hsa_circ_0000437與危險因素對胃癌患者術后 復發的影響
王瀧銳,隋子奇,章燕飛,徐樹明
hsa_circ_0000437與危險因素對胃癌患者術后 復發的影響
王瀧銳,隋子奇,章燕飛,徐樹明
浙江大學醫學院附屬第二醫院臨平院區消化科,浙江杭州 311100
探究血清環狀RNA hsa_circ_0000437水平與危險因素的交互作用對胃癌患者術后復發的影響。選取浙江大學醫學院附屬第二醫院臨平院區2019年6月至2020年12月收治的118例胃癌患者為研究對象。根據胃癌患者術后是否復發分為復發組和未復發組。比較兩組患者血清hsa_circ_0000437水平及臨床資料。采用多因素Logistic回歸分析影響胃癌患者術后復發危險因素及血清hsa_circ_0000437水平在兩組患者間的差異,并使用相乘和相加模型進行血清hsa_circ_0000437與其他胃癌術后復發風險因素的關聯強度和交互作用分析。118例胃癌患者中54例患者術后復發,術后復發率為45.76%。復發組患者病理分化程度、合并癥種類、漿膜浸潤、淋巴結數目、淋巴結清掃范圍分布與未復發組差異有統計學意義(<0.05);復發組腫瘤直徑大于未復發組(<0.05);血清hsa_circ_0000437水平高于未復發組(<0.05)。Logistic回歸分析顯示,腫瘤直徑(大)、病理分化程度(低)、漿膜浸潤(有)及血清hsa_circ_0000437水平(高)均是影響胃癌患者術后復發的危險因素(<0.05)。交互作用分析結果顯示,血清hsa_circ_0000437(高)和腫瘤直徑(大)對胃癌患者術后復發具有相加交互作用(=11.144,95%:2.257~18.145),超額危險度(excess relative risk,)=5.844,95%:1.264~11.357,交互作用歸因比(attributable proportion due to interaction,)=0.524,95%:0.236~0.891,交互作用指數(interaction index,)=2.359,95%:1.024~6.577。血清hsa_circ_0000437(高)和病理分化程度(低)對胃癌患者術后復發具有相加交互作用(=7.083,95%:4.372~13.159;=2.841,95%:1.152~6.339;=0.351,95%:0.188~0.754;=1.670,95%:1.006~4.351)。血清hsa_circ_0000437(高)與漿膜浸潤對胃癌患者術后復發具有相加交互作用(=7.157,95%:3.759~12.046;=4.067,95%:1.378~9.466;=0.568,95%:0.221~0.961;=2.947,95%:1.128~8.319)。血清hsa_circ_0000437水平(高)與腫瘤直徑(大)、病理分化程度(低)、漿膜浸潤(有)對胃癌患者術后復發具有相加交互作用。
胃癌;血清環狀RNA;危險因素分析;交互作用
