探究女性下生殖道性傳播病原體感染與輸卵管妊娠及預后的相關性
霍高翔 姚曉玲 崔鳳英
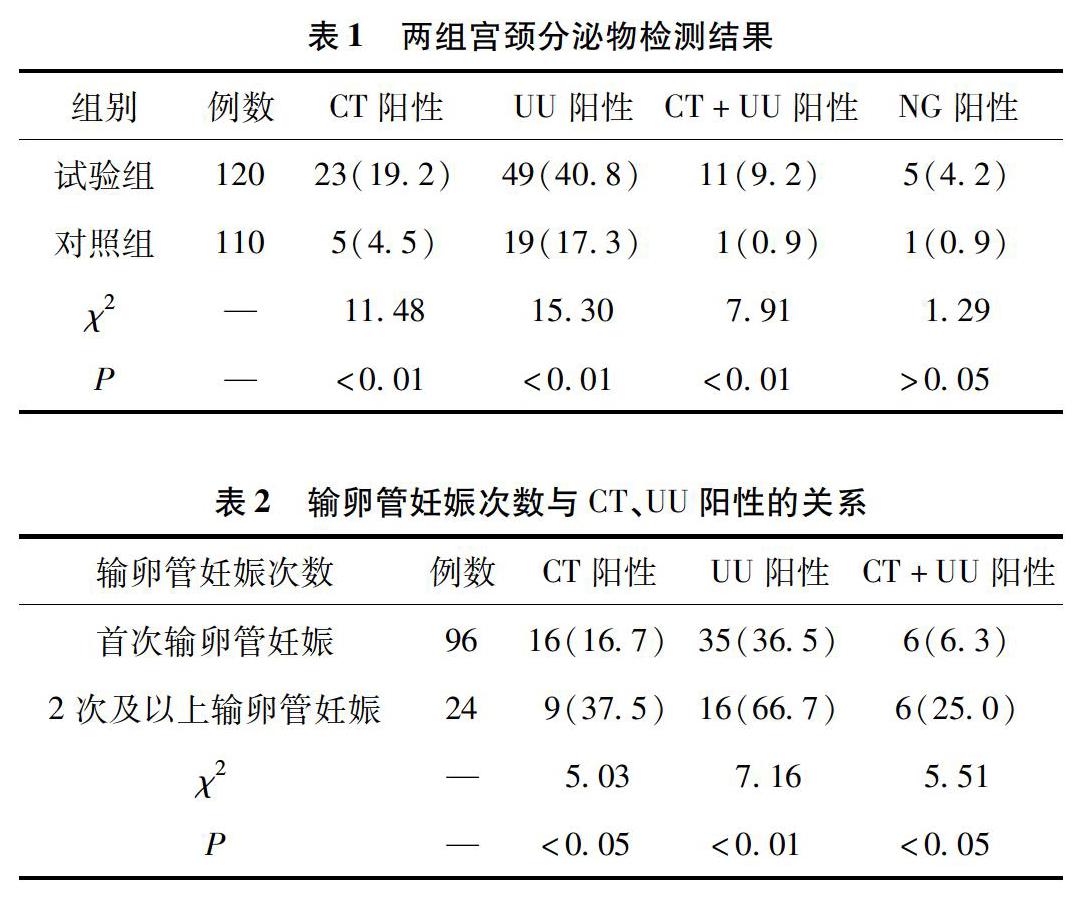

【摘要】目的:分析女性下生殖道性傳播病原體感染與輸卵管妊娠的相關性,探討輸卵管妊娠術后采用敏感抗生素治療的效果。方法:將2013年2月至2015年2月于我院行手術治療的120例輸卵管妊娠患者納入試驗組,同期于我院行人工或藥物流產的110例健康妊娠女性納入對照組,分析性傳播病原體陽性率與輸卵管妊娠發生的相關性,同時將試驗組中有生育需求的CT、UU陽性患者納入觀察組,其余納入預防組,探討敏感抗生素治療對患者預后的影響。結果:試驗組的CT、UU和CT+UU陽性率分別為19.2%、40.8%和9.2%,均高于對照組的4.5%、17.3%和0.9%,差異有顯著性意義(χ2=11.48、15.30、7.91,P<0.01);試驗組中,2次及以上輸卵管妊娠的患者CT、UU和CT+UU陽性率分別為37.5%、66.7%和25.0%,均高于首次輸卵管妊娠患者的16.7%、36.5%和6.3%,差異有顯著性意義(χ2=5.03、7.16、5.51,P<0.05);觀察組與預防組輸卵管通暢率分別為88.2%、74.1%,兩組差異相比無顯著性意義(χ2=0.78,P>0.05)。結論:CT、UU感染與輸卵管妊娠的發生有關,采用藥敏抗生素治療患者及其配偶能夠有效改善輸卵管妊娠患者的預后。
【關鍵詞】性傳播病原體;輸卵管妊娠;預后
【Abstract】Objectives: To analyze the correlation between sexually transmitted pathogens infection of female reproductive tract and tubal pregnancy (TP), to discuss the effect of postoperative sensitive antibiotic treatment. Methods: 120 TP patients in our hospital from February 2013 to February 2015 were selected into the experimental group, while 110 healthy pregnant women conducted artificial or medical abortion were included as the control group, to analyze the correlation between positive rate of sexually transmitted pathogens and TP. CT and UU positive patients with fertility requirements in experimental group were included as observation group while the rest were prevention group, to explore the effect of sensitive antibiotic treatment on the prognosis of patients. Results: The positive rate of CT, UU and CT + UU was 19.2%, 40.8% and 9.2% respectively, higher than the control group of 4.5%, 17.3% and 0.9%, with significant difference (χ2 = 11.48, 15.30, 7.91, P<0.01). In the experimental group, for patients with twice and more times of TP, the CT, UU and CT + UU were 37.5%, 66.7% and 25.0% respectively, higher than those of patients with once TP which were 16.7%, 36.5% and 6.3%, with significant differences (χ2 = 5.03, 7.16, 5.51, P< 0.05). The tubal patency rate of observation and prevention group were 88.2% and 88.2% respectively, without significant difference (χ2 = 0.78, P> 0.78). Conclusion: CT and UU infection is associated with the occurrence of TP, and drug sensitive antibiotics for patients and their spouses can effectively improve the prognosis of patients.
【Key words】Sexually transmitted pathogens; Tubal pregnancy; Prognosis
【中圖分類號】R714.2【文獻標志碼】A
異位妊娠又稱宮外孕,是一種極為兇險的急腹癥,嚴重威脅著婦女的生命安全。輸卵管妊娠(tubal pregnancy,TP)在異位妊娠的發病率中所占比重最大,近年來發病情況更是呈逐年增多、年輕化的趨勢[1]。相關文獻顯示,性傳播疾病是輸卵管妊娠發生的重要危險因素之一,有性傳播疾病史的婦女出現輸卵管妊娠的幾率是正常女性的14倍,因此探明性傳播病原體與輸卵管妊娠的相關性對輸卵管妊娠發生率的下降有重要意義[2]。當前的研究表明,沙眼衣原體(CT)、解脲支原體(UU)等感染是性傳播疾病的主要因素[3]。為此,本研究重點分析了CT、UU等性傳播病原體與輸卵管妊娠的相關性,并探討了輸卵管妊娠術后采用敏感抗生素治療的效果。……

