聚乙二醇干擾素α-2b治療慢性乙型肝炎患者血清HBsAg清除率的效果分析
李寬 寧會彬 靳慧鳴 彭真 尚佳

摘要:目的真實世界中評價聚乙二醇干擾素α-2b(PEG-IFNα-2b)在治療慢性乙型肝炎(CHB)中清除HBsAg的效果。方法回顧性納入2017年6月—2021年1月就診于河南省人民醫院感染科的411例CHB患者,所有患者均應用PEG-IFNα-2b治療。收集患者性別、年齡、抗病毒治療方案、基線HBsAg水平、治療后HBsAg水平,觀察分析24、48及96周HBsAg清除率。在不同HBsAg基線水平(<500 IU/mL、500~1 500 IU/mL、1 501~5 000 IU/mL)及不同既往治療情況和治療方案后應用PEG-IFNα-2b,比較各隨訪節點的HBsAg清除率。計量資料兩組間比較采用成組t檢驗,計數資料組間比較采用χ2檢驗和趨勢性χ2檢驗。結果完成24周治療患者HBsAg清除率9.9%(26/263)。完成48周治療患者HBsAg清除率19.7%(25/127)。完成96周治療患者HBsAg清除率41.7%(30/72)。不同基線HBsAg水平患者治療24、48及96周時HBsAg清除率比較差異均有統計學意義(χ2值分別為52.265、32.764、30.918,P值均<0.01),隨著治療時間延長,HBsAg清除率逐漸升高,并且這種趨勢有統計學意義(趨勢χ2值分別為44.517、29.147、22.260,P值均<0.01)。隨訪24、48及96周時,HBsAg 500~1 500 IU/mL組和1 501~5? ?000 IU/mL組的HBsAg清除率較HBsAg<500 IU/mL組均明顯下降(P值均<0.001)。在治療24、48及96周時,治療情況(初治或經治)及治療方案(單用或聯合)患者相比較,僅初治與經治組在男女比例上存在差異(χ2=5.029,P=0.025);初治或經治組間、單用或聯合治療組間HBsAg清除率比較差異均無統計學意義(P值均>0.05)。結論PEG-IFNα-2b在治療CHB中對清除HBsAg有良好的效果,并且基線HBsAg水平越低,HBsAg清除率越高,隨著治療時間的延長,HBsAg清除率呈上升趨勢。基線HBsAg 500 IU/mL可作為優勢人群的分界點。
關鍵詞:聚乙二醇干擾素α-2b; 乙型肝炎, 慢性; 乙型肝炎表面抗原
基金項目:中國降低乙肝患者肝癌發生率研究(綠洲)工程項目(LZGC2022-03)
Effect of pegylated interferon α-2b on serum HBsAg clearance rate in treatment of patients with chronic hepatitis
B LI Kuan, NING Huibin, JIN Huiming, PENG Zhen, SHANG Jia. (Department of Infectious Diseases, Henan Provincial Peoples Hospital, Zhengzhou 450003, China)
Corresponding author:SHANG Jia, shangjia666@126.com (ORCID:0000-0001-9197-8773)
Abstract:ObjectiveTo investigate the effect of pegylated interferon α-2b (PEG-IFNα-2b) on HBsAg clearance in the treatment of chronic hepatitis B (CHB) in a real-world setting. MethodsA retrospective analysis was performed for 411 CHB patients who attended Department of Infectious Diseases, Henan Provincial Peoples Hospital, from June 2017 to January 2021, and all these patients were treated with PEG-IFNα-2b. Related clinical data were collected, including sex, age, antiviral treatment regimen, baseline HBsAg level, and post-treatment HBsAg level, and HBsAg clearance rate was observed at 24, 48, and 96 weeks. HBsAg clearance rate at different time points of follow-up was compared between the patients with different baseline HBsAg levels (<500 IU/mL, 500-1 500 IU/mL, and 1 501-5 000 IU/mL) or with the use of PEG-IFNα-2b after different