氯沙坦聯(lián)合阿托伐他汀治療老年高血壓療效及對延緩動脈硬化的作用研究
林新宇+黃麗斯
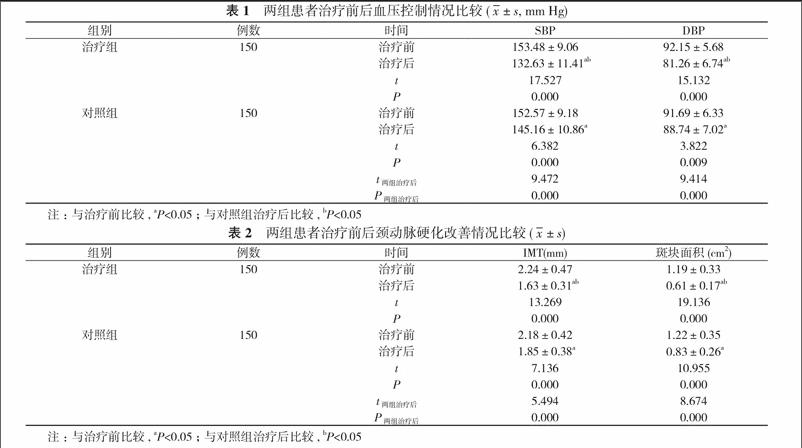
【摘要】 目的 研究氯沙坦聯(lián)合阿托伐他汀治療老年高血壓療效及對延緩動脈硬化的作用。方法 300例老年高血壓患者, 隨機分為治療組與對照組, 各150例。兩組均口服阿司匹林腸溶片, 對照組在此基礎(chǔ)上給予氯沙坦治療, 治療組在對照組基礎(chǔ)上聯(lián)合阿托伐他汀治療。比較兩組患者治療前后的血壓控制情況及頸動脈硬化改善情況。結(jié)果 治療后, 兩組收縮壓(SBP)、舒張壓(DBP)水平均低于治療前, 且治療組低于對照組, 差異有統(tǒng)計學意義(P<0.05)。治療后, 兩組頸動脈內(nèi)中膜厚度(IMT)、斑塊面積均小于治療前, 差異有統(tǒng)計學意義(P<0.05);治療組IMT(1.63±0.31)mm、斑塊面積(0.61±0.17)cm2均小于對照組的(1.85±0.38)mm、(0.83±0.26)cm2, 差異有統(tǒng)計學意義(P<0.05)。結(jié)論 在老年高血壓治療中聯(lián)合應(yīng)用氯沙坦與阿托伐他汀, 可有效控制血壓水平, 顯著改善頸動脈硬化狀況。
【關(guān)鍵詞】 氯沙坦;阿托伐他汀;高血壓;動脈硬化
DOI:10.14163/j.cnki.11-5547/r.2018.03.045
【Abstract】 Objective To study the efficacy of losartan and atorvastatin in the treatment of senile hypertension and study its effect on delaying arteriosclerosis. Methods A total of 300 senile patients with hypertension were randomly divided into treatment group and control group, with 150 cases in each group. Both groups received aspirin enteric-coated tablets. The control group was also treated with losartan, and the treatment group was treated with atorvastatin on the basis of the control group. Comparison were made on blood pressure control and improvement of carotid arteriosclerosis before and after treatment between two groups. Results After treatment, both groups had lower systolic blood pressure (SBP) and diastolic blood pressure (DBP) than before treatment, and the treatment group was lower than the control group. Their difference was statistically significant (P<0.05). After treatment, both groups had smaller carotid intima-media thickness (IMT) and plaque area than before treatment, and the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05). The treatment group had smaller IMT as (1.63±0.31) mm and plaque area as (0.61±0.17) cm2 than (1.85±0.38) mm and (0.83±0.26) cm2 in the control group, and the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05). Conclusion Combination of losartan and atorvastatin for senile hypertension can effectively control blood pressure level and significantly improve arteriosclerosis status.
【Key words】 Losartan; Atorvastatin; Hypertension; Arteriosclerosis
高血壓是高發(fā)于老年人群的一種心血管內(nèi)科疾病, 攝入過多鈉鹽、精神緊張及大量飲酒等均為其常見病因[1]。若患者動脈血壓長期處于較高水平, 常會導(dǎo)致其心、腦、腎等器官功能障礙, 嚴重者可引發(fā)心肌梗死、腎衰竭等并發(fā)癥, 從而增加患者死亡發(fā)生風險[2]。此外, 有文獻研究顯示[3], 大多數(shù)老年高血壓患者存在不同程度的頸動脈粥樣硬化斑塊, 當斑塊組織發(fā)生脫落時易引起腦梗死。目前, 針對老年高血壓臨床治療的主要目的為穩(wěn)定降壓、減少心腦血管不良事件的發(fā)生。氯沙坦是一種臨床常用的降壓藥物, 通過口服給藥方法能達到高效降壓效果, 但單用此藥物難以有效延緩動脈硬化發(fā)展[4]。阿托伐他汀屬于降脂藥物, 有研究指出[5], 聯(lián)合應(yīng)用氯沙坦與阿托伐他汀能顯著降低血脂水平, 有效抗頸動脈硬化。本文將研究氯沙坦聯(lián)合阿托伐他汀治療老年高血壓療效及對延緩動脈硬化的作用, 現(xiàn)報告如下。……

