他莫昔芬與神經系統及認知功能的相關研究進展
王金濃 田毅 曹晴祎

摘要:神經系統疾病包括了多種神經退行性病變及其他腦損傷疾病,目前對于神經系統疾病有效治療方案的相關研究仍在進行中。以往臨床和基礎研究已證實,傳統雌激素治療方法對神經系統有一定保護作用,但也會增加乳腺癌或子宮內膜癌發生的風險,而選擇性雌激素受體調節劑(SERM)的出現正好避免了此類風險發生。已有研究證實,他莫昔芬作為一種SERM,對神經系統有很好的保護作用,本文總結了他莫昔芬在神經系統及認知功能方面的相關作用及機制,以期對未來指導他莫昔芬用于神經系統疾病治療及改善認知功能方面的研究提供幫助。
關鍵詞:他莫昔芬;神經功能;神經系統疾病;認知功能障礙;保護作用
中圖分類號: R741.05文獻標志碼: A文章編號:1000-503X(2023)02-0334-07
DOI:10.3881/j.issn.1000-503X.15035
Research Progress in the Role of Tamoxifen in Nervous System and Cognitive Function
WANG Jinnong,TIAN Yi,CAO Qingyi
ABSTRACT:Neurological diseases include a variety of neurodegenerative diseases and other brain damage diseases.The treatment schemes for neurological diseases are still in research.The existing clinical and basic studies have confirmed that traditional estrogen therapy has certain protective effect on the nervous system,while it increases the risk of breast or endometrial cancer.The emergence of the selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs) can avoid the above mentioned problems.The available studies have confirmed the protective effect of tamoxifen as a SERM on the nervous system.This paper reviews the role and functioning mechanisms of tamoxifen in the nervous system and cognitive function,aiming to provide guidance for the future application of tamoxifen in the treatment of neurological diseases and the improvement of cognitive function.
Key words:tamoxifen;neurological function;neurological diseases;cognitive dysfunction;protective effect
Acta Acad Med Sin,2023,45(2):334-340
神經系統疾病是發生于中樞神經系統、周圍神經系統、自主神經系統的以感覺、運動、意識、自主神經功能障礙為主要表現的疾病,包括多種神經退行性病變及其他腦損傷疾病。隨著對神經系統疾病認識的不斷提高,對認知功能的治療水平也得到進一步提高。他莫昔芬為三苯基乙烯的衍生物,是一種非甾體雌激素類似物[1],也是第1代選擇性雌激素受體調節劑(selective estrogen receptor modulator,SERM),目前他莫昔芬正逐步成為神經系統及認知功能方面治療藥物的研究熱點。已有研究顯示,他莫昔芬可以通過抑制谷氨酸,減少炎癥,調節細胞凋亡,改善星形膠質細胞、小膠質細胞和突觸功能,影響多巴胺能系統等途徑產生神經保護作用以及一定程度地改善認知功能作用。本文總結了他莫昔芬在神經系統及認知功能方面的作用機制及研究進展,以期為未來研究他莫昔芬的具體作用靶點、治療方案和效果提供參考。
