CYP2E1基因啟動子區組蛋白高乙酰化作用促進異煙肼誘導的肝細胞凋
亡王雪 張咪 吳冬雪

摘要 目的:探討異煙肼(INH)誘導肝細胞CYP2E1啟動子區組蛋白乙酰化對肝細胞凋亡的影響。方法:INH濃度1000μg/mL,Garcinol為5μmol/L,藥物作用6 h。ELISA檢測乙酰化酶HAT與去乙酰化酶HDAC活性。Chip檢測H3K56、H4K5水平。RT-PCR檢測CYP2E1、JNK、Bax、Bcl2表達。結果:INH組與對照比,HAT活性降低,HDAC及CYP2E1啟動子區acH3K56和acH4K5水平升高,JNK、Bax的mRNA增加,Bcl2下降。與INH組比,INH + Garcinol組HAT活性、acH3K56、acH4K5表達及JNK、Bax降低,Bcl2升高。結論:抑制肝細胞CYP2E1基因啟動子乙酰化可減少INH誘導的肝細胞凋亡。
【關鍵詞】INH;肝損傷;組蛋白乙酰化;CYP2E1
中圖分類號? R575? ? 文獻標識碼? B? ? 文章編號? 1671-0223(2020)02-022-04
Abstract? ?Objective To investigate the effect of isoniazid (INH) on the apoptosis of hepatocytes induced by histone acetylation in the CYP2E1 promoter region of hepatocytes. Methods The concentration of INH was 1000μg / mL, Garcinol was 5μmol / L, and the duration of drug action was 6 h. ELISA detected the activity of acetylase HAT and deacetylase HDAC. Chip detects H3K56, H4K5 levels. RT-PCR detected the expression of CYP2E1, JNK, Bax, and Bcl2. Results Compared with the control group, the HAT activity decreased in the INH group, the levels of acH3K56 and acH4K5 in the promoter regions of HDAC and CYP2E1 were increased, the mRNAs of JNK and Bax were increased and dacreased expression of Bcl2 mRNA. Compared with the INH group, HAT activity, acH3K56, acH4K5 expression, JNK and Bax decreased, and Bcl2 increased in the INH + Garcinol group. Conclusion Inhibition of CYP2E1 gene promoter acetylation in hepatocytes can reduce hepatocyte apoptosis induced by INH.
Key words? INH; Liver injury; Histone acetylation; CYP2E1
1 引言