早期胃癌患者常無明顯癥狀,易被忽視[1-2];晚期胃癌患者可出現上腹飽脹不適、食欲下降、消瘦、貧血、胸骨后疼痛或吞咽困難等癥狀[3-4]。胃癌的治療主要包括胃大部或全胃切除+淋巴結清掃根治手術、新輔助放化療、靶向治療等[5]。近年來,手術治療已成為胃癌患者的最重要治療方式。根治性手術通過將癌灶整塊切除,是目前可能治愈胃癌的唯一治療手段[6];但胃癌根治術后患者仍存在約60.8%的復發風險,導致患者預后不良,病死率較高[7]。因此,探討胃癌術后復發危險因素,早期識別胃癌患者術后復發風險對胃癌患者后續康復具有積極意義。血清hsa_circ_0000437是一種參與多種疾病發生與發展的特異性指標,其水平變化是否與胃癌患者術后復發存在聯系尚不明確[8]。鑒于此,本研究以胃癌患者為研究對象,探究血清hsa_circ_0000437與危險因素的交互作用對胃癌患者術后復發的影響,為胃癌的治療方案的制定提供參考。
1 資料與方法
1.1 一般資料
選取浙江大學醫學院附屬第二醫院臨平院區2019年6月至2020年12月收治的118例胃癌患者為研究對象,其中男78例,女40例;年齡56~78歲,平均(65.44±3.90)歲;合并癥:糖尿病46例,高血壓41例,高脂血癥45例,低鉀血癥40例;腫瘤直徑3.0~7.8cm,平均(5.12±1.18)cm。納入標準:①符合《胃癌多學科綜合治療協作組診療模式專家共識》[9]中胃癌的診斷標準;②經病理學檢查確診為胃癌,并接受相關手術治療;③完成24個月隨訪;④臨床診療及隨訪資料完整;⑤患者自愿簽署知情同意書。排除標準:①合并嚴重其他系統疾病或嚴重感染;②僅接受姑息性手術治療;③圍手術期死亡;④伴有精神障礙。本研究經杭州市臨平區第一人民醫院倫理委員會批準(倫理審批號:臨平一院倫2020論第011號)。
1.2 研究方法
1.2.1 血清hsa_circ_0000437水平檢測 取患者空腹外周靜脈血4ml,經常規處理后獲得血清,采用實時熒光定量PCR(quantitative real-time PCR,RT-qPCR)檢測血清hsa_circ_0000437水平。
1.2.2 資料收集 收集可能影響胃癌患者術后復發的臨床和病理資料,包括性別、年齡,腫瘤直徑、病理分化程度、腫瘤原發位置,腫瘤浸潤深度、漿膜浸潤、淋巴結浸潤數目,手術淋巴結清掃范圍、合并癥種類、血清hsa_circ_0000437水平等。
1.2.3 隨訪及分組 患者出院后隨訪24個月,以門診就診及電話隨訪為主,每3~6個月進行一次胸部和全腹部增強CT檢查,每12個月進行一次胃鏡檢查,CT發現復發征象者,即時行胃鏡檢查和活檢診斷;隨訪截至2022年12月31日,記錄終點事件:患者經胃鏡、影像學檢查或手術病理檢查提示胃癌復發。根據是否發生終點事件將所有入組患者分為復發組(54例)和未復發組(64例)。
1.3 統計學方法
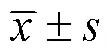
2 結果
2.1 兩組患者的臨床資料比較
復發組患者的性別、年齡、腫瘤原發位置、腫瘤浸潤深度與未復發組比較,差異無統計學意義(>0.05)。復發組患者的腫瘤直徑、病理分化程度、合并癥種類、漿膜浸潤、淋巴結浸潤數目、淋巴結清掃范圍及血清hsa_circ_0000437水平與未復發組比較,差異有統計學意義(<0.05),見表1。
2.2 明確相關變量最佳截斷值