他莫昔芬對神經系統的作用
他莫昔芬的應用 臨床上他莫昔芬因治療乳腺癌效果明顯而被大眾熟知[2-3],但對于他莫昔芬的研究不只是局限于乳腺癌及相關疾病的治療。Shagufta等[4]在他莫昔芬及其衍生物的研究中發現,其在治療不孕癥、男性乳房發育癥、腹膜后纖維化、骨質疏松[5-7]、心血管疾病等方面均能表現出益處,是一種具有開創性意義的藥物。此外,他莫昔芬對大腦有一定的保護作用[8],這與他莫昔芬穿過血腦屏障有關[9]。已知雌激素是通過與雌激素受體(estrogen receptor,ER)結合后,對認知和神經系統有保護作用,而他莫昔芬對ER具有較雌激素高100~1000倍的親和力,能加強認知和對神經系統的保護作用[10],提示他莫昔芬在神經系統方面具有獨特優勢和潛在發展前景。
他莫昔芬在神經系統的可能作用機制 他莫昔芬作為一種SERM,具備有雌激素激動劑、雌激素拮抗劑的雙重作用。在不同的條件下,對于行為和認知等方面表現出不同的作用:雌激素類似作用[11-12]、雌激素阻斷作用[13-14],本文將著重探討雌激素類似作用。目前已有多項研究表明,他莫昔芬可以通過抑制谷氨酸從大腦皮質中釋放[15],減少炎癥,調節細胞凋亡,改善星形膠質細胞、小膠質細胞和突觸功能等[16-17],對創傷性腦損傷和脊髓受損[18-19]、中風、癲癇、阿爾茨海默病(Alzheimers disease,AD)、帕金森病(Parkinsons disease,PD)等疾病產生神經保護作用[20]。ERα和ERβ在大腦中屬于不同的分布區域[21]:ERα是大多數下丘腦和杏仁核的主要亞型,主要參與自主神經、生殖和情感功能;ERβ是海馬體區域的主要亞型[22],參與更多的認知功能,他莫昔芬可以通過競爭性抑制雌二醇與ERα和ERβ的結合[23],調節影響神經系統及改善認知功能。G蛋白偶聯受體30可以通過增加抗氧化機制和生存信號通路的激活觸發神經保護作用,他莫昔芬的作用被證實與該通路密切相關[24]。研究表明,蛋白激酶C(protein kinase C,PKC)是治療腦相關疾病的又一靶點,而他莫昔芬可以通過血腦屏障發揮PKC抑制作用[10,25],又被稱為PKC抑制劑。Valvassori等[26]研究證實,他莫昔芬治療可以保護大腦免受PKC信號通路的改變,一定程度上防止大鼠躁狂樣行為。在脊髓損傷方面,他莫昔芬作為一種雌二醇的類似化合物,可以通過抗氧化、抗炎、抗神經膠質病、調節細胞凋亡等表現出神經保護功能,改善脊髓受損相關的感覺、運動神經障礙,且不良反應小[19]。ER調節劑在中樞神經系統中的重要作用被發現與細胞骨架蛋白的調節尤其相關,他莫昔芬能通過不同的機制和水平來調節細胞骨架蛋白,如tau蛋白、微管相關蛋白 (microtubule-associated protein,MAP)1、MAP2[27]、神經絲蛋白38、中間絲相關蛋白等。目前越來越多的證據表明,特異性蛋白(specificity protein,SP)1和SP4轉錄因子參與精神分裂癥的病理生理學過程。對接受雷諾昔芬(第2代SERM)輔助治療的精神分裂癥絕經后婦女SP水平與精神癥狀改善的研究表明,SP4可能參與雷諾昔芬輔助治療改善絕經后婦女精神癥狀,并且SP也有望成為未來研究雷諾昔芬有效性的血液生物標志物的潛在候選者[28]。Gogos等[29]的研究數據支持雌激素/SERMs在精神分裂癥中起保護作用的假設,可進一步推測SERMs在脈沖前抑制中的作用機制是通過直接或間接調節多巴胺能系統,而他莫昔芬也可以通過模仿雌激素與谷氨酸受體特異性結合,維持特定海馬區域的N-甲基-D-天冬氨酸(N-methyl-D-aspartic acid,NMDA)受體(又稱異構體受體)來增強記憶力,特別是主要位于海馬CA1區和扣帶皮層的異構體受體(又稱NMDA受體)的亞基1(NR1)和2B(NR2B),可能對AD和精神分裂癥等神經系統疾病有益[30]。Li等[31]在研究他莫昔芬與小鼠行為差異的實驗中證實,他莫昔芬的不同實驗方案對小鼠的行為模式產生不同的影響,并體現出不一樣的實驗結果,表明他莫昔芬的復雜多樣性。綜上可見他莫昔芬在神經系統中的作用機制有著雙重性、復雜性(表1)。