全世界大致200萬人每年因為結核病而死亡[1]。每年有100萬新病例出現在中國,其中13萬人因結核病失去生命[2]。一線抗結核藥物中的INH可有效治療結核病,但其在肝臟中的新陳代謝會使肝細胞受損,導致耐藥結核病的發生[3]。CYP450家族成員CYP2E1在內、外源化合物的代謝中起顯著作用,并且與肝臟的化學毒性和癌變有關[4,5]。異煙肼由肝細胞中的乙酰基轉移酶2和細胞色素P450酶催化,其最終有毒代謝物和乙酰基衍生物能與肝細胞中的大分子物質共價結合,生成內源性超氧陰離子,促進活性氧的產生[6,7]。JNK通路可被氧化應激激活,引起肝細胞凋亡促進肝損傷[8]。
組蛋白乙酰化是可逆的動態過程,是組蛋白修飾的主要形式,受HAT和HDAC調控。HAT可促進基因激活,而HDAC則抑制基因轉錄[9]。楊等發現HDAC抑制劑TSA可使胞中CYP2E1基因啟動子區的H3乙酰化,并增加CYP2E1的表達以促進肝癌細胞的凋亡[10]。但是,組蛋白乙酰化受乙酰酶和脫乙酰酶的調節,僅研究脫乙酰基酶抑制劑不能反映組蛋白的整體乙酰化。
2 材料和方法
2.1細胞和試劑
細胞系是購自上海科學院的人正常肝細胞HL-7702。配置含90%RPMI 1640(CORNING)、1%雙抗體和10%胎牛血清(CLARK)的培養基,細胞培養在5%CO2 37℃培養箱中。INH購自日本TCI公司,Garcinol購自開曼公司。
2.2細胞處理
異煙肼分別稀釋至600、800、1000和1200μg/mL,Garcinol分別稀釋至1、5和10μmol/L作用于肝細胞,CCK8法確定最佳實驗藥物濃度和試劑濃度。將細胞懸液調至密度為1×105/mL并接種在96孔板,每孔加100μL懸浮液培養24h,吸出培養液并取100μL培養液添加到對照孔,將不同濃度的藥物添加到測試孔并繼續孵化。24h后,吸出液體并用無菌PBS溶液洗滌。將100μLCCK8稀釋液加到每孔中。空白孔僅添加100μLCCK8稀釋液作為對照。將96孔板在培養箱中孵育1h,用酶標儀測量在450nm波長處測量吸光度并計算吸光度之比。
2.3 RT-PCR
用Trizol提取總RNA。反轉錄條件:37℃ 15min;85℃ 5s;4℃ 1min。20μL的PCR體系,其中SYRB Green為10μL,6.8μL的dH2O,上游和下游引物各0.4μL,0.4μL的Rox,cDNA為2μL。PCR條件:預變性95℃30 s,變性95℃5 s,退火60℃30 s,共40個循環。內參為GAPDH,mRNA用2-ΔΔct計算。
2.4 ELISA測定
收集細胞,按照ELISA試劑盒操作。試劑盒購自北京東格維業生物技術有限公司。
2.5免疫沉淀
甲醛交聯和細胞超聲處理用于免疫沉淀,收集特異性DNA并嚴格按照試劑盒說明使用q-PCR分析H3K56和H4K5乙酰化。試劑盒購自武漢愛寶泰生物技術有限公司。
2.6 統計分析
數據分析軟件用SPSS 22.0,計量資料采用“均值±標準差”表示,組間均數比較采用t檢驗,P <0.05為差異有統計學意義。
3 結果
3.1構建肝細胞損傷模型
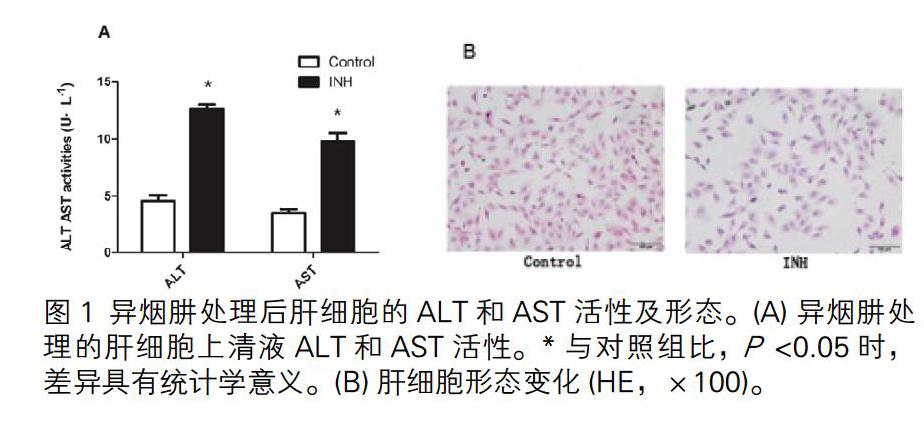
將不同稀釋濃度INH應用于肝細胞,CCK8法檢測細胞存活率在80%至85%之間的INH濃度(1000μg/ mL),選擇最大無毒劑量為抑制劑濃度(Garcinol 5μmol/ L)。該濃度下分別培養細胞6 h、24 h和48 h。CYP2E1 mRNA在給藥6h后表達增加,確定最佳給藥時間為6小時。圖1中INH組ALT和AST活性及細胞病理變化均表明肝細胞損傷模型建立成功。
3.2 INH組組蛋白乙酰化水平,CYP2E1 mRNA表達的變化
檢測HAT和HDAC活性、CYP2E1基因啟動子區域中acH3K56和acH4K5的表達水平及CYP2E1基因的mRNA表達。與對照組相比,INH組HAT活性降低,HDAC活性升高,CYP2E1基因啟動子區組蛋白乙酰化水平及CYP2E1 mRNA的表達均增加,表明異煙肼導致CYP2E1基因啟動子區組蛋白乙酰化水平增加。(圖2)