通過受試者操作特征曲線(receiver operating characteristic curve,ROC曲線)的約登指數明確表1中有統計學意義的連續變量的最佳截斷值,以最佳截斷值為分界點轉為二分類變量進行多因素分析,見表2。
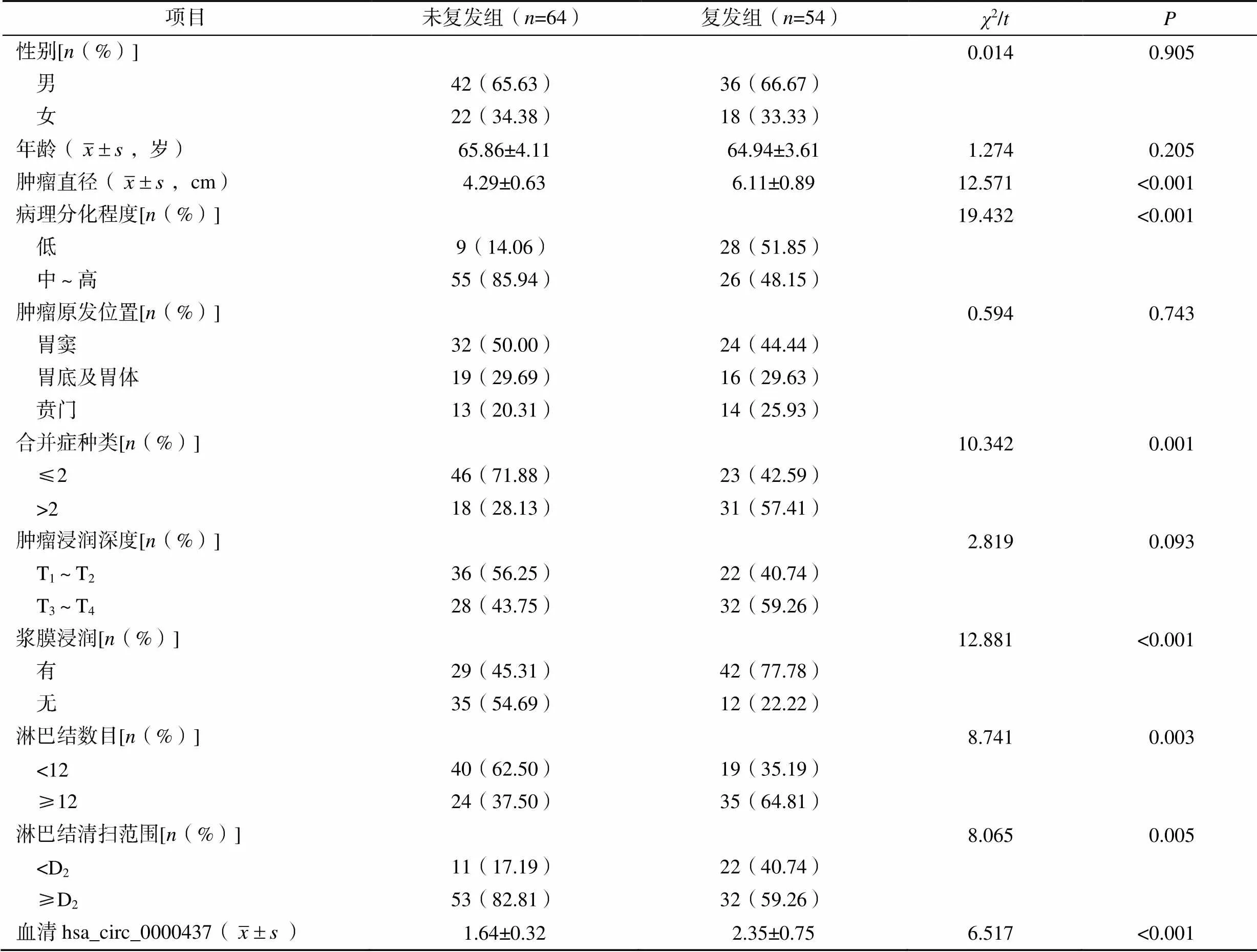
表1 兩組患者的臨床資料比較

表2 連續變量的最佳截斷值
2.3 Logistic回歸分析
腫瘤直徑(大)、病理分化程度(低)、漿膜浸潤(有)及血清hsa_circ_0000437水平(高)均是影響胃癌患者術后復發的危險因素(<0.05)。淋巴結清掃范圍(≥D2)是保護因素(<0.05),見表3。
2.4 相乘交互作用分析
以胃癌患者是否術后復發為因變量,以血清hsa_circ_0000437(高)、腫瘤直徑(大)及二者乘積,血清hsa_circ_0000437(高)、病理分化程度(低)及二者乘積,血清hsa_circ_0000437(高)、漿膜浸潤及二者乘積為自變量,進行多因素Logistic回歸分析。結果顯示,血清hsa_circ_0000437(高)×腫瘤直徑(大)、血清hsa_circ_0000437(高)×病理分化程度(低)、血清hsa_circ_0000437(高)×漿膜浸潤對胃癌患者術后復發均不存在相乘交互作用(>0.05),見表4。
2.5 相加交互作用分析
以胃癌患者是否術后復發為因變量,以血清hsa_circ_0000437(高)、腫瘤直徑(大)、病理分化程度、漿膜浸潤為自變量,進行多因素Logistic回歸分析,結果顯示,血清hsa_circ_0000437(高)和腫瘤直徑(大)、血清hsa_circ_0000437(高)和病理分化程度(低)、血清hsa_circ_0000437(高)與漿膜浸潤對胃癌患者術后復發具有相加交互作用,見表5。

表3 胃癌患者術后復發影響因素的多因素Logistic回歸分析

表4 血清hsa_circ_0000437水平與危險因素的相乘交互作用

表5 血清hsa_circ_0000437水平與危險因素的相加交互作用

血清hsa_circ_0000437(高)病理分化程度(低)回歸系數標準誤Waldχ2OR(95%CI)P 是是1.9581.24622.4677.083(4.372~13.159)<0.001 是否1.7030.88513.7025.488(2.012~8.315)0.002 否是6.0202.3756.4273.402(1.471~5.128)0.011
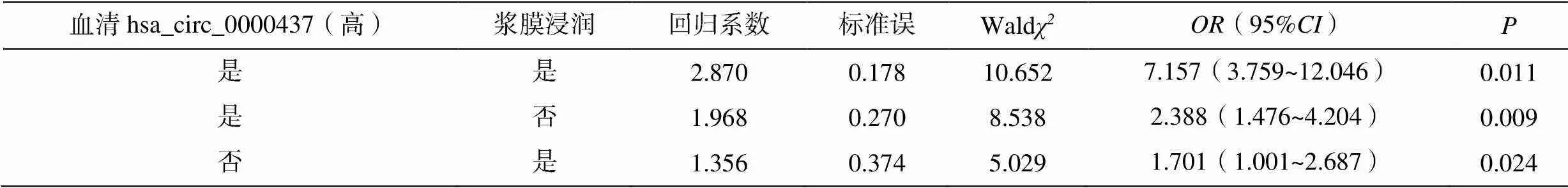
血清hsa_circ_0000437(高)漿膜浸潤回歸系數標準誤Waldχ2OR(95%CI)P 是是2.8700.17810.6527.157(3.759~12.046)0.011 是否1.9680.2708.5382.388(1.476~4.204)0.009 否是1.3560.3745.0291.701(1.001~2.687)0.024

