伐昔洛韋抗病毒抑制療法治療頻發性生殖器皰疹的臨床效果及預后效果觀察
王蓮鳳 周倩
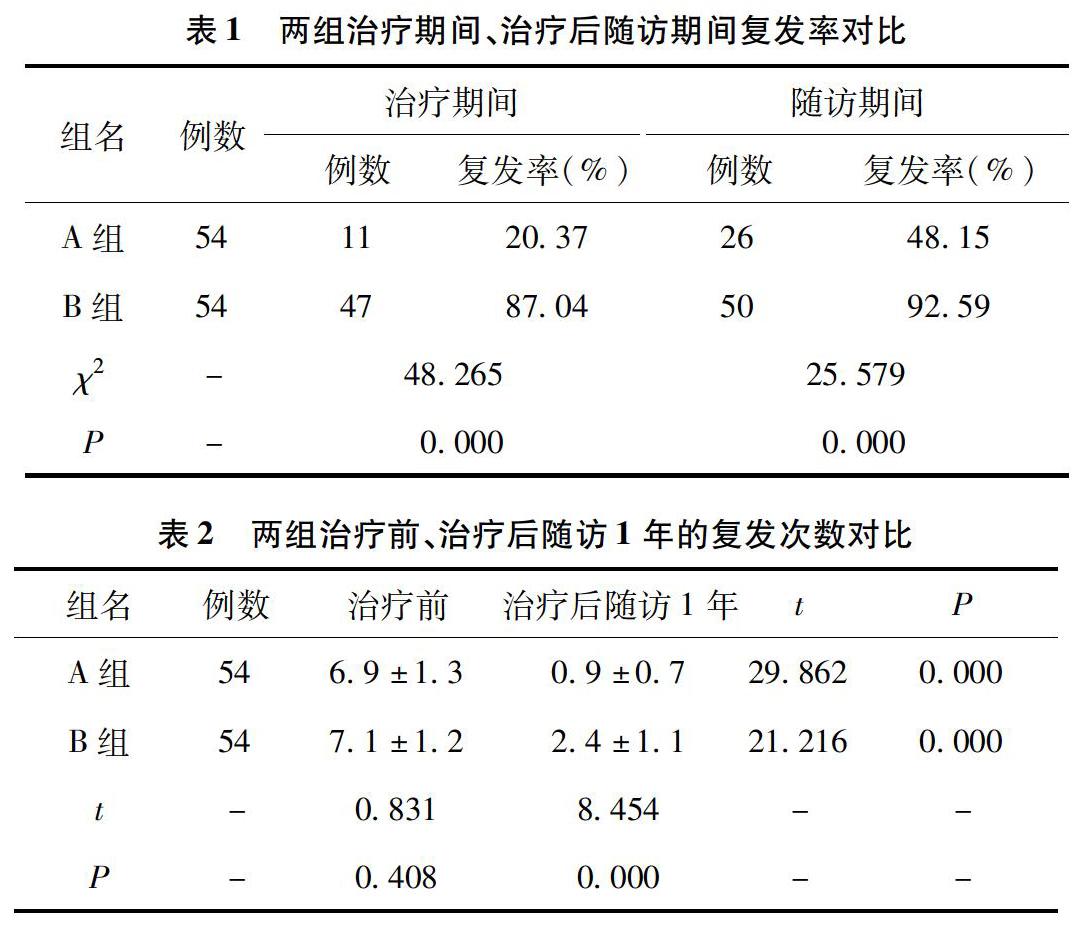
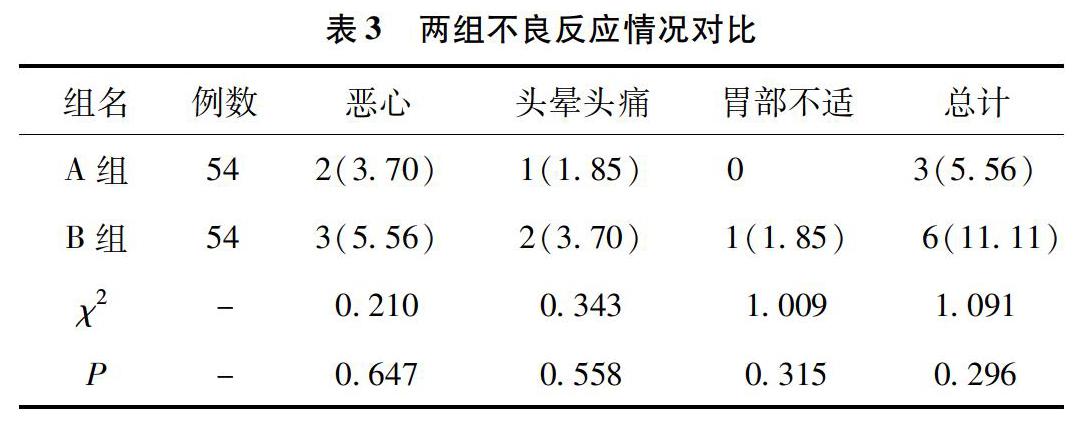
【摘要】目的:觀察伐昔洛韋抗病毒抑制療法治療頻發性生殖器皰疹的臨床效果及預后效果。方法:從2012年8月至2014年8月我院收治的頻發性生殖器皰疹中選取108例作為研究對象,按隨機分組法分為A組和B組,各54例。A組采用持續抑制療法,B組采用間歇療法。分別于用藥期間觀察兩組復發情況及不良反應。結果:A組在治療期間與治療后隨訪期間的復發率20.37%、48.15%,均低于B組的87.04%、92.59%;兩組治療后隨訪1年的復發次數均明顯減少,且A組復發次數為(0.9±0.7)次,低于B組的(2.4±1.1)次。上述差異均有統計學意義(P<0.05)。兩組的不良反應發生率比較,差異無統計學意義(P>0.05)。結論:伐昔洛韋抗病毒抑制療法治療頻發性生殖器皰疹臨床療效顯著,預后良好,值得臨床推薦。
【關鍵詞】伐昔洛韋;病毒抑制療法;頻發性生殖器皰疹;效果
【Abstract】Objectives: To observe the effect of valaciclovir suppressive antiviral therapy in the treatment of frequent clinical effect and prognosis of recurrent genital herpes. Methods: From August 2012 to August 2014, 108 patients with recurrent genital herpes were selected and randomly divided into group A and group B. The group A was inhibited by continuous treatment, and group B was intermittent therapy. Two groups were observed during the treatment and adverse reactions were observed. Results: The recurrence