K-12 AI curricula: A mapping of government-endorsed AI curricula(Ⅲ)
譯題? K-12人工智能課程:政府認(rèn)可的人工智能課程圖譜(三)
Product by UNESCO (United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization) 聯(lián)合國教科文組織
第一份關(guān)于K-12(學(xué)前教育至高中教育的基礎(chǔ)教育階段)人工智能課程全球狀況的報告,意在開發(fā)有效的支持工具和框架來促進(jìn)青少年人工智能素養(yǎng)的發(fā)展。
Curriculum integration and management
Curricula are integrated into existing education systems through a number of different models:
Discrete AI curricula are developed in an independent subject category within the national or local curriculum framework. These curricula have their own time allocations, textbooks and resources, as in the case of Chinas Foundations of AI under Information Science and Technology for grades 10 to 12.
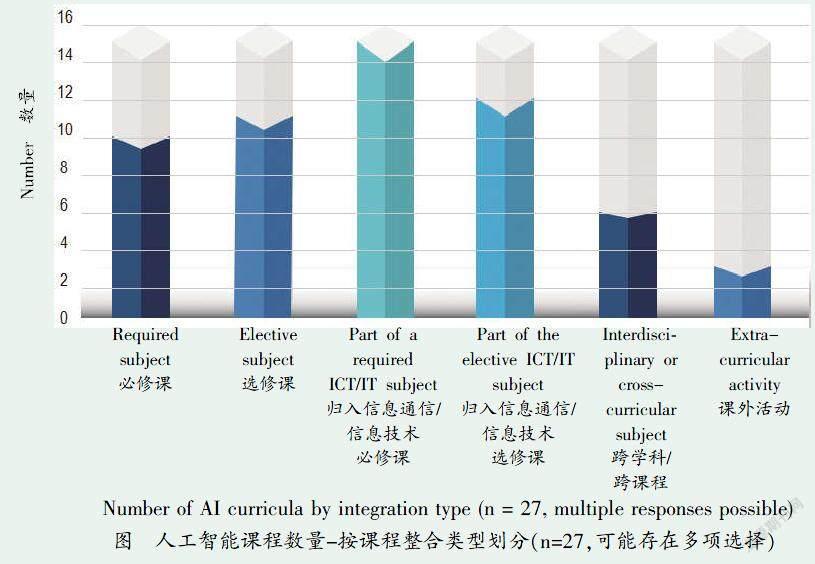
Embedded AI curricula are developed and contained within other subject categories in the national or local curriculum framework. AI most commonly becomes a topic within ICT or computer science but may alternatively be part of language, mathematics, science or engineering (see the right Figure). In the Republic of Korea, two elective AI subjects have been developed, one falling within the mathematics subject group and the other in technology and home economics. Curricula can also be designed to be embedded flexibly into any subject depending on teacher capacity and interest. This is the case for the MIT DAILy Curriculum.
Interdisciplinary AI curricula are implemented in systems with particular mandates for cross-subject work and associated time. These curricula target AI learning outcomes through project-based learning involving multiple subject areas. An example is seen in Portugals curriculum frameworks, which feature ‘a(chǎn)utonomous curriculum domains, or projects that must engage two or three disciplines in an interdisciplinary approach. In the UAE, AI is integrated into a range of subjects including ICT, science, maths, language, social studies and moral education.
Multiple-modality AI curricula have core requirements which are implemented during school time and supported by traditional resources such as facilitator guides and textbooks, but also leverage informal learning opportunities such as out-of-school resource networks and national or international competitions. An example of such a curriculum is the IBM-CBSE AI Curriculum for Grade XI & XII, which provides a gradual transition from guided to independent learning and links to competitions and industry mentorship.
Flexible AI curricula can be implemented through one or more integration mechanisms at the discretion of regions, school networks or individual schools. Examples include the ATL AI modules curriculum in India, which can be embedded, interdisciplinary or delivered through out-of-school models such as extracurricular activities; and Digital Skills in Saudi Arabia, which can be implemented as either a discrete or embedded curriculum. For some curricula, the embedding mechanisms are at the discretion of regions, schools or networks. These include the French-speaking Belgiums IT Repository (2nd and 3rd degree technical transition), and Germanys Algorithmen erkennen und formulieren [Identifying and Formulating Algorithms] curriculum.
譯文
課程整合與管理
人工智能課程可以通過多種方式被整合至現(xiàn)有的教育系統(tǒng):
獨立人工智能課程。該類型課程是在國家或地方課程框架內(nèi)開發(fā)的獨立學(xué)科類別。這些課程有自己的時間分配、教材和資源,比如,中國面向高中1~2年級的信息科技學(xué)科中設(shè)置的人工智能基礎(chǔ)課程。
歸入式的人工智能課程。該類課程在國家或地方課程框架下的其他學(xué)科類別中開發(fā),并被納入其中。人工智能不僅是信息通信技術(shù)或計算機(jī)科學(xué)中最常見的主題,也是語言、數(shù)學(xué)、科學(xué)或工程學(xué)科的一部分(見右上圖)。韓國已經(jīng)開發(fā)了兩門人工智能選修課程,其中一門隸屬于數(shù)學(xué)學(xué)科群,另一門被納入技術(shù)家庭經(jīng)濟(jì)學(xué)科群。人工智能課程也可以根據(jù)教師的能力和興趣,靈活地歸入任何學(xué)科。麻省理工學(xué)院的DAILy課程就屬于此種情況。
跨學(xué)科人工智能課程。此類課程往往在對跨學(xué)科工作和時間有特殊要求的系統(tǒng)中實施。這些課程旨在通過涵蓋多學(xué)科領(lǐng)域的基于項目的學(xué)習(xí),實現(xiàn)人工智能的學(xué)習(xí)結(jié)果。以葡萄牙的人工智能課程框架為例,其特點是“自主課程領(lǐng)域”,或項目必須涉及兩到三個學(xué)科的跨學(xué)科方法。在阿聯(lián)酋,人工智能被整合到包括信息通信技術(shù)、科學(xué)、數(shù)學(xué)、語言、社會研究和品德教育等在內(nèi)的一系列學(xué)科當(dāng)中。
多課程方式相結(jié)合的人工智能課程。該類課程的核心要求在于:不僅需要在開學(xué)期間實施,且需要傳統(tǒng)教學(xué)資源的支持(如教師指導(dǎo)和教材),同時也需利用校外資源網(wǎng)絡(luò)和國家或國際競賽等非正式的學(xué)習(xí)機(jī)會。此類課程的代表是“IBM-CBSE面向11和12年級的人工智能課程”,該課程結(jié)合競 賽和行業(yè)指導(dǎo),幫助學(xué)生實現(xiàn)從引導(dǎo)式學(xué)習(xí)到獨立學(xué)習(xí)的逐步過渡。
彈性人工智能課程。此類課程可根據(jù)地區(qū)、學(xué)校網(wǎng)絡(luò)或個別學(xué)校的實際情況,通過一個或多個整合機(jī)制去實施課程。例如,印度的ATL人工智能模塊課程,可通過歸入其他課程、跨學(xué)科合作或與課外活動結(jié)合等校外模式實施;沙特阿拉伯的數(shù)字技能課程,可作為獨立或歸入式的課程實施。
還有部分課程的歸入機(jī)制取決于地區(qū)、學(xué)校或網(wǎng)絡(luò)。這類課程包括比利時法語區(qū)的信息技術(shù)數(shù)據(jù)庫(二、三級技術(shù)過渡),以及德國的識別和表述算法課程。