血清hsa_circ_0000437水平危險因素RERI(95%CI)AP(95%CI)S(95%CI) 血清hsa_circ_0000437(高)腫瘤直徑(大)5.844(1.264~11.357)0.524(0.236~0.891)2.359(1.024~6.577) 血清hsa_circ_0000437(高)病理分化程度(低)2.841(1.152~6.339)0.351(0.188~0.754)1.670(1.006~4.351) 血清hsa_circ_0000437(高)漿膜浸潤4.067(1.378~9.466)0.568(0.221~0.961)2.947(1.128~8.319)
3 討論
胃癌根治術后復發率較高是導致胃癌患者預后差的重要原因,復發后患者生存期大大縮短,極大威脅患者的生命安全[12-13];劉苗等[14]研究顯示,部分接受根治性手術的胃癌患者在2年內復發;本研究118例患者中54例術后復發,術后復發率達45.76%,因此,明確影響胃癌患者術后復發的危險因素,對早期干預、改善胃癌患者預后、提高患者生存期意義重大。
本研究單因素分析結果顯示腫瘤直徑更大、分化程度更低、合并癥種類更多、有漿膜浸潤、淋巴結浸潤數目多及血清hsa_circ_0000437水平高的胃癌患者術后更易復發。Logistic回歸分析顯示,腫瘤直徑(大)、病理分化程度(低)、漿膜浸潤(有)及血清hsa_circ_0000437水平(高)均是影響胃癌患者術后復發的危險因素。分析其原因:①腫瘤直徑一定程度上反映胃癌發展進程,直徑越大,對癌周淋巴結的侵襲能力越強,更易浸潤周邊組織,導致淋巴結浸潤轉移的風險也越高;另外,癌細胞穿透漿膜層后,進入腹腔進而發生種植或轉移,增加周圍組織被侵犯的風險,進而增加胃癌患者術后復發的風險[15-17]。②高分化腫瘤組織侵襲性低,生長緩慢,轉移能力弱;反之,低分化腫瘤惡性度較高,癌細胞生長迅速,且侵襲能力更強,易于轉移擴散,加之手術在一定程度上對患者造成傷害,加重身體負擔,可能會提高患者術后復發的風險[18-20]。③癌癥患者身體各項功能較正常患者下降,機體對外界致病因素的抵抗力相對較弱,所以胃癌患者多合并各種基礎疾病,如糖尿病、高血壓、高脂血癥、低鉀血癥等,合并癥種類在2種以上的胃癌患者更易合并營養不良,加重患者免疫失衡,一定程度上影響患者的預后,增加術后復發風險[21-22]。本研究中血清hsa_circ_0000437水平的異常升高會增加胃癌患者術后復發風險。此結果與Li等[23]研究結果一致,其可歸因于hsa_circ_0000437過表達刺激胃癌細胞增殖,并通過強化上皮間質轉化進程加強癌細胞侵襲能力,從而增加術后復發風險[24]。因此,對低分化胃癌、合并癥較多、腫瘤直徑較大及血清hsa_circ_0000437水平較高的患者,應綜合考慮患者情況,采取最佳的治療方案,以降低術后復發的風險,改善患者預后。
綜上所述,腫瘤直徑(大)、病理分化程度(低)、漿膜浸潤(有)及血清hsa_circ_0000437水平(高)均是影響胃癌患者術后復發的危險因素,血清hsa_circ_0000437(高)與腫瘤直徑(大)、病理分化程度(低)、漿膜浸潤(有)對胃癌患者術后復發具有相加交互作用。
[1] 鄭南翔, 單廷. 胃癌根治術患者術后早期復發轉移的相關危險因素[J]. 中國老年學雜志, 2017, 37(17): 4301–4303.
