備用電源自投裝置非正確動作問題分析與探討
周建英
(連云港供電公司,江蘇連云港 222000)
備用電源自投裝置非正確動作問題分析與探討
周建英
(連云港供電公司,江蘇連云港 222000)
備用電源自投裝置動作可靠性高,因而在電力系統中得以廣泛應用。本文介紹了110kV某用戶變電站采用內橋式接線備用電源自投裝置不正確動作的案例,對其不正確動作原因作了詳細分析,并依據現場實際情況,對備自投裝置在應用過程中存在的細節問題進行探討,最后提出了改進方法。
備自投 動作行為 存在問題 改進方法
隨著地方經濟的快速發展,近幾年本地區新上許多一、二類重要負荷,這些電力用戶對供電可靠性要求高,需電網提供兩路以上電源供電。由于備自投裝置動作可靠性高,用戶在新建變電站時,也加裝了備用電源自投裝置,確保不會因一路電源故障而影響生產供電的連續性。因此,本文就備自投動作過程中的一些問題進行分析和探討,總結經驗教訓,提出改進意見,以便于今后更好地使用備用電源自投裝置,確保裝置能正確可靠動作。
1 備自投運行方式及閉鎖條件
1.1 主接線方式及備自投運行方式
110kV變電站采用內橋接線方式,主變高壓側配置差動、高后備和非電量保護,其中差動、非電量零時限,高后備過流一段延時1.7S跳相應高壓側、橋和低壓側兩分支。主變低后備保護為過流Ⅰ段保護,作為10kV母線和母線上出線保護Ⅰ段的后備保護,它有兩個動作時限,第一時限1.1S跳開10kV橋開關,第二時限1.4S跳開10kV本側開關,為了保證供電可靠性,裝設三套備用電源自投裝置,型號為國電南京自動化股份有限公司PSP642數字式備用電源自投裝置,可以實現110kV進線及橋開關備自投,10kVⅠⅡ段主變及橋備自投,10kVⅢ Ⅳ段主變及橋備自投功能,變電站主接線如圖1所示。
當進線733、橋710開關在合閘位置,進線744開關處于熱備用狀態,即進線733開關帶兩臺主變運行,啟用進線744開關備自投,將這種運行方式稱為備自投方式1。
當進線744、橋710開關在合閘位置,進線733關處于熱備用狀態,即進線744開關帶兩臺主變運行,啟用進線733開關備自投,將這種運行方式稱為備自投方式2。
當進線733開關帶1號主變運行,進線744開關帶2號主變運行,橋開關710熱備用時,啟用橋710開關備自投,橋備投有兩種動作過程,分別對應于備自投方式3和方式4。
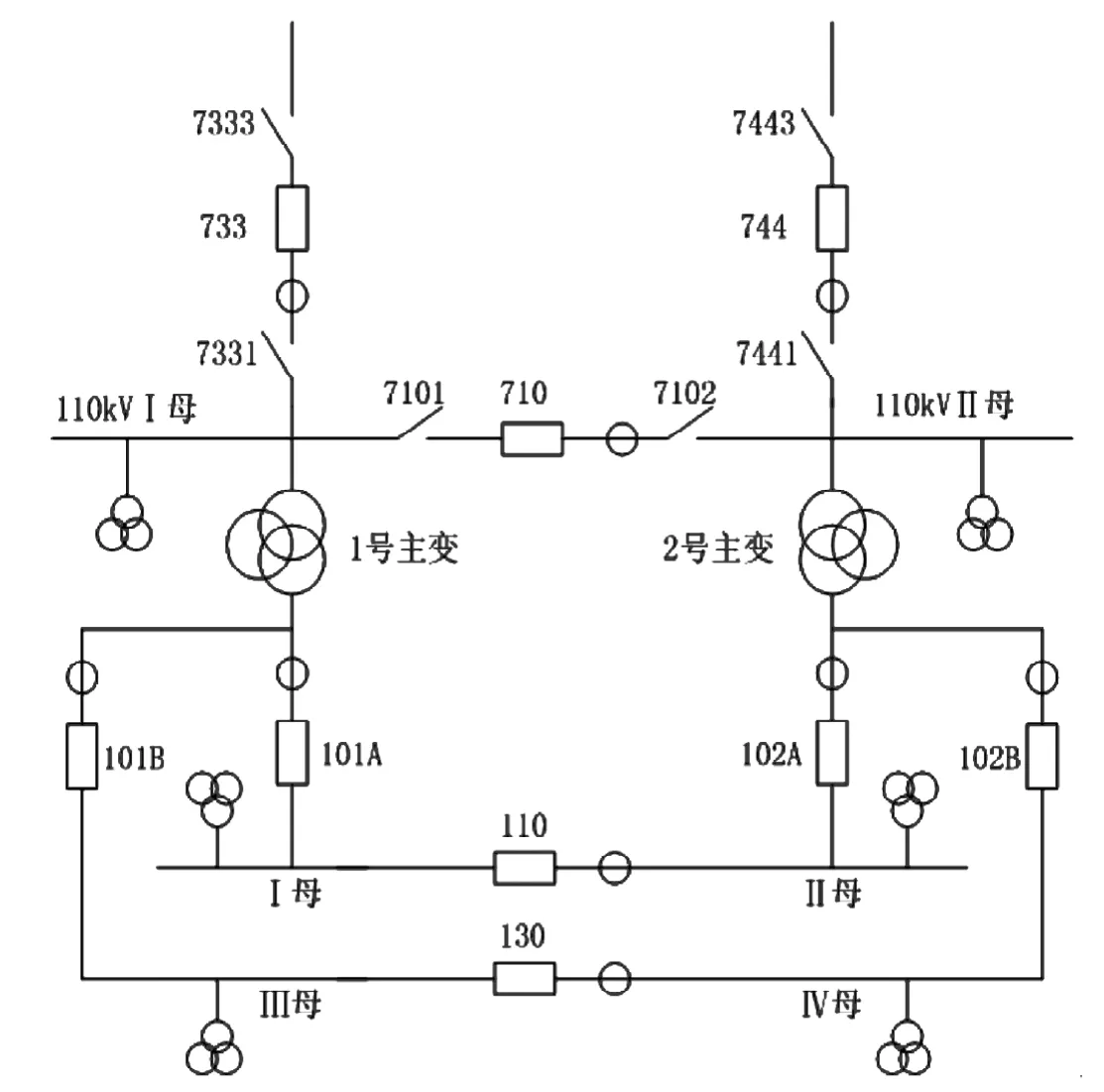
圖1 主接線示意圖
1.2 備自投裝置的閉鎖條件
為保證備自投動作的正確性,防止備自投裝置重合于故障而造成對系統的二次沖擊,備自投裝置只允許動作一次,并且在一定情況需對備自投裝置進行放電,即閉鎖備自投,閉鎖備自投的條件有以下一些,只要其中一個條件滿足備自投就放電。
(1)手動拉開運行狀態的開關;
(2)手動合上熱備用的自投開關;
(3)備自投開關合閘彈簧未儲能;
(4)備自投開關控制回路斷線;
(5)備自投裝置已經動作;
(6)備自投硬壓板退出;
(7)備自投軟壓板退出;
(8)主變差動/高后備/非電量保護動作。
2 備自投時間配合不當引起誤動作
2.1 事故經過
110kV某用戶變電站發生如下保護及自動裝置動作信號:110kV、35kV、10kV備自投動作,824、302、102開關跳閘、800、300、100開關合閘。2#主變負荷全部轉移至1#主變。