神經系統疾病相關的認知障礙
神經系統疾病相關認知障礙 認知障礙是大部分神經系統疾病的癥狀表現,例如在腦損傷、AD、PD等疾病中,患者往往會出現行動和認知功能的障礙。認知是大腦皮層復雜高級功能的反映,任何直接或間接的可導致大腦皮層損傷的機制均能引起認知障礙,這與多方面的因素相關,如神經退行性病變、神經元受損、神經遞質(多巴胺、去甲腎上腺素、乙酰膽堿等)或受體的傳導異常、星形膠質細胞的減少[32]、小膠質細胞受損、細胞凋亡、炎癥等因素。目前我國已進入老年社會,預計到2026年將進入超老齡化社會,這種人口老齡化現象將迅速增加AD發生的可能性,而AD的各個階段與認知功能下降密不可分,AD的臨床前階段,輕度認知障礙(mild cognitive impairment,MCI)位于正常老化和AD的認知連續線中間,日常生活活動(activities of daily living,ADL)和智力能力保持不變,但總體記憶和語言能力等部分認知功能障礙[33]。
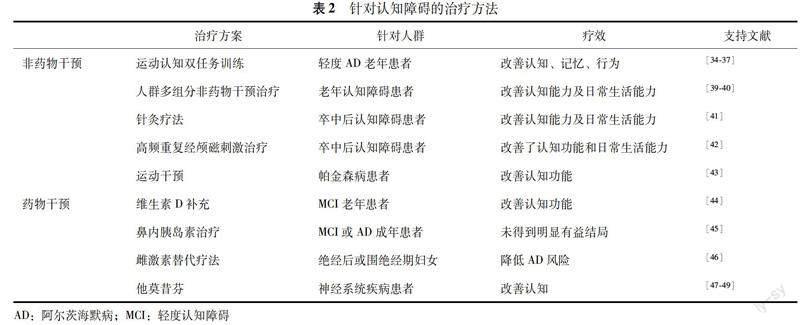
認知障礙的治療方法 目前針對于認知障礙的治療主要包括兩大類:非藥物策略和藥物干預(表2)。研究表明,運動認知雙任務訓練與常規護理相比,會對結局顯現出不一樣的有效性[34];運動認知雙任務訓練與單任務訓練對于老年輕度AD的結局參數有效性也具有差異性[35],在步幅、踏頻、步長、擺動階段、姿勢階段和雙支撐階段存在顯著差異,且雙任務訓練可改善MCI老年人的注意力和記憶力,并改善其整體認知功能[36],這可能是因為機體活動能增強與神經營養因子的關聯性,從而增強神經可塑性[37]。為了幫助維持或改善PD伴AD或PD伴MCI患者的認知和生活質量,Orgeta等[38]開展了小規模的認知訓練干預研究,但并未發現認知訓練對PD伴AD或MCI患者有幫助,當然這也不排除是因為小樣本問題,或者可能存在某些未知的影響因素。人群多組分非藥物干預治療是另一種干預策略[39],它是一種多組分、非藥物、團體治療,根據老年認知障礙患者的說明手冊進行干預,包括激活運動技能、ADL能力和認知的特定訓練,以及社交熱身課程。Straubmeier等[40]通過6個月干預階段的整群隨機、對照、單盲試驗研究,證實了隨著時間的推移,多組分非藥物干預治療可以改善認知能力及ADL能力,同時該結果的顯著性差異也提示未來可以將此治療方法更長時間的開展,以測定其更長時間的改善認知能力以及ADL能力的穩定性,由此可以探索更廣領域的應用性。最新的關于非藥物干預的研究探索包括了針灸療法[41]、左背側前額葉皮層上進行高頻重復經顱磁刺激[42]和運動干預[43]等。此外有研究顯示,連續補充12個月的維生素D似乎可以通過減少由端粒長度增加調節的氧化應激來改善認知功能,可能是預防認知能力下降的一種有前途的公共衛生策略[44]。 Craft等[45]通過鼻內胰島素治療MCI和AD患者的可行性、安全性和有效性研究,得出結論在主要意向治療隊列中,12個月內鼻內胰島素治療沒有觀察到認知或功能益處。Kawas等[46]研究顯示,雌激素替代療法可以幫助絕經后婦女降低患AD風險。諸多研究表明他莫昔芬及其類似物可以改善認知,降低AD風險,為未來臨床研究提供新的治療思路。[47-48]
他莫昔芬與認知
