用,如Han等[32]發現lncRNA LEIGC可增加胃癌細胞對5-氟尿嘧啶的敏感性。
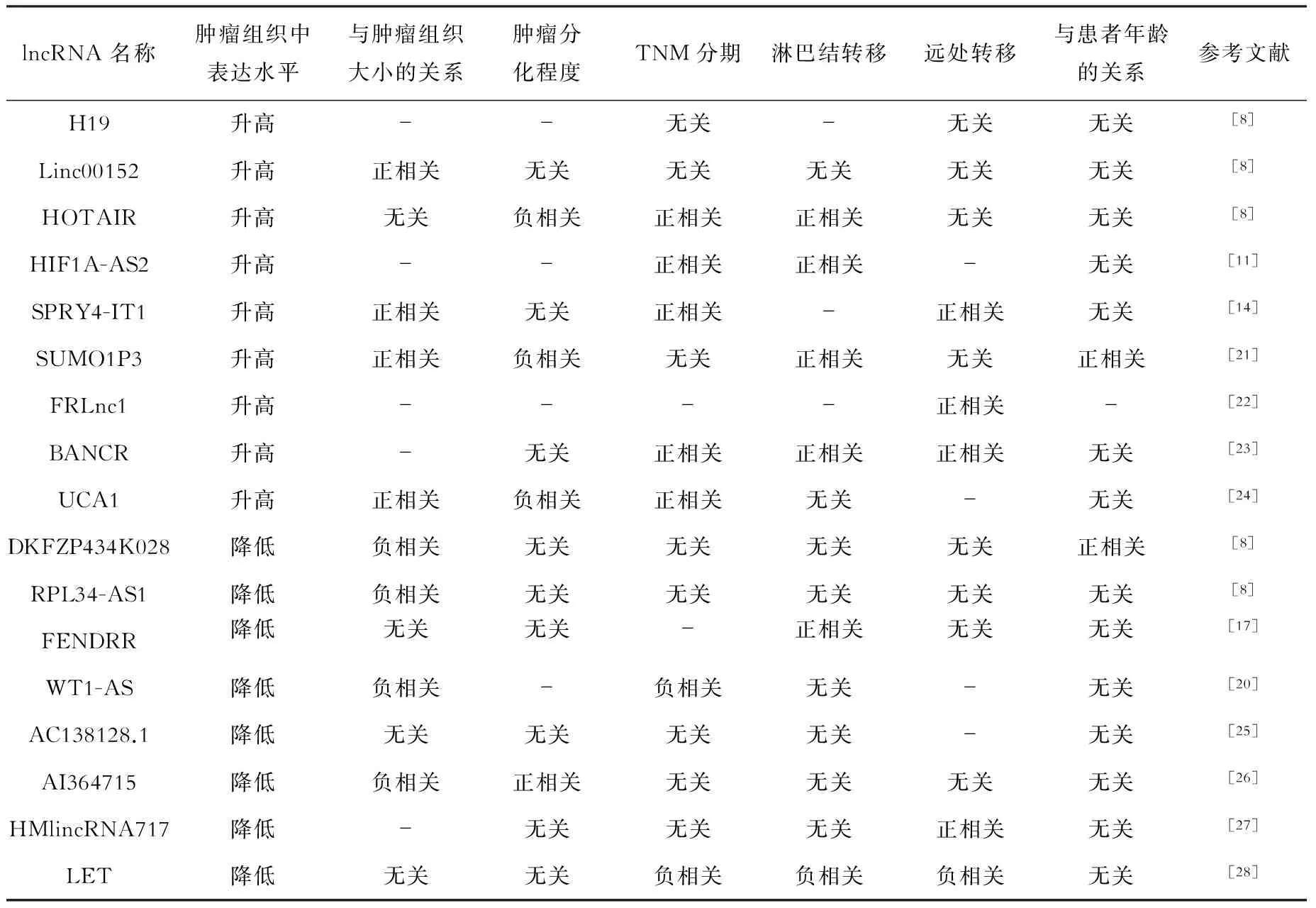
表1 lncRNA的表達與胃癌臨床病理特征的關系
2.3lncRNA在胃癌侵襲轉移中的作用
侵襲和轉移是惡性腫瘤的重要特征之一。越來越多的證據表明,上皮-間質轉化(EMT)及腫瘤細胞間的黏附能力下降,可能參與了腫瘤轉移的重要環節。Zhao等[8]的研究發現,lncRNA Linc00152能抑制胃癌細胞中EMT的進程。Han等[32]研究了lncRNA LEIGC在胃癌細胞中的作用,敲低其表達水平后,胃癌細胞發生了EMT。該研究進一步檢測了與EMT相關的一些蛋白,研究結果與此一致,因此可以認為lncRNA LEIGC在胃癌細胞中是一個潛在的EMT抑制劑。Zhao等[7]的研究發現,lncRNA HULC可抑制胃癌細胞凋亡、促進胃癌細胞增殖,其作用機制可能與誘導細胞自噬,促進EMT有關。轉化生長因子-β(TGF-β)信號通過miR-200家族和ZEB1/2之間的雙負反饋循環調節腫瘤EMT[33],Saito等[34]的研究發現,lncRNA ATB通過TGF-β誘導胃癌EMT變化以促進轉移發生。Xu等[17]發現過表達lncRNA FENDRR能誘導胃癌肺轉移結節增多,并使腫瘤細胞間的黏附分子FN1表達下降,證明了lncRNA FENDRR可能通過影響FN1來調節胃癌細胞的轉移。
2.4lncRNA與胃癌的診斷
lncRNA可存在于血漿、胃液及組織中,目前部分血漿中的lncRNA已被作為潛在的腫瘤標志物。Zhou等[35]的研究發現血漿中lncRNA H19能為早期胃癌的診斷提供可靠依據。胃液中lncRNA的獲得相對容易,并能夠為胃癌提供有效的診斷。Zheng等[36]收集了49份胃液標本(26份胃癌患者標本和23份健康者標本),發現胃癌標本中lncRNA UCA1的水平高于健康標本。Yang等[37]研究了130份胃液標本(包括胃良性病變、胃不典型增生、胃癌癌前病變和胃癌患者),發現胃癌患者的胃液中lncRNA ABHD11-AS1水平顯著高于正常胃、萎縮性胃炎、胃潰瘍,并與胃癌患者的性別、腫瘤大小、分期、勞倫分型及血清中癌胚蛋白(CEA)水平相關。值得注意的是,胃液中lncRNA ABHD11-AS1作為診斷胃癌的標志物時,早期胃癌的診斷率提高到71.4%。
2.5lncRNA可能的作用機制
