內(nèi)固定與人工關(guān)節(jié)置換治療糖尿病股骨粗隆間骨折患者的效果對比分析
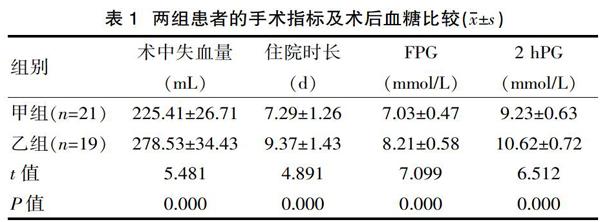
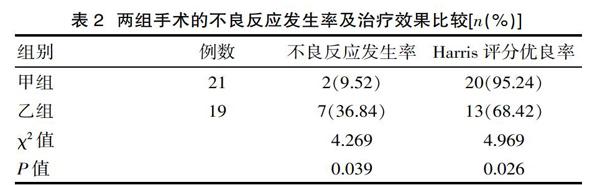
[摘要] 目的 比較內(nèi)固定術(shù)與人工關(guān)節(jié)置換術(shù)治療糖尿病合并股骨粗隆間骨折患者的臨床效果。方法 選取2016年4月—2019年1月在該院接受手術(shù)治療的糖尿病股骨粗隆間骨折患者共40例分為甲組和乙組,兩組患者在圍術(shù)期均接受血糖控制管理,在此基礎(chǔ)上,甲組采用人工關(guān)節(jié)置換術(shù),乙組采用內(nèi)固定術(shù),比較兩組患者的血糖控制效果以及手術(shù)治療效果。結(jié)果 甲組的術(shù)中出血量、住院時長、術(shù)后血糖水平、不良反應(yīng)發(fā)生率(9.52%)以及Harris評分優(yōu)良率(95.24%)均明顯優(yōu)于乙組。結(jié)論 人工關(guān)節(jié)置換術(shù)治療糖尿病股骨粗隆間骨折患者的臨床效果更為理想。
[關(guān)鍵詞] 內(nèi)固定術(shù);人工關(guān)節(jié)置換術(shù);糖尿病;股骨粗隆間骨折
[中圖分類號] R687? ? ? ? ? [文獻標識碼] A? ? ? ? ? [文章編號] 1672-4062(2020)03(a)-0048-02
Comparative Observation of the Effects of Internal Fixation and Artificial Joint Replacement on Patients with Diabetic Femoral Intertrochanteric Fractures
XU Zhan-hui
Department of Orthopaedics, Mudanjiang Second People's Hospital, Mudanjiang, Heilongjiang Province, 157000 China
[Abstract] Objective To compare the clinical effects of internal fixation and artificial joint replacement in the treatment of diabetic patients with intertrochanteric fractures. Methods A total of 40 patients with diabetic femoral intertrochanteric fracture who underwent surgical treatment in our hospital from April 2016 to January 2019 were divided into group A and group B. Both groups received blood glucose control during the perioperative period. Based on this, group A used artificial joint replacement, and group B used internal fixation. The blood glucose control effect and surgical treatment effect of the two groups were compared. Results Intraoperative blood loss, length of hospital stay, postoperative blood glucose level, incidence of adverse reactions(9.52%) and Harris score excellent rate (95.24%)in group A were significantly better than those in group B. Conclusion The clinical effect of artificial joint replacement in patients with diabetic femoral intertrochanteric fracture is more ideal.
[Key words] Internal fixation; Artificial joint replacement; Diabetes; Femoral intertrochanteric fracture
糖尿病的臨床發(fā)病率較高,不僅會導(dǎo)致患者出現(xiàn)糖代謝異常,還可能引發(fā)骨代謝異常,增加骨質(zhì)疏松癥的發(fā)生風(fēng)險。相關(guān)臨床研究表明,糖尿病人群發(fā)生股骨粗隆間骨折的幾率更高,且治療難度更大,如果不采取有效措施加強圍術(shù)期血糖管理,還可能引發(fā)骨折延遲愈合等嚴重情況,不僅危害了患者的身心健康,也對其生活質(zhì)量造成了不利的影響[1]。手術(shù)治療是目前臨床上治療股骨粗隆間骨折的常用手段,但由于糖尿病患者大多存在骨質(zhì)疏松的情況,因此傳統(tǒng)內(nèi)固定術(shù)的治療效果不佳,術(shù)后患者極易發(fā)生內(nèi)固定失效或者髖內(nèi)翻畸形等嚴重情況[2]。人工關(guān)節(jié)置換術(shù)主要通過植入人造假體來幫助患者恢復(fù)關(guān)節(jié)運動功能,不會對患者的骨折愈合過程產(chǎn)生任何影響,目前在臨床上的應(yīng)用也越來越廣泛。……