3.3 INH+Garcinol組組蛋白乙酰化水平,CYP2E1 mRNA表達的變化
檢測CYP2E1基因啟動子區acH3K56、acH4K5的表達水平及CYP2E1基因mRNA表達(圖3)。與INH組比,INH + Garcinol組acH3K56和acH4K5表達水平降低,表明Garcinol激活了CYP2E1基因。對該區域的乙酰化水平也具有抑制作用。CYP2E1基因mRNA表達,表明在啟動子區域中組蛋白乙酰化受到抑制CYP2E1基因可以被還原。
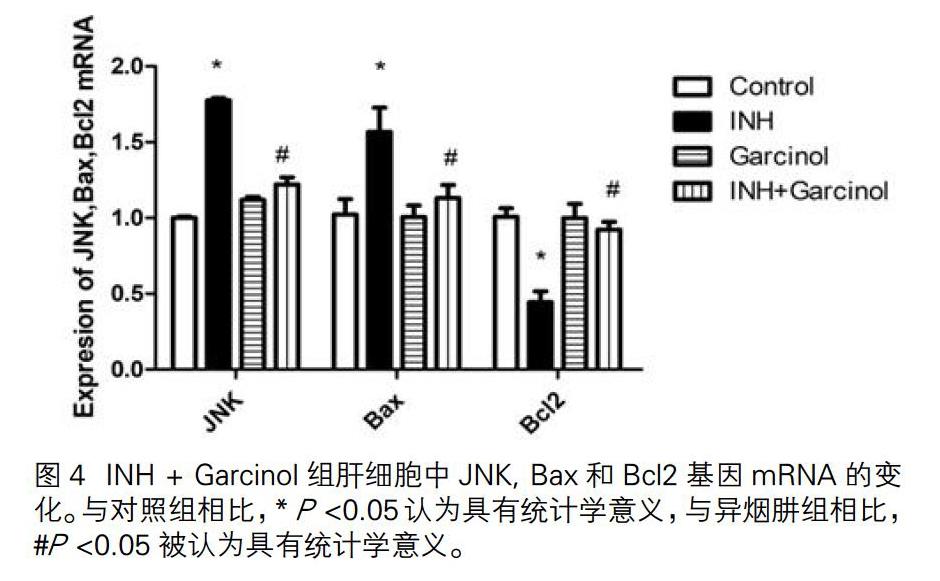
3.4 INH和 INH+Garcinol組對肝細胞凋亡的影響
檢測JNK, Bax和Bcl2的mRNA水平。與對照組相比,INH組JNK和Bax的mRNA水平升高。Bcl2的mRNA水平下降。與INH組比,INH+Garcinol組JNK和Bax mRNA水平降低,Bcl2 mRNA水平升高(圖4),表明肝細胞凋亡是由異煙肼引起的,且異煙肼與抑制劑組合可抑制細胞凋亡。與對照組相比,抑制劑對照組中JNK,Bax和Bcl2基因的mRNA水平變化不大,表明單獨使用抑制劑不會引起肝細胞凋亡。
4 討論
實驗證實INH加重肝損傷并使CYP2E1表達增加,INH引起的肝損傷中CYP2E1表達的增加與組蛋白乙酰化水平的變化有關。Garcinol對INH引起的肝損傷具有保護作用,可以為預防和治療INH致肝損傷提供理論基礎。
異煙肼可使20%的患者血清丙氨酸氨基轉移酶水平增加,2%的患者表現出明顯肝細胞毒性[11]。肝細胞用INH處理后,HAT活性降低而HDAC升高,CYP2E1基因啟動子區域中acH3K56和acH4K5表達增加。CYP2E1基因mRNA表達增加。
CYP2E1亞型主要分布在肝臟中,是一種重要的藥物代謝酶,可將INH中間體乙酰肼氧化為肝毒素,如乙酰二氮烯和乙酰乙酸銨[12]。Yang的研究表明,細胞中CYP2E1基因啟動子區的組蛋白乙酰化會影響CYP2E1基因的表達[13]。組蛋白受HAT和HDAC調節,HAT使組蛋白賴氨酸乙酰化,促進基因轉錄。HDAC使高度乙酰化的組蛋白脫乙酰化,從而抑制基因轉錄。在本研究中,異煙肼導致細胞HAT活性降低和HDAC升高,CYH2E1啟動子區域acH3K56和acH4K5表達水平升高,Garcinol組的HAT活性低于對照組,表明Garcinol對HAT活性有明顯抑制作用。INH +Garcinol組與INH組比,HAT活性降低,CYH2E1啟動子區域acH3K56和acH4K5表達水平降低,并且CYP2E1 mRNA表達水平降低,提示降低CYP2E1基因啟動子區組蛋白乙酰化水平可以抑制CYP2E1的轉錄。Garcinol是體內和體外組蛋白乙酰基轉移酶p300和PCAF的有效抑制劑[14,15,16]. Garcinol已被證明具有乙酰基轉移酶抑制劑的抗炎和抗氧化作用,并且在某些腫瘤細胞中已顯示出劑量依賴性的腫瘤細胞特異性生長抑制作用。以上結果表明,改變CYP2E1基因的啟動子區域中的組蛋白乙酰化水平可以改變CYP2E1基因的表達。
檢測JNK, Bax和Bcl2 mRNA表達及細胞形態發現,對照組相比實驗組JNK和Bax mRNA表達增加,而Bcl2 mRNA的表達下降。與異煙肼組相比,異煙肼聯合Garcinol抑制CYP2E1的表達,降低JNK和Bax mRNA的表達,并增加Bcl2 mRNA的表達。
參考文獻
[1]Fattorini L, Piccaro G, Mustazzolu A, et al. Targeting dormant bacilli to fight tuberculosis[J]. Mediterr J Hematol Infect Dis, 2013, 5(1): e2013072.