lncRNA的調節機制復雜且多樣化:可調控下游基因轉錄或作為分子阻斷劑阻斷該分子發生作用;亦可通過與蛋白結合,定位到特定的DNA序列上;也可與多個相關轉錄因子結合發揮作用;還可競爭性結合miRNA以調控基因表達。Cai等[22]發現lncRNA FRLnc1可通過調節FOXM1參與腫瘤生長及血管生成。Wang等[13]研究了lncRNA MALAT1的功能,發現其可能通過調節SF2/ASF來促進胃癌細胞增殖。有研究表明,lncRNA GAS5通過下調E2F1和p21的表達來誘導胃癌細胞增殖[16],而lncRNA WT1-AS則通過抑制細胞外信號調節激酶(ERK)蛋白磷酸化水平來阻止胃癌發生[20]。
競爭性內源RNA(ceRNA)在轉錄后調節及腫瘤的發生發展中具有重要的作用[38]。ceRNA通過競爭性結合miRNA以調節基因表達,是RNA之間相互作用的一種新機制。如Liu等[39]發現胃癌中lncRNA HOTAIR可通過競爭性抑制miR-331-3p來調節表皮生長因子受體2(HER2)的表達,增加了轉錄后調控的水平。lncRNA H19可通過調控miR-675抑制RUNX1而促進腫瘤細胞增殖[40]。lncRNA H1F1A-AS2在胃癌發展中發揮了重要的作用,通過調節與腫瘤相關的缺氧誘導因子-1α(HIF-1α)途徑促進腫瘤發展。lncRNA ANRIL在胃癌組織中表達上調,通過表觀沉默miR-99a/miR-449a促進腫瘤生長[11]。
3問題與展望
lncRNA在組織生理及病理過程中發揮了重要的調節作用,其作用機制仍有待進一步探索。lncRNA在疾病發生發展中的作用是錯綜復雜的,一方面可能是由于lncRNA在物種間的低保守性,使得物種中lncRNA的功能不確定[41];另一方面由于缺乏相關的研究工具,lncRNA的數據庫還不夠充足,很難全面揭示lncRNA的生物學功能;此外,lncRNA與腫瘤轉移或耐藥的機制研究尚不成熟[42-43]。無論當前研究顯示lncRNA是抑癌基因或是促癌基因,可以確定的是lncRNA與胃癌有著密切的聯系,以lncRNA為靶點的藥物有望在胃癌的臨床治療中起到重要的作用。因此,明確lncRNA在胃癌及其他疾病中的具體作用尤為重要,有助于全面深入地認識胃癌的發生發展機制,并為臨床治療胃癌提供更多的途徑。
參考文獻
1 Niazi F, Valadkhan S. Computational analysis of functional long noncoding RNAs reveals lack of peptide-coding capacity and parallels with 3′ UTRs[J]. RNA, 2012, 18: 825-843.
