多層螺旋CT檢查與DR平片檢查在診斷外傷性肋骨骨折方面的臨床價(jià)值對比
王培
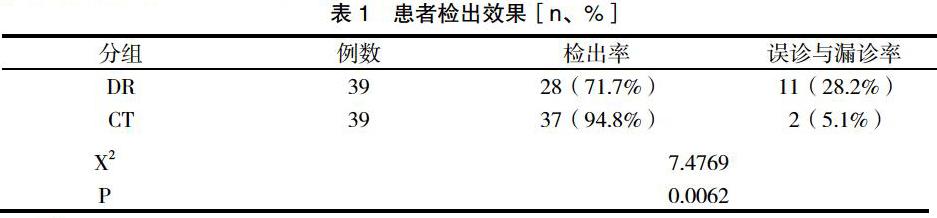
【摘 要】目的:研究多層螺旋CT檢查與DR平片檢查在診斷外傷性肋骨骨折方面的臨床價(jià)值。方法:選擇78例骨折疾病診斷和預(yù)后治療患者,分別進(jìn)行CT檢查(多層螺旋CT檢查)和DR檢查(DR平片檢查),各小組39例,觀察兩種方法檢出率。結(jié)果:檢查后,DR檢出率為71.7%,CT檢出率為94.8%,差異有意義(P<0.05)。結(jié)論:外傷性肋骨骨折患者診斷時(shí),多層螺旋CT檢查具有較高診斷價(jià)值,可以保證其診斷結(jié)果具有較高準(zhǔn)確性,以便于醫(yī)生觀察和了解,從而科學(xué)制定疾病治療方法,加快患者康復(fù)速度。
【關(guān)鍵詞】多層螺旋CT;DR平片檢查;外傷性肋骨骨折
【中圖分類號】R816.8 【文獻(xiàn)標(biāo)識碼】 B 【文章編號】1002-8714(2020)08-0018-01
【Abstract】 Objective: To study the clinical value of multi-slice spiral CT and plain radiography in the diagnosis of traumatic rib fractures. Methods: Seventy-eight patients with fracture disease diagnosis and prognostic treatment were selected, and CT examination (multi-slice spiral CT examination) and DR examination (DR plain film examination) were performed.9 patients in each group were observed for the detection rate of the two methods. Results: After the examination, the detection rate of DR was1.7% and the detection rate of CT was4.8%, and the difference was significant (P <0.05). Conclusion: Multi-slice spiral CT examination has high diagnostic value when diagnosing patients with traumatic rib fractures, which can ensure its diagnostic results with high accuracy, so that doctors can observe and understand, so as to scientifically formulate disease treatment methods and speed up the recovery .
【Keywords】 multi-slice spiral CT; plain radiography; traumatic rib fractures
肋骨骨折是臨床常見骨折疾病,結(jié)合患者病情骨折情況發(fā)現(xiàn),多數(shù)患者病情較為嚴(yán)重,如果患者發(fā)生肋骨骨折應(yīng)該及時(shí)去醫(yī)院治療,只有盡快控制病情,才可以保證患者生命安全。對于外傷性肋骨骨折患者來講,通常是在外力作用下導(dǎo)致,即人體結(jié)構(gòu)受到猛烈撞擊后,使其超出正常人體承受極限,從而發(fā)生損傷與骨折等[1]。目前,對外傷性肋骨骨折患者進(jìn)行診斷時(shí),常見診斷方法包括:CT檢查、DR檢查等,對患者予以準(zhǔn)確診斷,是保證患者早日恢復(fù)的關(guān)鍵。
1 資料與方法
1.1 基本資料
選擇78例骨折疾病診斷和預(yù)后治療患者,時(shí)間在2018年11月-2019年11月期間,全部患者為外傷性肋骨骨折,分別進(jìn)行CT檢查和DR檢查,均39例。在CT檢查中,男性患者人數(shù)23例,女性患者人數(shù)16例,最小15歲,最大66歲,均值為(40.5±5.5)歲;在DR檢查中,男性患者人數(shù)22例,女性患者人數(shù)17例,最小16歲,最大66歲,均值為(41±5)歲。患者資料比較差異無意義(P>0.05)。
1.2 方法
在進(jìn)行多層螺旋CT檢查時(shí),要求患者維持仰臥位狀態(tài),同時(shí)需要維持吸氣和屏氣狀態(tài)。實(shí)際檢查過程,主要選擇16排螺旋CT裝置進(jìn)行,首先對肋骨薄層予以橫斷面掃描,經(jīng)過詳細(xì)掃描獲取圖像[2]。在……

