剪切體蛋白PRPF8的研究進展
曹滌非,姜 洋,黃國慶,薛佳瑩,吳 瓊,王 雷 ,孫 堯,王東凱,李 瑤,邢 言,劉兆良
(1.黑龍江省科學院高技術研究院,哈爾濱 150020; 2.哈爾濱醫科大學,哈爾濱 150020)
剪切體蛋白PRPF8的研究進展
曹滌非1,姜 洋1,黃國慶1,薛佳瑩1,吳 瓊1,王 雷1,孫 堯1,王東凱1,李 瑤1,邢 言1,劉兆良2
(1.黑龍江省科學院高技術研究院,哈爾濱 150020; 2.哈爾濱醫科大學,哈爾濱 150020)
真核生物中,mRNA前體的可變剪切是一個重要過程,在這過程中剪切體蛋白起到重要的作用。PRPF8是剪切體的核心蛋白,它的突變可引起一些模型細胞的死亡,并且與疾病的發生有重要的關系。
mRNA前體;可變剪切;PRPF8
真核生物中,絕大多數基因的初始轉錄產物前 mRNA(pre-mRNA)必須經過剪切等加工過程,才能形成成熟的mRNA。可變剪切是指同一種pre-mRNA具有多種剪切程序,形成不同的mRNA。pre-mRNA 的可變剪切是控制基因表達和產生蛋白質多樣性的重要機制,在產生受體多樣性、調節控制生長發育等方面起著決定性作用[1]。
1 mRNA前體可變剪切的機制
以外顯子和內含子為單元的基因結構形式在真核生物中普遍存在,人類基因中的大多數都含有內含子。因此,通過切除內含子把外顯子按一定的順序拼接起來形成成熟的 mRNA,再經過翻譯產生蛋白質就是一種最普遍的基因表達方式[2]。現已經知道,mRNA 的剪切是基于對剪切位點的識別基礎上,由被稱為剪切體的核酸蛋白復合物完成。剪切體包含了 5 種SnRNP 和超過200種的蛋白質因子,這些蛋白質因子有富含精氨酸和絲氨酸的SR 蛋白和非SR 蛋白,包括hnRNP、RNA螺旋酶、激酶等[3-4]。剪切復合體的形成開始于 U1snRNP 結合至 5′剪切位點和SF1(splicing factor 1)、U2snRNP 結合至 3′剪切位點處的分支點,U2snRNP的結合需要輔助因子U2AF。U2AF 由 65kDa 和 35kDa 兩個亞基組成,U2AF65 識別多聚嘧啶區域,U2AF35 識別 3′剪接位點的AG,隨后 U2snRNP 結合到分支點上,從而形成了剪切前體。最后 U5 和 U4/U6snRNP 的結合完成剪切體的組裝,經過兩個連續的轉酯反應,完成了內含子的切除和外顯子的連接[5]。
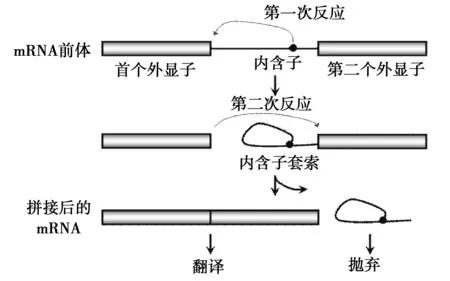
圖1 剪切體剪切調控過程Fig.1 Regulation of splicing
2 剪切體蛋白PRPF8的生物學功能
PRPF8 是 U5snRNP 的重要組成成分,是剪切體的核心蛋白。它在剪切體的組裝和催化兩步的轉酯化酶促反應中均發揮作用,是剪切體蛋白中在進化上最保守的蛋白之一[6]。酵母實驗和哺乳動物細胞的體外實驗證明了PRPF8 在剪切中不可或缺的作用[7]。但是關于這個蛋白的生理和細胞生物學功能卻很少研究。模型動物中的有限研究表明:PRPF8 是維持生物生存的重要蛋白。酵母中 PRPF8 突變會引起溫度敏感的細胞周期阻滯[7]。在線蟲和斑馬魚中廢除PRPF8 的表達會造成胚胎期的死亡[7]。在果蠅的 S2 細胞中沉默 PRPF8 可以引起大量的細胞死亡[8]。而PRPF8 調控細胞生存能力這一功能在哺乳動物細胞中也一樣保守。小鼠中完全敲除 PRPF8 會引起小鼠胚胎的早期死亡[9]。在一個由歐盟資助的篩選與有絲分裂相關的基因的項目中(MitoCheck),在 Hela 細胞中用 4種不同的 siRNA 沉默 PRPF8均導致了細胞死亡。而相似的現象也在另外兩個完全獨立的實驗中得到證實[10]。