他莫昔芬在認知相關疾病中的作用 神經系統相關疾病大多會出現認知方面障礙,而他莫昔芬在以下研究中均體現了其益處:Weickert等[50]在2015年實施的一項隨機、雙盲的交叉試驗中對診斷為精神分裂癥或情感性精神障礙的患者進行了雷諾昔芬輔助治療,結論肯定了雷諾昔芬改善患者認知功能方面的作用,表明持續性雷諾昔芬輔助治療可用作精神分裂癥相關的認知缺陷輔助治療。他莫昔芬作為SERM對于認知也有類似作用,一項比較他莫昔芬與雷洛昔芬對全局和領域特異性認知功能影響的臨床試驗結果表明,兩者對乳腺癌風險增加的絕經后婦女的認知功能模式相似[51],說明兩者對認知功能改善相似。Underwood等[52]研究顯示,他莫昔芬治療與芳香化酶抑制劑(aromatase inhibitor,AI)治療效果在總體認知相關領域差別不大;在幾個亞組分析方面,他莫昔芬治療的患者表現優于非甾體類AI治療的患者,但相對于類固醇AI治療的患者表現出很少的差異,當然這項試驗也有小樣本誤差存在的可能。Phillip等[53]比較了接受來曲唑(非甾體類AI)與他莫昔芬輔助內分泌治療的絕經后婦女在第5年的認知功能情況,結果顯示來曲唑輔助治療對認知功能的改善更明顯,不過這一結論也有可能是樣本并不完全匹配的偏差造成,需要進一步研究證實。AD作為一種常見的神經退行性疾病,其病理特征在于細胞外淀粉樣斑塊沉積和細胞內神經原纖維纏結,β淀粉樣蛋白斑塊沉積主要位于大腦皮層和海馬體[54-55]。研究顯示,他莫昔芬可以改善AD患者MCI,在延緩疾病進展方面具有極大潛力[49,56]。此外雌激素治療在性別方面體現出的差異也提供了新的研究思路,雖然目前大部分相關實驗都是在雌性動物上進行的,但越來越多的證據表明,雌激素在雌性和雄性動物實驗中可能具有不同的作用,這可能是因為潛在的大腦性別二態性,在提供大腦額葉前皮層不同區域的皮質神經元中,ER的細胞結構定位表現出性別差異[57],而且海馬合成雌二醇對于成年女性的海馬功能影響大于成年男性[58]。已知幾乎所有中樞神經系統疾病的發病率和表現都存在明顯的性別差異,雖然具體機制尚不明確[59],但由此可見深入研究雌激素和他莫昔芬等的作用對于探索新型激素治療方案非常重要。
他莫昔芬改善認知功能的作用機制 雖然具體機制尚不完全明確,但可能集中于以下幾個方面:減少多巴胺代謝,增加乙酰膽堿水平,通過影響多巴胺能神經系統達到改善認知的目的[49]。多巴胺在多個神經過程中發揮重要作用,多巴胺轉運蛋白是多巴胺從神經元釋放后從細胞外空間除去的關鍵機制,他莫昔芬可以通過非典型方式抑制多巴胺轉運蛋白。McMillan等[60]研究表明,大鼠基底前腦區域對雌激素高度敏感,起源于該區域的膽堿能神經元為皮層和海馬體提供神經支配,而膽堿能神經元變性、衰老與AD等神經退行性疾病的認知缺陷相關,他莫昔芬可通過增加膽堿乙酰轉移酶的表達,改善AD等疾病的認知缺陷。此外,他莫昔芬不僅對大鼠海馬背側CA1區受損后海馬依賴性認知功能障礙、CA1細胞凋亡和膠質細胞增生有保護作用[61],還可以增加大鼠海馬體CA1錐體神經元中樹突棘密度,在沒有雌二醇受體的情況下發揮ER激動劑功能[62]。 Chen等[63]在小鼠慢性腦灌注不足誘導腦白質病變的實驗中發現,他莫昔芬可以緩解腦白質病變導致的認知障礙,對神經系統發揮多靶點保護作用。此外有研究表明,他莫昔芬可以模仿雌二醇增加大腦前緣/下緣前額葉皮層中第3層錐體神經元中樹突棘密度,達到改善認知功能的目的[11,17];還可以模仿雌激素對海馬體和紋狀體中NMDA受體和α-氨基-3-羥基-5-甲基-4-異唑丙酸受體的調節作用[64],但需要注意的是雌二醇和他莫昔芬在樹突棘上還存在重要差異,雌二醇可以特異性增加薄樹突棘的數值密度,而他莫昔芬是以類似物方式影響所有的樹突棘類型,需要加以區別。
綜上,他莫昔芬可通過抑制谷氨酸,抑制炎癥反應,調節細胞凋亡,改善膠質細胞和突觸功能,影響多巴胺能系統等機制,保護神經系統和改善認知功能。未來對他莫昔芬新靶點、雌激素阻斷作用及具體機制、有效治療窗、性別差異等方面的研究可為深入了解他莫昔芬對神經系統和認知方面的影響提供依據。
參 考 文 獻
[1]Neven P,Jongen L,Lintermans A,et al.Tamoxifen metabolism and efficacy in breast cancer:a prospective multicenter trial[J].Clin Cancer Res,2018,24(10):2312-2318.DOI:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-17-3028.