2 Kaikkonen MU, Lam MT, Glass CK, et al. Non-coding RNAs as regulators of geneexpression and epigenetics[J]. Cardiovasc Res, 2011, 90: 430-440.
3 Kim J, Kim KM, Noh JH, et al. Long noncoding RNAs in diseases of aging[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta, 2016, 1859: 209-221.
4 Xiao B, Guo J. Long noncoding RNA AC096655.1-002 has been officially named as gastric cancer-associated transcript 1, GACAT1[J]. Tumour Biol, 2013, 34: 2697-2701.
5 Yang F, Bi J, Xue X, et al. Up-regulated long non-coding RNA H19 contributes to proliferation of gastric cancer cells[J]. FEBS J, 2012, 279: 3159-3165.
6 Li H, Yu B, Li J, et al. Overexpression of lncRNA H19 enhances carcinogenesis and metastasis of gastric cancer[J]. Oncotarget, 2014, 5: 2318-2329.
7 Zhao Y, Guo Q, Chen J, et al. Role of long non-coding RNA HULC in cell proliferation, apoptosis and tumor metastasis of gastric cancer: a clinical and in vitro investigation[J]. Oncol Rep, 2014, 31: 358-364.
8 Zhao J, Liu Y, Zhang W, et al. Long non-coding RNA Linc00152 is involved in cell cycle arrest, apoptosis, epithelial to mesenchymal transition, cell migration and invasion in gastric cancer[J]. Cell Cycle, 2015, 14: 3112-3123.
9 Endo H, Shiroki T, Nakagawa T, et al. Enhanced expression of long non-coding RNA HOTAIR is associated with the development of gastric cancer[J]. PLoS One, 2013, 8: e77070.
10 Kong R, Zhang EB, Yin DD, et al. Long noncoding RNA PVT1 indicates a poor prognosis of gastric cancer and promotes cell proliferation through epigenetically regulating p15 and p16[J]. Mol Cancer, 2015, 14: 82.
11 Chen WM, Huang MD, Kong R,et al. Antisense long noncoding RNA HIF1A-AS2 is upregulated in gastric cancer and associated with poor prognosis[J]. Dig Dis Sci, 2015, 60: 1655-1662.
12 Fei ZH, Yu XJ, Zhou M, et al. Upregulated expression of long non-coding RNA LINC00982 regulates cell proliferation and its clinical relevance in patients with gastric cancer[J]. Tumour Biol, 2016, 37: 1983-1993.
13 Wang J, Su L, Chen X, et al. MALAT1 promotes cell proliferation in gastric cancer by recruiting SF2/ASF[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2014, 68: 557-564.
14 Peng W, Wu G, Fan H, et al. Long noncoding RNA SPRY4-IT1 predicts poor patient prognosisand promotes tumorigenesis in gastric cancer[J]. Tumor Biol, 2015, 36: 6751-6758.
15 Peng W, Si S, Zhang Q, et al. Long non-coding RNA MEG3 functions as a competing endogenous RNA to regulate gastric cancer progression[J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2015, 34: 79.
16 Sun M, Jin FY, Xia R, et al. Decreased expression of long noncoding RNA GAS5 indicates a poor prognosis and promotes cell proliferation in gastric cancer[J]. BMC Cancer, 2014, 14: 319.
17 Xu TP, Huang MD, Xia R, et al. Decreased expression of the long non-coding RNA FENDRR is associated with poor prognosis in gastric cancer and FENDRR regulates gastric cancer cell metastasis by affecting fibronectin1 expression[J]. J Hematol Oncol, 2014, 7: 63.
18 Han Y, Ye J, Wu D, et al. LEIGC long non-coding RNA acts as a tumor suppressor in gastric carcinomaby inhibiting the epithelial-to-mesenchymaltransition[J]. BMC Cancer, 2014, 14: 932.
19 Xia T, Chen S, Jiang Z, et al. Long noncoding RNA FER1L4 suppresses cancer cell growth by acting as a competing endogenous RNA and regulating PTEN expression[J]. Sci Rep, 2015, 5: 13445.
20 Du T, Zhang B, Zhang S, et al. Decreased expression of long non-coding RNA WT1-AS promotes cell proliferation and invasion in gastriccancer[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta, 2015, 1862: 12-19.
21 Mei D, Song H, Wang K, et al. Up-regulation of SUMO1 pseudogene 3 (SUMO1P3) in gastric cancer and its clinical association[J]. Med Oncol, 2013, 30: 709.