previous treatment conditions and regimens. The independent-samples t test was used for comparison of continuous data between two groups, and the chi-square test and the trend chi-square test were used for comparison of categorical data between groups. ResultsThe HBsAg clearance rate was 9.9% (26/263) in the patients who completed 24 weeks of treatment, 19.7% (25/127) in the patients who completed 48 weeks of treatment, and 41.7% (30/72) in the patients who completed 96 weeks of treatment. There was a significant difference in HBsAg clearance rate between the patients with different baseline HBsAg levels at 24, 48, and 96 weeks of treatment (χ2=52.265, 32.764, and 30.918, all P<0.01), and HBsAg clearance rate gradually increased over the time of treatment (χ2trend=44.517, 29.147, and 22.260, all P<0.01). Compared with the HBsAg <500 IU/mL group, the 500-1 500 IU/mL group and the 1 501-5 000 IU/mL group had a significant reduction in HBsAg clearance rate at 24, 48, and 96 weeks of follow-up (all P<0.001). As for the comparison of the patients with different treatment conditions (previously untreated or treatment-experienced) and treatment regimens (monotherapy or combined therapy) at 24, 48, and 96 weeks of treatment, there was a significant difference in fame/female ration between the previously untreated group and the treatment-experienced group (χ2=5.029, P=0.025), and there was no significant difference in HBsAg clearance rate between the previously untreated group and the treatment-experienced group and between the monotherapy group and the combined therapy group (all P>0.05). ConclusionPEG-IFNα-2b has a marked effect on HBsAg clearance in the treatment of CHB, and patients with a lower baseline HBsAg level tend to have a higher HBsAg clearance rate. HBsAg clearance rate tends to increase over the time of treatment. A baseline HBsAg level of 500 IU/mL can be used as the cut-off point to identify the dominant population.
Key words:Pegylated Interferon α-2b; Hepatitis B, Chronic; Hepatitis B Surface AntigensResearch funding:China
Research on Reducing the Incidence of Liver Cancer in Hepatitis B Patients (Oasis) Project(LZGC2022-03)
