地塞米松聯(lián)合甘露醇治療對(duì)急性重癥腦血管病腦保護(hù)作用的臨床觀察
彭亮
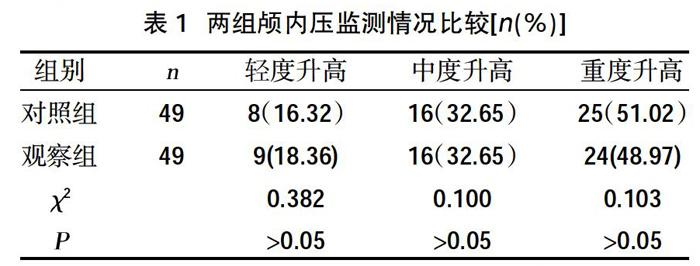
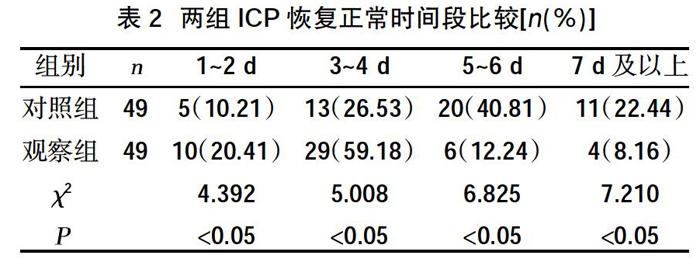

摘要:目的 ?觀察地塞米松聯(lián)合甘露醇應(yīng)用于急性重癥腦血管病腦保護(hù)作用。方法 ?選取2018年5月~2019年5月在我院診治的98例急性重癥腦血管病患者為研究對(duì)象,采用隨機(jī)數(shù)字表法分為對(duì)照組和觀察組,各49例。對(duì)照組采用甘露醇治療,觀察組在對(duì)照組基礎(chǔ)上聯(lián)合地塞米松治療,比較兩組患者顱內(nèi)壓(ICP)檢測(cè)情況(正常、輕度、中度、重度)、ICP恢復(fù)正常時(shí)間段比例、格拉斯哥昏迷(GCS)評(píng)分情況、病死率以及并發(fā)癥發(fā)生情況。結(jié)果 ?觀察組顱內(nèi)壓輕度、中度、重度升高發(fā)生率與對(duì)照組比較,差異無(wú)統(tǒng)計(jì)學(xué)意義(P>0.05);觀察組1~2 d、3~4 d患者ICP恢復(fù)正常發(fā)生率均高于對(duì)照組,5~6 d、7 d及以后發(fā)生率均低于對(duì)照組,差異有統(tǒng)計(jì)學(xué)意義(P<0.05);觀察組GCS 評(píng)分3~8分發(fā)生率低于對(duì)照組,9~12分、13~14分發(fā)生率均高于對(duì)照組,差異有統(tǒng)計(jì)學(xué)意義(P<0.05);觀察組病死率為12.24%,低于對(duì)照組的14.28%,差異無(wú)統(tǒng)計(jì)學(xué)意義(P>0.05);兩組并發(fā)癥發(fā)生率比較,差異無(wú)統(tǒng)計(jì)學(xué)意義(P>0.05)。結(jié)論 ?臨床采用地塞米松聯(lián)合甘露醇應(yīng)用于急性重癥腦血管病治療可減輕顱內(nèi)壓升高程度,縮短ICP恢復(fù)時(shí)間,提高GCS評(píng)分,降低顱內(nèi)壓,具有顯著的腦保護(hù)作用。同時(shí)不會(huì)增加并發(fā)癥,影響病死率,具有顯著的臨床應(yīng)用價(jià)值。
關(guān)鍵詞:地塞米松;甘露醇;急性;重癥腦血管病;腦保護(hù)作用
中圖分類號(hào):R969.4 ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?文獻(xiàn)標(biāo)識(shí)碼:A ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-1959.2020.18.048
文章編號(hào):1006-1959(2020)18-0145-03
Clinical Observation of the Protective Effect of Dexamethasone Combined with Mannitol
on the Cerebral Protection of Acute Severe Cerebrovascular Disease
PENG Liang
(Department of Neurosurgery,Dongli District Hospital,Tianjin 300300,China)
Abstract:Objective ?To observe the protective effect of dexamethasone combined with mannitol in acute severe cerebrovascular disease.Methods ?A total of 98 patients with acute severe cerebrovascular disease diagnosed and treated in our hospital from May 2018 to May 2019 were selected as the research objects, and were divided into the control group and the observation group by random number table method, with 49 cases in each group. The control group was treated with mannitol, and the observation group was treated with dexamethasone on the basis of the control group. The intracranial pressure (ICP) detection status (normal, mild, moderate, severe) of the two groups of patients was compared, and the ratio of the time period when ICP returned to normal, Glasgow coma (GCS) score, case fatality rate and complications.Results ?Compared with the control group, the incidence of mild, moderate, and severe increases in intracranial pressure in the observation group was not statistically different (P>0.05); the incidence of ICP returned to normal in patients in the observation group on 1-2 d and 3-4 d Higher than the control group, the incidence rates of 5-6 d, 7 d and later were lower than those of the control group, the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05); the incidence of GCS scores of 3-8 points in the observation group was lower than that of the control group,the incidence rates of 9-12 points and 13-14 points were higher than those of the control group,the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05); the mortality rate of the observation group was 12.24%, which was lower than the control group's 14.28%,the difference was not statistically significant (P>0.05); There was no statistically significant difference in the incidence of complications between the two groups (P>0.05).Conclusion ?The clinical application of dexamethasone combined with mannitol in the treatment of acute severe cerebrovascular disease could reduce the increase in intracranial pressure, shorten the recovery time of ICP, increase the GCS score, reduce intracranial pressure, and had ?a significant brain protection effect. At the same time, it would not increase complications and affect the mortality rate, and had significant clinical application value.
Key words:Dexamethasone;Mannitol;Acute;Severe cerebrovascular disease;Brain protection
急性重癥腦血管疾病(acute severe cerebrovascular disease)是臨床常見多發(fā)病,病情相對(duì)較急,會(huì)引起患者腦血管突發(fā)性血栓、腦梗塞、腦出血等,嚴(yán)重威脅患者的生命安全[1]。臨床主要伴有失語(yǔ)、肢體偏癱、眩暈以及其他精神癥狀等,嚴(yán)重者會(huì)出現(xiàn)昏迷甚至是死亡。目前,對(duì)于該類患者主要給予降低顱內(nèi)壓、減輕腦水腫、保護(hù)腦細(xì)胞以及預(yù)防并發(fā)癥治療[2,3]。甘露醇是……