[2]Chang BY,Kim SA,Malla B,et al.The effect of selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs) on the tamoxifen resistant breast cancer cell[J].Toxicol Res,2011,27(2):85-93.DOI:10.5487/tr.2011.27.2.085.
[3]Peng J,Sengupta S,Jordan VC.Potential of selective estrogen receptor modulators as treatments and preventives of breast cancer[J].Anticancer Agents Med Chem,2009,9(5):481-499.DOI:10.2174/187152009788451833.
[4]Shagufta,Ahmad I.Tamoxifen a pioneering drug:an update on the therapeutic potential of tamoxifen derivatives[J].Eur J Med Chem,2018,143:515-531.DOI:10.1016/j.ejmech.2017.11.056.
[5]Steiner AZ,Terplan M,Paulson RJ.Comparison of tamoxifen and clomiphene citrate for ovulation induction:a meta-analysis[J].Hum Reprod,2005,20(6):1511-1515.DOI:10.1093/humrep/deh840.
[6]Akram S,Pardi DS,Schaffner JA,et al.Sclerosing mesenteritis:clinical features,treatment,and outcome in ninety-two patients[J].Clin Gastroent erol Hepatol,2007,5(5):589-596.DOI:10.1016/j.cgh.2007.02.032.
[7]Van Bommel EF,Hendriksz TR,Huiskes AW,et al.Brief communication:tamoxifen therapy for nonmalignant retroperitoneal fibrosis[J].Ann Intern Med,2006,144(2):101-106.DOI:10.7326/0003-4819-144-2-200601170-00007.
[8]Barreto G,Santos-Galindo M,Diz-Chaves Y,et al.Selective estrogen receptor modulators decrease reactive astrogliosis in the injured brain:effects of aging and prolonged depletion of ovarian hormones[J].Endocrinology,2009,150(11):5010-5015.DOI:10.1210/en.2009-0352.
[9]Zarate CA Jr,Singh JB,Carlson PJ,et al.Efficacy of a protein kinase C inhibitor (tamoxifen) in the treatment of acute mania:a pilot study[J].Bipolar Disord,2007,9(6):561-570.DOI:10.1111/j.1399-5618.2007.00530.x.
[10]Gogos A,Ney LJ,Seymour N,et al.Sex differences in schizophrenia,bipolar disorder,and post-traumatic stress disorder:are gonadal hormones the link[J].Br J Pharmacol,2019,176(21):4119-4135.DOI:10.1111/bph.14584.
[11]Velázquez-Zamora DA,Garcia-Segura LM,González-Burgos I.Effects of selective estrogen receptor modulators on allocentric working memory performance and on dendritic spines in medial prefrontal cortex pyramidal neurons ofovariectomized rats[J].Horm Behav,2012,61(4):512-517.DOI:10.1016/j.yhbeh.2012.01.010.
[12]Newhouse P,Albert K,Astur R,et al.Tamoxifen improves cholinergically modulated cognitive performance in postmenopausal women[J].Neuropsychopharmacology,2013,38(13):2632-2643.DOI:10.1038/npp.2013.172.
[13]Chen X,Li J,Chen J,et al.Decision-making impairments in breast cancer patients treated with tamoxifen[J].Horm Behav,2014,66(2):449-456.DOI:10.1016/j.yhbeh.2014.07.005.
[14]Chen D,Wu CF,Shi B,et al.Tamoxifen and toremifene cause impairment of learning and memory function in mice[J].Pharmacol Biochem Behav,2002,71(1):269-276.DOI:10.1016/S0091-3057(01)00656-6.
[15]Kuo JR,Wang CC,Huang SK,et al.Tamoxifen depresses glutamate release throughinhibition of voltage-dependent Ca2+entry and protein kinase Cαin rat cerebral cortex nerve terminals[J].Neurochem Int,2012,60(2):105-114.DOI:10.1016/j.neuint.2011.11.014.