慢性乙型肝炎(CHB)是由HBV感染引起的慢性傳染性疾病,是引起肝炎肝硬化、肝衰竭和肝癌的主要原因之一。規范有效的抗病毒治療是控制疾病進展、降低HBV感染相關終末期肝病發生風險的重要手段。近年來,多項研究證實CHB患者獲得血清HBsAg清除后可使肝癌發生風險降到最低。相對于核苷(酸)類似物,由于具有直接抗病毒和免疫調節雙重作用, IFNα治療在清除血清HBsAg方面更具優勢。本研究旨在評價真實世界應用聚乙二醇干擾素α-2b(PEG-IFNα-2b)治療CHB患者清除血清HBsAg的效果。
1資料與方法
1.1一般資料納入2017年6月—2021年1月本科診治的CHB患者,所有患者符合《慢性乙型肝炎防治指南(2019年版) 》[1]診斷標準,且符合以下納入標準:(1)血清 HBsAg 陽性,HBV DNA陽性;(2)患者臨床檢查結果及既往病史排除失代償期肝硬化,包括有消化道出血、腹水、肝性腦病等并發癥病史;(3)臨床檢查證據排除無IFNα禁忌證;(4)女性患者在治療期間無生育要求,孕產婦不能入組;(5)簽署IFN知情同意書。排除標準: 合并心肺腎等重要臟器疾病,妊娠或哺乳期婦女,合并HCV或HIV感染;臨床明確診斷為肝硬化、肝癌或其他系統惡性腫瘤,合并自身免疫性、遺傳性肝病或藥物性肝損傷,酗酒或吸毒者。
1.2治療方法給予所有患者PEG-IFNα-2b (廈門特寶生物工程股份有限公司,國藥準字 S20160001) 180 μg皮下注射,1次/周。
1.3血清HBV標志物檢測使用雅培I-2000全自動免疫分析儀和Abbort公司配套Architect HBV標志物檢測試劑盒檢測。
1.4統計學方法應用SPSS 16.0統計學軟件進行數據分析。計量資料以x±s表示,兩組間比較采用成組t檢驗;計數資料組間比較采用χ2檢驗和趨勢性χ2檢驗。P<0.05為差異有統計學意義。
2結果
2.1人口學資料及基線情況共入組411例患者,男287例(69.8%),女124例(30.2%),年齡為(36.4±8.7)歲,平均病程(60.3±9.9)個月,核苷(酸)類似物經治338例(82.2%),IFN單用106例(25.8%),IFN聯合核苷(酸)類似物305例(74.2%),HBeAg陽性94例(22.9%),ALT異常108例(26.3%)。
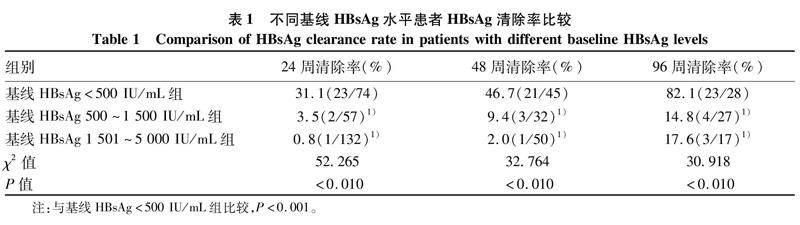
2.2基本療效和血清HBsAg陰轉情況完成24周治療患者263例,其中HBsAg轉陰26例(9.9%);完成48周治療患者127例,其中HBsAg轉陰25例(19.7%);完成96周治療患者72例(41.7%),其中HBsAg轉陰30例(41.7%)。不同基線HBsAg水平患者治療24、48及96周時HBsAg清除率比較差異均有統計學意義(P值均<0.01),隨著治療時間延長, HBsAg清除率逐漸升高,并且這種趨勢有統計學意義(趨勢χ2值分別為44.517、29.147、22.260,P值均<0.01)。進一步組內比較顯示:隨訪24、48及96周時,HBsAg 500~1 500 IU/mL組和1 501~5 000 IU/mL組的HBsAg清除率較HBsAg<500 IU/mL組均明顯下降(P值均<0.001)(表1)。
根據既往治療情況(初治或經治)及治療方案(單用或聯合)對患者分組比較,僅初治與經治組在男女比例上差異有統計學意義(P=0.025),其他基線指標在初治或經治組間、單用或聯合組間差異均無統計學意義(P值均>0.05)。在治療24、48及96周時,初治或經治組間、單用或聯合組間HBsAg清除率比較差異均無統計學意義(P值均>0.05)(表2)。
2.3合并癥和不良事件情況411例CHB患者中,76例合并基礎疾病,其中合并糖尿病7例(1.7%),高血壓病15例(3.6%),吉爾伯特綜合征27例(6.6%),低骨量47例(11.4%)。245例合并其他用藥,粒細胞集落刺激因子180例(43.8%),甘草酸二胺112例(27.3%),氟哌噻噸美利曲辛87例(21.1%),氨氯地平11例(2.7%),硝苯地平4例(1.0%),二甲雙胍6例(1.5%),胰島素1例(0.2%)。主要不良事件為骨髓抑制、焦慮、失眠、乏力, 167例患者出現中性粒細胞計數<2×109/L,給予粒細胞集落刺激因子治療,11例患者因血小板計數<30×109/L,給予停藥觀察,87例患者出現焦慮癥狀,給予氟哌噻噸美利曲辛藥物治療,1例出現皮下軟組織感染,給予停藥觀察后緩解,無進一步嚴重不良事件發生。
3討論根據《2020中國衛生健康統計年鑒》[2]發布的最新數據顯示,我國2019年仍然有超過100萬的新發乙型肝炎患者。《慢性乙型肝炎防治指南(2019年版)》[1]中指出,我國慢性HBV感染者約7 000萬例,其中CHB患者為2 000萬~3 000萬例。2020年最新數據[3]顯示, 2020年中國新發肝癌病例數為 410 038 例,因肝癌死亡人數為391 152例,而我國肝癌由HBV感染引起的比例高達92.05%。2015年《慢性乙型肝炎防治指南》[4]同國際接軌,將CHB的治療終點分為基本終點(HBV DNA轉陰)、滿意終點(HBeAg血清學轉換)及理想終點(HBsAg清除)。隨著治療目標的逐步實現,CHB患者的5年肝癌累積發生率逐步遞減,從獲得基本終點的3.6%~11.4%[5-7],下降到獲得滿意終點的<2.58%[8],再到獲得理想終點的僅1%左右[9-12]。目前我國最新CHB防治指南也積極推薦為對于部分適合條件的患者,應追求臨床治愈,即功能性治愈或稱為臨床治愈[2]。雖然目前CHB仍然不能完全治愈,但通過實現HBsAg轉陰大大改善了患者遠期結局。HBsAg清除成為CHB患者追求的主要目標及各項研究的主要療效指標,且HBsAg被認為是共價閉合環狀DNA轉錄活性的替代標志物,同時也是HBV感染肝細胞的標志物[13]。研究發現根據CHB患者早期HBsAg應答情況,可更好地預測臨床治愈情況。近期北京地壇醫院的相關研究[14]發現24周HBsAg水平對臨床治愈率的預測能力顯著優于12周。2017年《聚乙二醇干擾素α治療慢性乙型肝炎專家共識》[15]及《慢性乙型肝炎臨床治愈(功能性治愈)專家共識》[16]中均采用了24周HBsAg水平來決策后續治療。