[2]Yang C, Gao Q. Recent transmission of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in China: the implication of molecular epidemiology for tuberculosis control[J]. Front Med, 2018, 12(1): 76-83.
[3]Sonika U, Kar P. Tuberculosis and liver disease: management issues[J]. Trop Gastroenterol. 2012, 33(2): 102-106.
[4]Toussirot ?, Wendling D, Herbein G. Biological treatments given in patients with rheumatoid arthritis or ankylosing spondylitis modify HAT/HDAC (histone acetyltransferase/histone deacetylase) balance[J]. Joint Bone Spine, 2014, 81(6): 544-545.
[5]Chen H P, Zhao Y T, Zhao T C. Histone deacetylases and mechanisms of regulation of gene expression[J]. Crit Rev Oncog, 2015, 20(1-2): 35-47.
[6]Sarich T C, Youssefi M, Zhou T, et al. Role of hydrazine in the mechanism of isoniazid hepatotoxicity in rabbits[J]. Arch Toxicol, 1996, 70(12): 835-840.
[7]Singh N, Dubey S, Chinnaraj S, et al. Study of NAT2 gene polymorphisms in an Indian population: association with plasma isoniazid concentration in a cohort of tuberculosis patients[J]. Mol Diagn Ther, 2009, 13(1): 49-58.
[8]Wang X, Wu D, Yang L, et al. Hepatotoxicity mediated by pyrazole (cytochrome P450 2E1) plus tumor necrosis factor alpha treatment occurs in c-Jun N-terminal kinase 2 ?/? but not in c-Jun N-terminal kinase 1 ?/? mice ? ?[J]. Hepatology, 2011, 54(5): 1753–1766.
[9]Chen H P, Zhao Y T, Zhao T C. Histone deacetylases and mechanisms of regulation of gene expression[J]. Crit Rev Oncog, 2015, 20(1-2): 35-47.
[10]Yang H, Nie Y, Li Y, et al. Histone modification-mediated CYP2E1 gene expression and apoptosis of HepG2 cells[J]. Exp Biol Med (Maywood), 2010, 235(1): 32-39.
[11]Hassan H M, Guo H L, Yousef B A, et al. Hepatotoxicity mechanisms of isoniazid: A mini-review[J]. J Appl Toxicol, 2015, 35(12): 1427-1432.
[12]Wang F J, Wang Y, Niu T, et al. Update meta-analysis of the CYP2E1 RsaI/PstI and DraI polymorphisms and risk of antituberculosis drug-induced hepatotoxicity: evidence from 26 studies[J]. J Clin Pharm Ther, 2016, 41(3): 334.
[13]Yang H, Nie Y, Li Y, et al. Histone modification-mediated CYP2E1 gene expression and apoptosis of HepG2 cells[J]. Exp Biol Med (Maywood), 2010, 235(1): 32.
[14]Yamaguchi F, Saito M, Ariga T, et al. Free radical scavenging activity and antiulcer activity of garcinol from Garcinia indica fruit rind[J]. J Agric Food Chem, 2000, 48(6): 2320-2325.
[15]Padhye S, Ahmad A, Oswal N, et al. Emerging role of Garcinol, the antioxidant chalcone from Garcinia indica Choisy and its synthetic analogs[J]. J Hematol Oncol, 2009, 2: 38.
[16]Yuan H, Wan J, Li L, et al. Therapeutic benefits of the group B3 vitamin nicotinamide in mice with lethal endotoxemia and polymicrobial sepsis[J]. Pharmacol Res, 2012, 65(3): 328-337.
[2020-01-07收稿]