[16]Burda JE,Sofroniew MV.Reactive gliosis and the multicellular response to CNS damage and disease[J].Neuron,2014,81(2):229-248.DOI:10.1016/j.neuron.2013.12.034.
[17]Arevalo MA,Diz-Chaves Y,Santos-Galindo M,et al.Selective oestrogen receptor modulators decrease the inflammatory response of glial cells[J].J Neuroendocrinol,2012,24(1):183-190.DOI:10.1111/j.1365-2826.2011.02156.x.
[18]Colón JM,Torrado AI,Cajigas ,et al.Tamoxifen administration immediately or 24 hours after spinal cord injury improves locomotor recovery and reduces secondarydamage in female rats[J].J Neurotrauma,2016,33(18):1696-1708.DOI:10.1089/neu.2015.4111.
[19]Colon JM,Miranda JD.Tamoxifen:an FDA approved drug with neuroprotective effects for spinal cord injury recovery[J].Neural Regen Res,2016,11(8):1208-1211.DOI:10.4103/1673-5374.189164.
[20]Meldrum BS.Glutamate as a neurotransmitter in the brain:review of physiology and pathology[J].J Nutr,2000,130(4):1007S-1015S.DOI:10.1093/jn/130.4.1007S.
[21]Hadjimarkou MM,Vasudevan N.GPER1/GPR30 in the brain:crosstalk with classical estrogen receptors and implications for behavior[J].J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol,2018,176:57-64.DOI:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2017.04.012.
[22]sterlund MK,Hurd YL.Estrogen receptors in the human forebrain and the relationto neuropsychiatric disorders[J].Prog Neurobiol,2001,64(3):251-267.DOI:10.1016/S0301-0082(00)00059-9.
[23]Kuhl H.Pharmacology of estrogens and progestogens:influence of different routes of administration[J].Climacteric,2005,8( Suppl 1):3-63.DOI:10.1080/13697130500148875.
[24]Baez-Jurado E,Rincon-Benavides MA,Hidalgo-Lanussa O,et al.Molecular mechanisms involved in the protective actions of selective estrogen receptor modulators in brain cells[J].Front Neuroendocrinol,2019,52:44-64.DOI:10.1016/j.yfrne.2018.09.001.
[25]Ali SM,Ahmad A,Shahabuddin S,et al.Endoxifen is a new potent inhibitor of PKC:a potential therapeutic agent for bipolar disorder[J].Bioorg Med Chem Lett,2010,20(8):2665-2667.DOI:10.1016/j.bmcl.2010.02.024.
[26]Valvassori SS,Dal-Pont GC,Resende WR,et al.Lithium and tamoxifen modulate behavior and protein kinase C activity in the animal model of mania induced by ouabain[J].Int J Neuropsychopharmacol,2017,20(11):877-885.DOI:10.1093/ijnp/pyx049.
[27]Segura-Uribe JJ,Pinto-Almazdan R,Coyoy-Salgado A,et al.Effects of estrogen receptor modulators on cytoskeletal proteins in the central nervous system[J].Neural Regen Res,2017,12(8):1231-1240.DOI:10.4103/1673-5374.213536.
[28]Vila ,Huerta-Ramos E,Núez C,et al.Specificity proteins 1 and 4 in peripheral blood mononuclear cells in postmenopausal women with schizophrenia:a 24-week double-blind,randomized,parallel,placebo-controlled trial[J].Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci,2019,269(8):941-948.DOI:10.1007/s00406-018-0938-7.
[29]Gogos A,van den Buuse M,Comparing the effects of 17β-oestradiol and the selective oestrogen receptor modulators,raloxifene and tamoxifen,on prepulse inhibition in female rats[J].Schizophr Res,2015,168(3):634-639.DOI:10.1016/j.schres.2015.04.029.
[30]Cyr M,Thibault C,Morissette M,et al.Estrogen-like activity of tamoxifen and raloxifene on NMDA receptor binding and expression of its subunitsin rat brain[J].Neuropsychopharmacology,2001,25(2):242-257.DOI:10.1016/S0893-133X(01)00233-0.
[31]Li X,Du ZJ,Chen MQ,et al.The effects of tamoxifen on mouse behavio[J].Genes Brain Behav,2020,19(4):e12620.DOI:10.1111/gbb.12620.