22 Cai H, Chen J, He B, et al. A FOXM1 related long non-coding RNA contributes to gastric cancer cell migration[J]. Mol Cell Biochem, 2015, 406: 31-41.
23 Li L, Zhang L, Zhang Y, et al. Increased expression of LncRNA BANCR is associated with clinical progression and poor prognosis in gastric cancer[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2015, 72: 109-112.
24 Zheng Q, Wu F, Dai WY, et al. Aberrant expression of UCA1 in gastric cancer and its clinical significance[J]. Clin Transl Oncol, 2015, 17: 640-646.
25 Chen X, Sun J, Song Y, et al. The novel long noncoding RNA AC138128.1 may be a predictive biomarkerin gastric cancer[J]. Med Oncol, 2014, 31: 262.
26 Zhu S, Mao J, Shao Y, et al. Reduced expression of the long non-coding RNA AI364715 in gastric cancer and its clinical significance[J]. Tumour Biol, 2015, 36: 8041-8045.
27 Shao Y, Chen H, Jiang X, et al. Low expression of lncRNA-HMlincRNA717 in human gastric cancer and its clinical significances[J]. Tumor Biol, 2014, 35: 9591-9595.
28 Zhou B, Jing XY, Wu JQ, et al. Down-regulation of long non-coding RNA LET is associated with poor prognosis in gastric cancer[J]. Int J Clin Exp Pathol, 2014, 7: 8893-8898.
29 Zhang XW, Bu P, Liu L, et al. Overexpression of long non-coding RNA PVT1 in gastric cancer cells promotes the development of multidrug resistance[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2015, 462: 227-232.
30 Ding J, Li D, Gong M, et al. Expression and clinical significance of the long non-coding RNA PVT1 in human gastric cancer[J]. Onco Targets Ther, 2014, 7: 1625-1630.
31 Wang Y, Zhang D, Wu K, et al. Long noncoding RNA MRUL promotes ABCB1 expression in multidrug-resistant gastric cancer cell sublines[J]. Mol Cell Biol, 2014, 34: 3182-3193.
32 Han Y, Ye J, Wu D, et al. LEIGC long non-coding RNA acts as a tumor suppressor in gastric carcinoma by inhibiting the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition[J]. BMC Cancer, 2014, 14: 932.
33 Burk U, Schubert J, Wellner U, et al. A reciprocal repression between ZEB1 and members of the miR-200 family promotes EMT and invasion in cancer cells[J]. EMBO Rep, 2008, 9: 582-589.
34 Saito T, Kurashige J, Nambara S, et al. A long non-coding RNA activated by transforming growth factor-beta is an independent prognostic marker of gastric cancer[J]. Ann Surg Oncol, 2015, 22: 915-922.
35 Zhou X, Yin C, Dang Y, et al. Identification of the long non-coding RNA H19 in plasma as a novel biomarker for diagnosis of gastric cancer[J]. Sci Rep, 2015, 5: 11516.
36 Zheng Q, Wu F, Dai WY, et al. Aberrant expression of UCA1 in gastric cancer and its clinical significance[J]. Clin Transl Oncol, 2015, 17: 640-646.
37 Yang Y, Shao Y, Zhu M, et al. Using gastric juice lncRNA-ABHD11-AS1 as a novel type of biomarker in the screening of gastric cancer[J]. Tumour Biol, 2016, 37: 1183-1188.
38 Tay Y, Kats L, Salmena L, et al. Coding-independent regulation of the tumor suppressor PTEN by competing endogenous mRNAs[J]. Cell, 2011, 147: 344-357.
39 Liu X, Sun M, Nie F, et al. Lnc RNA HOTAIR functions as a competing endogenous RNA to regulate HER2 expression by sponging miR-331-3p in gastric cancer[J]. Mol Cancer, 2014, 13: 92.
40 Zhuang M, Gao W, Xu J, et al. The long non-coding RNA H19-derived miR-675 modulates human gastric cancer cell proliferation by targeting tumor suppressor RUNX1[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2014, 448: 315-322.
41 Struhl K.Transcriptional noise and the fidelity of initiation by RNA polymerase Ⅱ[J]. Nat Struct Mol Biol, 2007, 14: 103-105.
42 Fischer KR, Durrans A, Lee S, et al. Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transitionis not required for lung metastasis but contributes to chemoresistance[J]. Nature, 2015, 527: 472-476.
43Zheng X, Carstens JL, Kim J, et al. Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transitionis dispensable for metastasis but induces chemoresistance in pancreatic cancer[J]. Nature, 2015, 527: 525-530.
(本文編輯:林磊)
基金項目:國家自然科學基金(81573747,81302093,81272752)
通信作者:朱金水,Email: zhujs1803@163.com
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1673-534X.2016.03.005
(收稿日期:2015-12-20)