相比核苷(酸)類似物, PEG-IFN具有直接抗病毒作用和免疫調節雙重作用,更容易使部分患者達到臨床治愈。為實現這一目標,國內外專家對臨床治愈的優化治療方案的探索已經持續了10余年,研究發現以PEG-IFNα為基礎的抗病毒治療更容易實現臨床治愈的目標。相比PEG-IFNα-2a,國內新藥PEG-IFNα-2b(Y型,40 kD)采用新型Y型分支聚乙二醇分子,選擇性修飾IFNα-2b 134位賴氨酸,在治療HBeAg陽性CHB患者的方案中具有相當的療效和安全性[17]。另一方面,優勢患者的治療策略在獲得臨床治愈方面隨著循證醫學證據的不斷累積逐漸受到專家的認可和驗證, OSST、S-C、NEW SWITCH等研究[18-21]證實了優勢患者采用基于PEG-IFNα治療后可獲得30%~80%的臨床治愈率。優勢患者為HBsAg水平較低,和/或HBeAg、HBV DNA水平低,且在治療過程中HBsAg指標下降幅度較大的患者。本研究中基線HBsAg<500 IU/mL患者在治療同期的HBsAg清除率明顯高于其他兩組,可作為優勢人群的分界點。對于HBsAg水平極低的非活動性HBsAg攜帶者接受短期的PEG-IFNα-2b治療可獲得高達93.8%的HBsAg清除率[22]。一項隨機對照研究[23]顯示,與PEG-IFNα-2b單藥相比,恩替卡韋和PEG-IFNα-2b聯合治療病毒學應答率更高,然而 HBsAg 陰轉率兩組間差異無統計學意義(9.5% vs 4.8%)。另一項薈萃分析[24]顯示,與核苷(酸)類似物單藥治療相比, 初始聯合核苷(酸)類似物治療HBsAg清除率顯著升高,但與PEG-IFNα單藥相比, 聯合治療沒有顯著升高HBsAg清除率。本研究中24、48及96周隨訪患者中IFN單用和聯用并無統計學差異。本隨訪研究中完成96周治療患者72例,其中HBsAg轉陰30例(41.7%)。本研究發現HBsAg基線水平越低,在24、48及96周隨訪患者的HBsAg清除率越高,隨著治療時間的延長這種趨勢有統計學意義(P值均<0.01)。因此對于48周未獲得HBsAg清除的患者,除了依據HBsAg水平預測患者陰轉率之外,可根據患者情況來適當延長PEG-IFNα療程,但具體的cut-off值還未達成共識,而對于決定停藥的這部分患者,如何來進一步追求臨床治愈,這都是今后需要探索的重要研究方向。來自加拿大的最新研究[25]發現,IFNα治療HBeAg陽性CHB患者21周(中位)可獲得16.9%的HBsAg清除率,且IFNα治療后隨訪10年的累積HBsAg清除率達32%,另外也證實了HBeAg清除和HBsAg清除可顯著改善CHB患者的長期臨床結局。
另外在治療過程中要關注IFN相關不良反應的出現及處理,其中最常見不良事件包括流感樣癥狀、焦慮、骨髓抑制等,以輕度為主,及時給予對癥藥物治療。尤其是對于合并肝硬化患者需密切觀察。
對于PEG-IFNα序貫/聯合治療優勢患者的研究和理念一直在推進和深入,CHB患者應積極采取有效的抗病毒治療方案,追求臨床治愈,降低肝癌發生風險,爭取最大獲益。對于相關各項檢測指標的分層細化,需要進一步長期隨訪數據,將會使得治療療程更加明確化。
利益沖突聲明:本文不存在任何利益沖突。作者貢獻說明:李寬負責撰稿和收集數據;靳慧明負責分析數據;寧會彬、彭真負責收集數據;尚佳負責指導寫作和最終定稿。
參考文獻:
[1]Chinese Society of Infectious Diseases, Chinese Medical Association, Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association. Guidelines for the prevention and treatment of chronic hepatitis B (version 2019)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35(12): 2648-2669. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.12.007.中華醫學會感染病學分會, 中華醫學會肝病學分會. 慢性乙型肝炎防治指南(2019年版)[J]. 臨床肝膽病雜志, 2019, 35(12): 2648-2669. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.12.007.