rate of group A during and after treatment was 20.37% and 48.15%, which was lower than that of B group of 92.59% and 87.04%. In the 1 year follow-up, the number of recurrence of group A was (0.9 ± 0.7), lower than the group B (2.4 ± 1.1). The difference was statistically significant (P < 0.05). Difference in the incidence of adverse reactions in the two groups was not statistically significant (P > 0.05). Conclusion: Valacyclovir antiviral suppression therapy in the treatment of frequent sexual genital bleb has a significant clinical efficacy with good prognosis, worthy of clinical recommendations.
【Key words】Valaciclovir; Viral suppression therapy; Recurrent genital herpes; Effect
【中圖分類號】R752.1【文獻標志碼】A
生殖器皰疹(genital herpes,GH)是由單純皰疹病毒感染而引起的一種常見的性傳播疾病[1]。據WHO統計,生殖器皰疹的發病率呈逐年上升的趨勢[2]。由于該病具有治愈難、傳播性強且反復發作等特點,可以通過性、母嬰傳播,因而嚴重影響患者及其家庭的生活質量。伐昔洛韋是治療頻發性生殖器皰疹的首選藥物,在2009年之前,其劑量多以300mg為主。而大量研究顯示,應用500mg伐昔洛韋抑制療法對生殖器皰疹進行治療,其臨床療效確定,不良反應少[3,4]。為此,本文應用伐昔洛韋間歇療效和持續抑制療法對頻發性生殖器皰疹患者進行治療,旨在探究大劑量持續抑制療法治療頻發性生殖器皰疹的臨床療效及預后效果。現報道如下。……