[32]Santello M,Toni N,Volterra A.Astrocyte function from information processing to cognition and cognitive impairment[J].Nat Neurosci,2019,22(2):154-166.DOI:10.1038/s41593-018-0325-8.
[33]Ko JJ.A review of long-term care insurance for the elderly by access to an aging society[J].Law Policy Review,2018,24(1):27-61.DOI:10.36727/jjlpr.24.1.201803.002.
[34]Fritz NE,Cheek FM,Nichols-Larsen DS.Motor-cognitive dual-task training in persons with neurologic disorders:a systematic review[J].J Neurol Phys Ther,2015,39(3):142-153.DOI:10.1097/npt.0000000000000090.
[35]Koo DK,Jang TS,Kwon JW.Effects of dual-task training on gait parameters in elderly patients with mild dementia[J].Healthcare (Basel),2021,9(11):1444.DOI:10.3390/healthcare9111444.
[36]Hwang JH,Park MS.Effect of a dual-task virtual reality program for seniors with mild cognitive impairment[J].Korean J Clin Lab Sci,2018,50(4):492-500.DOI:10.15324/kjcls.2018.50.4.492.
[37]Voss MW,Erickson KI,Prakash RS,et al.Functional connectivity:a source of variance in the association between cardiorespiratory fitness and cognition[J].Neuropsychologia,2010,48(5):1394-1406.DOI:10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2010.01.005.
[38]Orgeta V,McDonald KR,Poliakoff E,et al.Cognitive training interventions for dementia and mild cognitive impairment in Parkinsons disease[J].Cochrane Database Syst Rev,2020,2(2):CD011961.DOI:10.1002/14651858.CD011961.pub2.
[39]Luttenberger K,Graessel E,Behrndt EM,et al.Responder analysis of a multicomponent non-pharmacological intervention (MAKS) for people with cognitive impairmentin the German day-care study (DeTaMAKS)[J].Front Psychiatry,2019,10:587.DOI:10.3389/fpsyt.2019.00587.
[40]Straubmeier M,Behrndt EM,Seidl H,et al.Non-pharmacological treatment in people with cognitive impairment results from the randomized controlled German day care study[J].Dtsch Arztebl Int,2017,114(48):815-821.DOI:10.3238/arztebl.2017.0815.
[41]Du Y,Zhang L,Liu W,et al.Effect of acupuncture treatment on post-stroke cognitive impairment:a randomized controlled trial[J].Medicine (Baltimore),2020,99(51):e23803.DOI:10.1097/MD.0000000000023803.
[42]Yin M,Liu Y,Zhang L,et al.Effects of rTMS treatment on cognitive impairment and resting-state brain activity in stroke patients:a randomized clinical trial[J].Front Neural Circuits,2020,14:563777.DOI:10.3389/fncir.2020.563777.
[43]Da Silva FC,Lop RDR,De Oliveira LC,et al.Effects of physical exercise programson cognitive function in Parkinsons disease patients:a systematic review of randomized controlled trials of the last 10 years[J].PLoS one,2018,13(2):e0193113.DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0193113.
[44]Yang T,Wang H,Xiong Y,et al.Vitamin D supplementation improves cognitive function through reducing oxidative stress regulated by telomere length in older adults with mild cognitive impairment:a 12-month randomized controlled trial[J].J Alzheimers Dis,2020,78(4):1509-1518.DOI:10.3233/jad-200926.
[45]Craft S,Raman R,Chow TW,et al.Safety,efficacy,and feasibility of intranasal insulin for the treatment of mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer disease dementiaa randomized clinical trial[J].JAMA Neurol,2020,77(9):1099-1109.DOI:10.1001/jamaneurol.2020.1840.
[46]Kawas C,Resnick S,Morrison A,et al.A prospective study of estrogen replacement therapy and the risk of developing Alzheimers disease:the Baltimore longitudinal study of aging[J].Neurology,1997,48(6):1517-1521.DOI:10.1212/wnl.48.6.1517.
[47]Novick AM,Scott AT,Epperson CN,et al.Neuropsychiatric effects of tamoxifen:challenges and opportunities[J].Front Neuroendocrinol,2020,59:100869.DOI:10.1016/j.yfrne.2020.100869.
[48]Finney CA,Shvetcov A,Westbrook RF,et al.The selective estrogen receptor modulator tamoxifen protects against subtle cognitive decline and early markers of injury 24 h after hippocampal silent infarct in male Sprague-Dawley rats[J].Horm Behav,2021,134:105016.DOI:10.1016/j.yhbeh.2021.105016.