[2]National Health Commission. China health statistical yearbook 2020[M]. Beijing: China Union Medical College Press, 2020.國家衛生健康委員會. 2020中國衛生健康統計年鑒[M]. 北京: 中國協和醫科大學出版社, 2020.
[3]Latest global cancer data: Cancer burden rises to 19.3 million new cases and 10.0 million cancer deaths in 2020[EB/OL]. [2020-12-15].? https://www.iarc.fr/fr/news-events/latest-global-cancer-data-cancer-burden-rises-to-19-3-million-new-cases-and-10-0-million-cancer-deaths-in-2020/.
[4]Chinese Society of Hepatology and Chinese Society of Infectious Diseases, Chinese Medical Association. The guideline of prevention and treatment for chronic hepatitis B: a? 2015 update[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2015, 31(12): 1941-1960. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2015.12.002.中華醫學會肝病學分會, 中華醫學會感染病學分會. 慢性乙型肝炎防治指南(2015年更新版)[J]. 臨床肝膽病雜志, 2015, 31(12): 1941-1960. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2015.12.002.
[5]PAPATHEODORIDIS GV, MANOLAKOPOULOS S, TOULOUMI G, et al. Virological suppression does not prevent the development of hepatocellular carcinoma in HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B patients with cirrhosis receiving oral antiviral(s) starting with lamivudine monotherapy: results of the nationwide HEPNET. Greece cohort study[J]. Gut, 2011, 60(8): 1109-1116. DOI: 10.1136/gut.2010.221846.
[6]ZHANG W, WANG X, WANG Y, et al. Effective viral suppression is necessary to reduce hepatocellular carcinoma development in cirrhotic patients with chronic hepatitis B: Results of a 10-year follow up[J]. Medicine (Baltimore), 2017, 96(44): e8454. DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000008454.
[7]CHO JY, PAIK YH, SOHN W, et al. Patients with chronic hepatitis B treated with oral antiviral therapy retain a higher risk for HCC compared with patients with inactive stage disease[J]. Gut, 2014, 63(12): 1943-1950. DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2013-306409.
[8]ZHOU TC, LAI X, FENG MH, et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis: Development of hepatocellular carcinoma in chronic hepatitis B patients with hepatitis e antigen seroconversion[J]. J Viral Hepat, 2018, 25(10): 1172-1179. DOI: 10.1111/jvh.12928.
[9]LIU F, WANG XW, CHEN L, et al. Systematic review with meta-analysis: development of hepatocellular carcinoma in chronic hepatitis B patients with hepatitis B surface antigen seroclearance[J]. Aliment Pharmacol Ther, 2016, 43(12): 1253-1261. DOI: 10.1111/apt.13634.
[10]ZHANG XY, JIA RR, XIANG X, et al. Letter: older age and male gender increase the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma after hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) seroclearance[J]. Aliment Pharmacol Ther, 2017, 46(9): 906-908. DOI: 10.1111/apt.14272.
[11]YIP TC, CHAN HL, WONG VW, et al. Impact of age and gender on risk of hepatocellular carcinoma after hepatitis B surface antigen seroclearance[J]. J Hepatol, 2017, 67(5): 902-908. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2017.06.019.
[12]TATEDA K, SUZUKI F, KOBAYASHI M. Predictive factors associated with hepatocellular carcinoma incidence and mortality after hepatitis B surface antigen seroclearance in patients with chronic hepatitis B[J]. Hepatology, October, 2018, AASLD Abstract(oral 213).
[13]LIAW YF. Hepatitis B flare after cessation of nucleos(t)ide analogue therapy in HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B: to retreat or not to retreat[J]. Hepatology, 2021, 73(2): 843-852. DOI: 10.1002/hep.31525.
[14]LI M, ZHANG L, LU Y, et al. Early serum HBsAg kinetics as predictor of HBsAg loss in patients with HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B after treatment with pegylated interferonα-2a[J]. Virol Sin, 2021, 36(2): 311-320. DOI: 10.1007/s12250-020-00290-7.
