鈥激光碎石與氣壓彈道碎石術對復雜輸尿管上段結石患者氧化應激及遠期的影響
韓超 劉肇華 陳敏堅 楊志堅 龐程 吳炳權
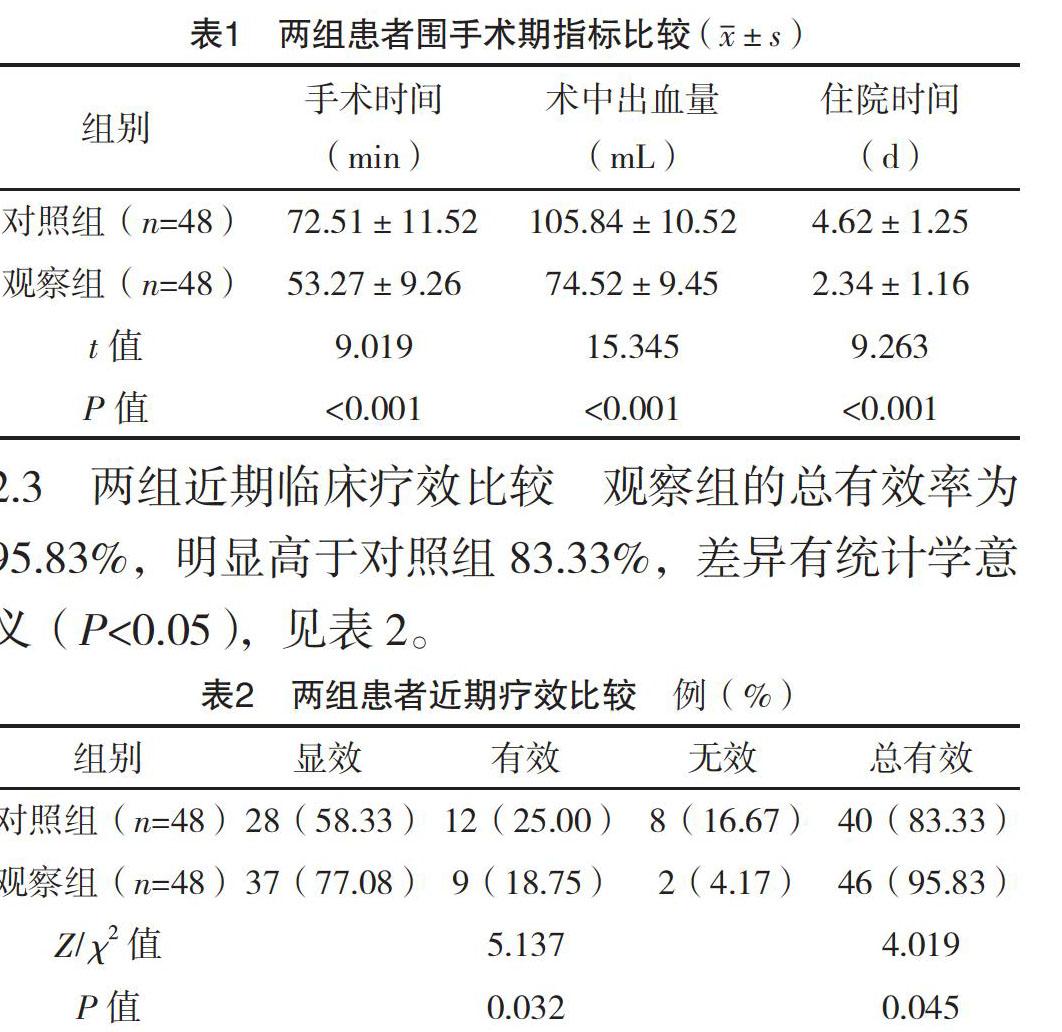
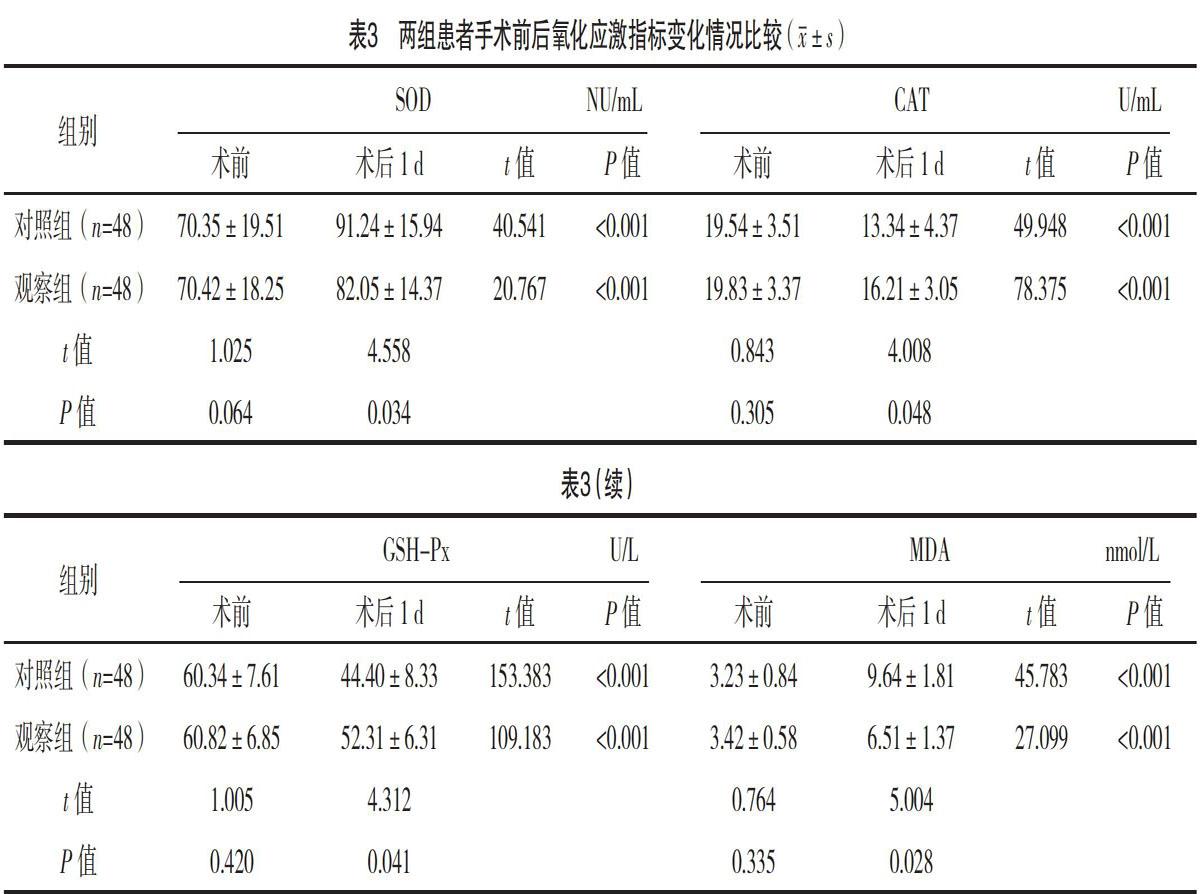
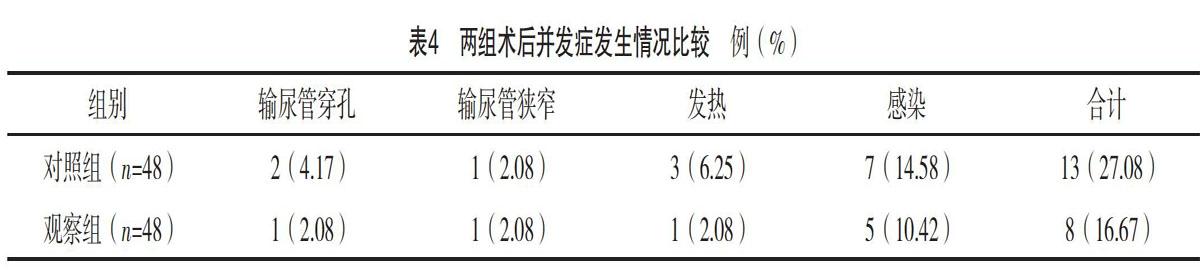
【摘要】 目的:探討鈥激光碎石與氣壓彈道碎石術對復雜輸尿管上段結石患者氧化應激及遠期的影響。方法:選取2017年2月-2018年1月本院收治的96例復雜輸尿管上段結石患者,按手術方法不同分成觀察組和對照組,各48例。對照組行氣壓彈道碎石術,觀察組行鈥激光碎石。比較兩組患者的氧化應激水平、近期療效、并發癥發生情況及遠期復發率。結果:觀察組患者手術時間及住院時間均較對照組明顯縮短(P<0.05),且術中出血量明顯少于對照組(P<0.05);觀察組的總有效率為95.83%,明顯高于對照組83.33%(P<0.05);術后1 d,兩組SOD、MDA均較治療前顯著增高(P<0.05),CAT、GSH-Px均較治療前顯著降低(P<0.05),但觀察組患者各氧化應激指標改變幅度均明顯小于對照組(P<0.05);觀察組術后復發率為6.25%,低于對照組的16.67%,差異有統計學意義(字2=4.315,P=0.042);兩組術后并發癥發生率比較,差異無統計學意義(P>0.05)。結論:鈥激光碎石術較氣壓彈道碎石術治療復雜輸尿管上段結石能獲得更佳的近期臨床效果,降低遠期復發率,值得擴大樣本量深入研究。
【關鍵詞】 鈥激光碎石 氣壓彈道碎石術 輸尿管鏡 輸尿管上段結石 氧化應激
[Abstract] Objective: To investigate the effects of holmium laser lithotripsy and pneumatic lithotripsy on oxidative stress and long-term in patients with complicated upper ureteral calculi. Method: A total of 96 patients with complicated upper ureteral calculi admitted to our hospital from February 2017 to January 2018 were