該變電站正常運行方式如圖2,110kV電一線、電二線運行,110kV母聯800熱備用。1#主變運行帶35kV1#母線、10kV1#母線負荷。2#主變運行帶35kV2#母線、10kV2#母線負荷。35kV母聯300、10kV母聯100開關在熱備用狀態。110kV、35kV、10kV備自投啟用,由于是無人值班變電站,備自投壓板在全投狀態。
本變電站為內橋接線,屬受電終端變電站,110kV824、800、823開關均不設保護,110kV線路故障靠上級線路保護動作切除,主變差動、重瓦斯、高后備保護動作將跳開各側開關。

圖2 一次接線圖
去現場查看備用電源自動投入裝置動作情況,發現與上傳至調度信號一致,無其他保護動作信號,設備無異常,2#主變帶電但無負荷。上級調度告知,系110kV電二線線路故障,電源側保護動作重合不成引起該變電站備自投動作。
調度遙控合上302、102開關,拉開300、100開關,35kV、10kV恢復原方式,2#主變帶負荷。
筆者查看備自投定值單,定值單中110kV備自投與35kV備自投及10kV備自投時限級差為0.3S,滿足規程規定微機保護0.3S級差的時限要求。110kV備自投動作后,2#主變已帶電,35kV備自投及10kV備自投不應該再動作。增加調度人員不必要的倒方式操作。可見,此次各級備自投均動作為不正常動作行為。
2.2 原因分析
110kV電二線電源側保護動作跳閘,重合不成。110kV備自投檢110kV2#母線無壓,檢824開關無電流流過,檢110kV電一線線路有壓,110kV備自投動作,跳824開關,合800開關,110kV備自投動作行為正確。
110kV備自投動作后,2#主變已帶電, 35kV、10kV備自投不應該動作。
保護人員去現場調取故障報告及動作行為,分析如下:110kV備自投在2309ms跳824開關,2498ms合800開關。35kV備自投在2616ms時跳302開關,10kV備自投在2615ms時跳102開關,符合0.3S級差的整定定值要求。但調取裝置故障濾波圖發現,800開關合后要經85ms才能檢測到開關合位,檢測到合位后再經41ms才能檢測到有壓,2498+85+41=2624ms,2624ms遲于35kV備自投、10kV備自投開始動作時間,故導致110kV備自投動作后,2#主變已帶電,而35kV、10kV備自投繼續動作的情況。
2.3 防范措施
根據上述分析,為保證備自投裝置正確、可靠動作,在進行備自投裝置時限整定上,要充分考慮到設備動作過程中的各種情況,確保備自投動作時上下級時限配合正確。
3 線路有流定值對備自投影響
一分段開關備自投裝置,取線路電流作為母線失電的閉鎖依據,防止PT斷線時誤動。在定值設定中,線路有流定值設為0.2A,而由于新投變壓器往往出線較少,負荷不重,加上CT變比有時選取較大,使得線路的正常運行電流小于線路有流定值。在這種情況下,曾發生過線路誤合環現象:某種原因導致PT斷線,但由于線路實際負荷電流小于線路有流定值,備自投裝置沒有被閉鎖,此時備自投誤動作造成合環。為了防止這樣的情況出現,我們把線路有流定值根據實際負荷情況設定。
4 結語
上文對國電南自PSP642數字式備用電源自投裝置現場不正確動作情況作了詳細的分析,找出其原因,并提出了改進措施,對今后裝置定值時限整定、運行方式安排及備自投裝置的使用有一定的指導意義。
[1]陶蘇東.國家電網公司生產技能人員職業能力培訓專用教材變電運行(110kV及以下)[M].北京:中國電力出版社,2010.
[2]賀家李.電力系統繼電保護原理與實用技術[M].北京:中國電力出版社,2009.
[3]王家華.國電南自PSP 642數字式備用電源自投裝置技術說明書[Z].國電南京自動化股份有限公司,2003.