[2] 石琳, 喬曉娟, 李文新. 呼和浩特市2439例胃癌發病資料及發生部位特征分析[J]. 內蒙古醫科大學學報, 2020, 42(4): 373–377.
[3] TANG M, SHEN X, CHAI J, et al. Dose-effect relationship between gastric cancer and common digestive tract symptoms and diagnoses in Anhui, China[J]. Cancer Manag Res, 2021, 13: 4955–4966.
[4] TANG D, LIU S, SHEN H, et al. Extracellular vesicles promote the formation of pre-metastasis niche in gastric cancer[J]. Front Immunol, 2022, 13: 813015.
[5] WANG F H, ZHANG X T, LI Y F, et al. The Chinese Society of Clinical Oncology (CSCO): Clinical guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of gastric cancer, 2021[J]. Cancer Commun (Lond), 2021, 41(8): 747–795.
[6] 王輝, 馬伯恒, 徐方正. ALC/AMC聯合AGR對胃癌根治術患者預后的預測價值[J]. 中國醫藥導報, 2022, 19(26): 116–119.
[7] 曹孟軒, 胡燦, 張延強, 等. 胃癌根治術后早期復發轉移的危險因素分析[J]. 中國癌癥雜志, 2022, 32(7): 588–595.
[8] WU N, JIN L, CAI J. Profiling and bioinformatics analyses reveal differential circular RNA expression in hypertensive patients[J]. Clin Exp Hypertens, 2017, 39(5): 454–459.
[9] 中國研究型醫院學會消化道腫瘤專業委員會, 中國醫師協會外科醫師分會多學科綜合治療專業委員會. 胃癌多學科綜合治療協作組診療模式專家共識[J]. 中國實用外科雜志, 2017, 37(1): 37–38.
[10] ROTTHMAN K J. Epidemiology: An introduction[M]. New York: Oxford University Press, 2002: 168–180.
[11] ANDERSSON T, ALFREDSSON L, KALLBERG H, et al. Calculating measures of biological interaction[J]. Eur JEpidemiol, 2005, 20(7): 575–579.
[12] ZHANG Y, GU X, QIN X, et al. Evaluation of serum tRF-23-Q99P9P9NDD as a potential biomarker for the clinical diagnosis of gastric cancer[J]. Mol Med, 2022, 28(1): 63.
[13] HUANG L, FENG B, LI Y, et al. Computed tomography-based radiomics nomogram: Potential to predict local recurrence of gastric cancer after radical resection[J]. Front Oncol, 2021, 11: 638362.
[14] 劉苗, 王英南, 張韶辰, 等. 影響胃癌根治術后早期復發的危險因素分析[J]. 臨床腫瘤學雜志, 2020, 25(10): 905–910.
[15] KUNISAKI C, TAKAHASHI M, SATO S, et al. Prognostic impact of dimensional factors in pT1 gastric cancer[J]. Surg Oncol, 2021, 38: 101584.
[16] JI L, QIAN W, GUI L, et al. Blockade of β-catenin- induced CCL28 suppresses gastric cancer progression via inhibition of Treg cell infiltration[J]. Cancer Res, 2020, 80(10): 2004–2016.
[17] 翟俊, 肖學文. GOLPH3、Livin蛋白表達水平與胃癌患者臨床病理特征的相關性研究[J]. 醫學臨床研究, 2021, 38(1): 22–24, 28.
[18] TANG B, ZHANG Y, WANG W, et al. PARP6 suppresses the proliferation and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma by degrading XRCC6 to regulate the Wnt/β-catenin pathway[J]. Am J Cancer Res, 2020, 10(7): 2100–2113.
[19] ZHENG G, YOU C, QIU Z, et al. Expression of MACC1 protein in gastric cancer and its effect on proliferation and invasion of gastric cancer cells[J]. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand), 2020, 66(2): 111–117.