selected, patients were divided into the observation group andcontrol group, according to different surgical methods, 48 cases in each group. The control group underwent pneumatic lithotripsy, the observation group underwent holmium laser lithotripsy. The oxidative stress level, short-term efficacy, complications and long-term recurrence rate of the two groups were compared. Result: The operation time and hospitalization time of the observation group were significantly shorter than those of the control group (P<0.05), and the intraoperative blood loss was significantly less than that of the control group (P<0.05). The total effective rate was 95.83%, which was significantly higher than 83.33% of the control group (P<0.05). The SOD and MDA of the two groups were significantly higher than those before treatment (P<0.05), and CAT and GSH-Px were significantly lower than those before treatment (P<0.05), but the change of oxidative stress index in the observation group were significantly lower than those in the control group (P<0.05). The postoperative recurrence rate in the observation group was 6.25%, lower than 16.67% in the control group, the difference was statistically significant (字2=4.315, P=0.042). There was no significant difference in the incidence of postoperative complications between the two groups (P>0.05). Conclusion: Holmium laser lithotripsy can achieve better short-term clinical efficacy and lower long-term recurrence rate than pneumatic lithotripsy in the treatment of complex upper ureteral calculi, it is worth to expand the sample size in-depth study.[Key words] Holmium laser lithotripsy Pneumatic ballistic lithotripsy Ureteroscopy Upper ureteral calculi Oxidative stressFirst-authors address: The First Peoples Hospital of Zhaoqing City, Zhaoqing 526000, China
輸尿管結石為泌尿外科最常見病癥之一,多發于中老年人[1]。目前臨床治療復雜性輸尿管上段結石有多種微創手術,輸尿管鏡碎石術具有碎石效率高、術后并發癥少的優勢,已逐步取代傳統開放手術成為輸尿管結石的首選方法[2-3]。經尿道輸尿管鏡碎石術主要包括鈥激光與氣壓彈道碎石術,雖已有較多研究比較兩者的優劣,但專門針對復雜輸尿管上段結石方面的研究鮮有報道。氧化還原狀態的失衡導致機體多種病理改變,參與了泌尿系結石的發生、發展與惡化[4]。本研究選取96例復雜輸尿管上段結石患者分別予以鈥激光碎石與氣壓彈道碎石術,旨在尋找復雜輸尿管上段結石更佳的治療方法,現報道如下。……