[15]ZHANG WH, ZHANG DZ, DOU XG, et al. Consensus on pegylated interferon alpha in treatment of chronic hepatitis B[J]. Chin J Hepatol, 2017, 25(9): 678-686. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-3418.2017.09.007.張文宏, 張大志, 竇曉光, 等. 聚乙二醇干擾素α治療慢性乙型肝炎專家共識[J]. 中華肝臟病雜志, 2017, 25(9): 678-686. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-3418.2017.09.007.
[16]Chinese Society of Infectious Disease, Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association. The expert consensus on clinical cure (functional cure) of chronic hepatitis B[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35(8): 1693-1701. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.08.008.中華醫學會感染病學分會, 中華醫學會肝病學分會. 慢性乙型肝炎臨床治愈(功能性治愈)專家共識[J]. 臨床肝膽病雜志, 2019, 35(8): 1693-1701. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.08.008.
[17]HOU FQ, YIN YL, ZENG LY, et al. Clinical effect and safety of pegylated interferon-α-2b injection (Y shape, 40 kD) in treatment of HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B patients[J]. Chin J Hepatol, 2017, 25(8): 589-596. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-3418.2017.08.007.侯鳳琴, 尹亞琳, 曾玲英, 等. 聚乙二醇干擾素α-2b(Y型,40kD)注射液治療HBeAg陽性慢性乙型肝炎患者的療效和安全性分析[J]. 中華肝臟病雜志, 2017, 25(8): 589-596. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-3418.2017.08.007.
[18]NING Q, HAN M, SUN Y, et al. Switching from entecavir to PegIFN alfa-2a in patients with HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B: a randomised open-label trial (OSST trial)[J]. J Hepatol, 2014, 61(4): 777-784. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2014.05.044.
[19]HAN M, JIANG J, HOU J, et al. Sustained immune control in HBeAg-positive patients who switched from entecavir therapy to pegylated interferon-α2a: 1 year follow-up of the OSST study[J]. Antivir Ther, 2016, 21(4): 337-344. DOI: 10.3851/IMP3019.
[20]LI GJ, YU YQ, CHEN SL, et al. Sequential combination therapy with pegylated interferon leads to loss of hepatitis B surface antigen and hepatitis B e antigen (HBeAg) seroconversion in HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B patients receiving long-term entecavir treatment[J]. Antimicrob Agents Chemother, 2015, 59(7): 4121-4128. DOI: 10.1128/AAC.00249-15.
[21]HU P, SHANG J, ZHANG W, et al. HBsAg Loss with Peg-interferon Alfa-2a in hepatitis B patients with partial response to nucleos(t)ide analog: new switch study[J]. J Clin Transl Hepatol, 2018, 6(1): 25-34. DOI: 10.14218/JCTH.2017.00072.
[22]ZENG QL, YU ZJ, SHANG J, et al. Short-term peginterferon-induced high functional cure rate in inactive chronic hepatitis B virus carriers with low surface antigen levels[J]. Open Forum Infect Dis, 2020, 7(6): ofaa208. DOI: 10.1093/ofid/ofaa208.
[23]TANGKIJVANICH P, CHITTMITTRAPRAP S, POOVORAWAN K, et al. A randomized clinical trial of peginterferon alpha-2b with or without entecavir in patients with HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B: Role of host and viral factors associated with treatment response[J]. J Viral Hepat, 2016, 23(6): 427-438. DOI: 10.1111/jvh.12467.
[24]LIU J, WANG T, ZHANG W, et al. Effect of combination treatment based on interferon and nucleos(t)ide analogues on functional cure of chronic hepatitis B: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Hepatol Int, 2020, 14(6): 958-972. DOI: 10.1007/s12072-020-10099-x.
[25]CHOI H, van CAMPENHOUT M, van VUUREN AJ, et al. Ultra-long-term follow-up of interferon alfa treatment for HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B virus infection[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2021, 19(9): 1933-1940.e1. DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2020.09.004.
收稿日期:2022-11-29;錄用日期:2023-02-01
本文編輯:王瑩
引證本文:LI K, NING HB, JIN HM, et al. Effect of pegylated interferon α-2b on serum HBsAg clearance rate in treatment of patients with chronic hepatitis B[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2023, 39(8): 1819-1824.