[20] WEI C J, ZHANG Z W, LU J H, et al. MiR-638 regulates gastric cardia adenocarcinoma cell proliferation, apoptosis, migration and invasion by targeting MACC1[J]. Neoplasma, 2020, 67(3): 537–546.
[21] 王曉明. 老年胃癌患者術后復發的影響因素研究[J]. 中國藥物與臨床, 2020, 20(23): 3953–3955.
[22] 陳玲, 林晶, 陳麗珠, 等. 胃癌根治術后早期復發轉移的影響因素分析[J]. 腫瘤學雜志, 2020, 26(12): 1052–1055.
[23] LI F, CAI Y, DENG S, et al. A peptide CORO1C-47aa encoded by the circular noncoding RNA circ-0000437 functions as a negative regulator in endometrium tumor angiogenesis[J]. J Biol Chem, 2021, 297(5): 101182.
[24] 申嫻娟, 沈蕾, 馬碩, 等. 血清hsa_circ_0000437對胃癌輔助診斷及預后判斷的意義[J]. 中華檢驗醫學雜志, 2022, 45(5): 509–515.
Effect of hsa_circ_0000437 and risk factors on postoperative recurrence in patients with gastric cancer
Department of Digestive, Linping District, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Hangzhou 311100, Zhejiang, China
To explore the effect of interaction between serum circular RNA hsa_circ_0000437 level and risk factors on postoperative recurrence in patients with gastric cancer.A total of 118 patients with gastric cancer admitted to Linping District, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Zhejiang University School of Medicine from June 2019 to December 2020 were selected as the study objects. Patients with gastric cancer were divided into recurrence group and non-recurrence group according to whether they had recurrence after operation. The serum hsa_circ_0000437 level and clinical data of the two groups were compared. Multivariate Logistic regression analysis was used to analyze the risk factors affecting postoperative recurrence in patients with gastric cancer and the differences in serum hsa_circ_0000437 levels between the two groups, and the correlation strength and interaction between serum hsa_circ_0000437 and other risk factors for postoperative recurrence of gastric cancer were performed using the multiplicative and additive models.A total of 54 of 118 patients with gastric cancer recurred after operation, and the recurrence rate was 45.76%. There were significant differences between the recurrence group and the non-recurrence group in the degree of pathological differentiation, types of complications, serous infiltration, number of lymph nodes and distribution of lymph node dissection (<0.05). The tumor diameter of recurrent group was higher than that of non-recurrent group (<0.05). The serum hsa_circ_0000437 level was higher than that of the non-recurrence group (<0.05). Logistic regression analysis showed that tumor diameter (large), pathological differentiation degree (low), serous membrane infiltration (present) and serum hsa_circ_0000437 level (high) were all risk factors for postoperative recurrence in gastric cancer patients (<0.05). Interaction analysis results showed that serum hsa_circ_0000437 (high) and tumor diameter (large) had additive interaction on postoperative recurrence in patients with gastric cancer (=11.144, 95%: 2.257?18.145), excess relative risk ()=5.844, 95%: 1.264?11.357, attributable proportion due to interaction () =0.524, 95%: 0.236?0.891, interaction index ()=2.359, 95%: 1.024?6.577. Serum hsa_circ_0000437 (high) and pathological differentiation (low) had additive interaction on postoperative recurrence of gastric cancer patients (=7.083, 95%: 4.372?13.159;=2.841, 95%: 1.152?6.339;=0.351, 95%: 0.188?0.754;=1.670, 95%: 1.006?4.351). Serum hsa_circ_0000437 (high) and serous infiltration had a summative interaction on postoperative recurrence in patients with gastric cancer (=7.157, 95%: 3.759?12.046;=4.067, 95%: 1.378?9.466;=0.568, 95%: 0.221?0.961;=2.947, 95%: 1.128?8.319).Serum hsa_circ_0000437 level (high) has additive interaction with tumor diameter (large), pathological differentiation degree (low) and serous membrane infiltration (present) on postoperative recurrence of gastric cancer patients.
Gastric cancer; Serum circular RNA; Risk factor analysis; Interaction
R735.2
A
10.3969/j.issn.1673-9701.2023.30.008
王瀧銳,電子信箱:1244139634@qq.com
(2023–01–23)
(2023–10–09)

