醒腦靜治療急性期腦出血患者的療效和安全性評估
于忠芹
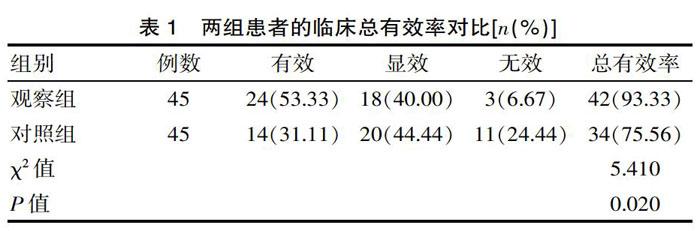
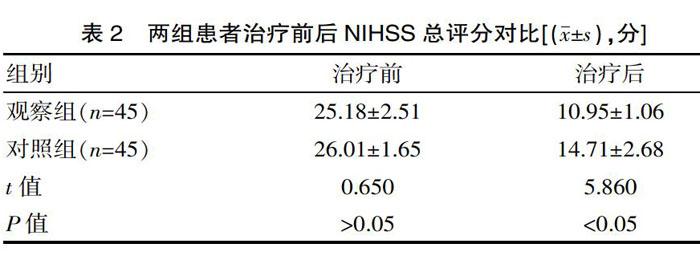
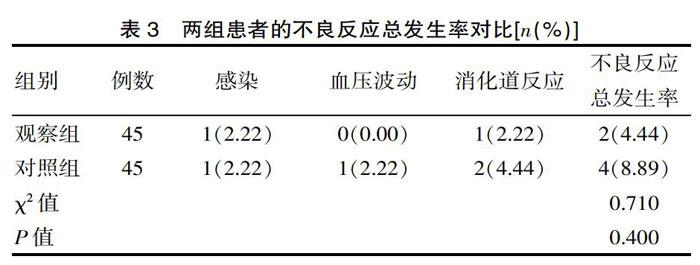
[摘要] 目的 研究予以急性期腦出血患者醒腦靜治療的臨床療效和安全性評估。方法 方便選取2018年5月—2019年8月該院收治的90例急性期腦出血患者參與該次研究,按照隨機數表法將其分為觀察組和對照組,每組45例,對照組進行脫水、抗腦水腫等常規治療,觀察組在此基礎上加以醒腦靜治療。對比兩組的臨床療效、治療前后神經功能的變化情況及治療后不良反應的發生情況。 結果 治療后,觀察組的臨床總有效率顯著高于對照組(χ2=5.410,P<0.05);治療前兩組NIHSS評分差異無統計學意義(t=0.650,P>0.05),治療后觀察組的NIHSS總評分明顯低于對照組(t=5.860,P<0.05);治療后,觀察組的不良反應總發生率為4.44%,低于對照組(8.89%),但差異無統計學意義(χ2=0.710,P>0.05)。 結論 應用醒腦靜治療急性期腦出血患者,其臨床療效良好,能夠有效緩解患者的臨床癥狀,促進患者神經功能的恢復,提高患者的生活質量,且兩組患者治療后均未存在嚴重不良反應的發生,安全性高,具有較高的臨床意義。
[關鍵詞] 醒腦靜;急性期腦出血;療效;安全性
[中圖分類號] R743.34 ? ? ? ? ?[文獻標識碼] A ? ? ? ? ?[文章編號] 1674-0742(2020)04(c)-0001-03
Efficacy and Safety Evaluation of Xingnaojing in Treating Patients with Acute Cerebral Hemorrhage
YU Zhong-qin
Department of Neurology, Laixi People's Hospital, Laixi, Shandong Province, 266600 China
[Abstract] Objective To evaluate the clinical efficacy and safety of Xingnaojing treatment in patients with acute cerebral hemorrhage. Methods 90 patients with acute cerebral hemorrhage treated in the hospital from May 2018 to August 2019 were conveniently selected to participate in this study. They were divided into observation group and control group according to the random number table method, with 45 cases in each group and the control group. Conventional treatments such as dehydration and anti-edema were performed, and the observation group was treated with Xingnaojing on this basis. The clinical efficacy, changes in neurological function before and after treatment, and occurrence of adverse reactions after treatment were compared between the two groups. Results After treatment, the total clinical effective rate in the observation group was significantly higher than that in the control group (χ2=5.410, P<0.05); there was no significant difference in the NIHSS scores between the two groups before treatment(t=0.650, P>0.05). The total NIHSS score of the group was significantly lower than that of the control group(t=5.860, P<0.05). After treatment, the total incidence of adverse reactions in the observation group was 4.44%, which was lower than that of the control group (8.89%), but the difference was not statistically significant(χ2=0.710, P>0.05). Conclusion The application of Xingnaojing in the treatment of patients with acute cerebral hemorrhage has good clinical effects, can effectively alleviate the clinical symptoms of patients, promote the recovery of patients' neurological function, and improve the quality of life of patients. There were no serious adverse reactions occurrence, high safety and high clinical significance after treatment in the two groups of patients.
[Key words] Xingnaojing; Acute cerebral hemorrhage; Efficacy; Safety
急性期腦出血是一種臨床常見的危急重癥,指非外傷醒腦實質內小血管急性破裂出血,其主要出血部位為小腦、腦干及基底節區[1]。頭痛、昏迷、惡心等是該病的臨床癥狀,病情嚴重時可能會出現腦水腫、顱內高壓,進而給患者的身體造成不利的影響。多數患者在治療后會出現后遺癥,存在語言、行動等障礙,降低了患者的日常生活能力,影響其生活質量。目前,臨床上尚未明確治療急性腦期出血的對應藥物[2],多以調整血壓、抗感染、降顱內壓等方式進行常規治療,雖然常規治療對病情有一定的控制作用,但效果不甚理想。……