[49]Pandey D,Banerjee S,Basu M,et al.Memory enhancement by tamoxifen on amyloidosis mouse model[J].Horm Behav,2016,79:70-73.DOI:10.1016/j.yhbeh.2015.09.004.
[50]Weickert TW,Weinberg D,Lenroot R,et al.Adjunctive raloxifene treatment improves attention and memory in men and women with schizophrenia[J].Mol Psychiatry,2015,20(6):685-694.DOI:10.1038/mp.2015.11.
[51]Legault C,Maki PM,Resnick SM,et al.Effects of tamoxifen and raloxifene on memory and other cognitive abilities:cognition in the study of tamoxifen and raloxifene[J].J Clin Oncol,2009,27(31):5144-5152.DOI:10.1200/jco.2008.21.0716.
[52]Underwood EA,Rochon PA,Moineddin R,et al.Cognitive sequelae of endocrine therapy in women treated for breast cancer:a meta-analysis[J].Breast Cancer Res Treat,2018,168(2):299-310.DOI:10.1007/s10549-017-4627-4.
[53]Phillips KA,Ribi K,Sun Z,et al.Cognitive function in postmenopausal women receiving adjuvant letrozole or tamoxifen for breast cancer in the BIG 1-98 randomized trial[J].Breast,2010,19(5):388-395.DOI:10.1016/j.breast.2010.03.025.
[54]Vaz M,Silvestre S.Alzheimers disease:recent treatment strategies[J].Eur J Pharmacol,2020,887:173554.DOI:10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.173554.
[55]Soria Lopez JA,González HM,Léger GC.Alzheimers disease[J].Handb Clin Neurol,2019,167:231-255.DOI:10.1016/b978-0-12-804766-8.00013-3.
[56]Veenman L.Raloxifene as treatment for various types of brain injuries and neurodegenerative diseases:a good start[J].Int J Mol Sci,2020,21(20):7586.DOI:10.3390/ijms21207586.
[57]Kritzer MF,Creutz LM.Region and sex differences in constituent dopamine neurons and immunoreactivity for intracellular estrogen and androgen receptors in mesocortic al projections in rats[J].J Neurosci,2008,28(38):9525-9535.DOI:10.1523/jneurosci.2637-08.2008.
[58]Koss WA,Frick KM.Sex differences in hippocampal function[J].J Neurosci Res,2017,95(1-2):539-562.DOI:10.1002/jnr.23864.
[59]Gillies GE,McArthur S.Estrogen actions in the brain and the basis for differential action in men and women:a case for sex-specific medicines[J].Pharmacol Rev,2010,62(2):155-198.DOI:10.1124/pr.109.002071.
[60]McMillan PJ,LeMaster AM,Dorsa DM.Tamoxifen enhances choline acetyltransferase mRNA expression in rat basal forebrain cholinergic neurons[J].Brain Res Mol Brain Res,2002,103(1):140-145.DOI:10.1016/S0169-328X(02)00195-X.
[61]Eberling JL,Wu C,Tong-Turnbeaugh R,et al.Estrogen-and tamoxifen-associated effects on brain structure and function[J].Neuroimage,2004,21(1):364-371.DOI:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2003.08.037.
[62]González-Burgos I,Rivera-Cervantes MC,Velázquez-Zamora DA,et al.Selective estrogen receptor modulators regulate dendritic spine plasticity in the hippocampus of male rats[J].Neural Plast,2012:309494.DOI:10.1155/2012/309494.
[63]Chen Y,Tian Y,Tian H,et al.Tamoxifen promotes white matter recovery and cognitive functions in male mice after chronic hypoperfusion[J].Neurochem Int,2019,131:104566.DOI:10.1016/j.neuint.2019.104566.
[64]Cyr M,Ghribi O,Thibault C,et al.Ovarian steroids and selective estrogen receptor modulators activity on rat brain NMDA and AMPA receptors[J].Brain Res Brain Res Rev,2001,37(1):153-161.DOI:10.1016/S0165-0173(01)00115-1.
(收稿日期:2022-04-07)
基金項目:海南省自然科學基金高層次人才項目(821RC724)、國家自然科學基金(81660195)和海南省醫藥衛生項目(20A200157)