在遺傳性疾病中,PRPF8與常染色體顯性遺傳視網膜色素變性有關[11]。此外,在非轉化的和轉化的乳腺上皮細胞系(human mammary epithelial cells, HMEC)中,在利用乳腺癌細胞系 Cal51 和 HCC1954 中,在結腸癌細胞系 HCT116和 DLD1,沉默 PRPF8 都可以導致細胞死亡。這證明 PRPF8 是一個功能非常保守的,可以調節細胞生存能力的原癌基因[12-14],并且 PRPF8 可能在腫瘤的生長中發揮重要作用[15]。劉兆良等通過免疫印跡的方法檢查了多個乳腺癌細胞系中 PRPF8的表達情況,發現與正常乳腺上皮細胞相比較,PRPF8 的表達在檢測的所有的乳腺癌細胞中都有不同程度的上調。通過檢索了腫瘤基因組圖譜計劃(the Cancer Genome Atlas, TCGA)的數據庫,發現 PRPF8 在乳腺癌中頻繁地發生突變、缺失和擴增。這些數據表明 PRPF8 作為一個剪切體的核心蛋白,對于細胞生長具有重要作用,可能在乳腺癌中發揮重要作用。
3 展望
可變剪切是真核生物細胞中不可或缺的過程,對基因的轉錄和蛋白的表達具有重要的調控作用。最近的研究表明,在可變剪切過程中的突變會導致許多疾病的發生,因此,從mRNA前體的剪切水平上尋找疾病發生的原因,有助于臨床對疾病發病機制的深刻認識和對疾病靶向治療的幫助。可變剪切將是今后臨床醫學研究的方向,剪切體蛋白的研究將成為熱點。
[1] Alastair Thompson,Keith Brennan,Angela Cox,et al. Evaluation of the current knowledge limitations in breast cancer research: a gap analysis[J].Breast Cancer Res.,2008,10(2):R26.
[2] Scott,L. M. and V. I. Rebel. Acquired mutations that affect pre-mRNA splicing in hematologic malignancies and solid tumors[J]. J Natl Cancer Inst,2013,105(20):1540-1549.
[3] Naoki Sato,Masao Maeda,Mai Sugiyama,et al.Inhibition of SNW1 association with spliceosomal proteins promotes apoptosis in breast cancer[J].Cells.cancer medicine,2014,(09):80-84.
[4] Wahl,M. C.,Will,C. L.,& Lührmann,R. The spliceosome: design principles of a dynamic RNP machine[J].Cell,2009,136(4):701-718.
[5] Grainger,R. J., J. D. Beggs. Prp8 protein:at the heart of the spliceosome[J].RNA,2008,11(5):533-557.
[6] Keightley, M.-C. et al. In vivo mutation of pre-mRNA processing factor 8 (Prpf8) affects transcript splicing,cell survival and myeloid differentiation[J].FEBS Lett,2013,(587):2150-2157.
[7] Graziotto,J. J. et al. Three gene-targeted mouse models of RNA splicing factor RP show late-onset RPE and retinal degeneration[J].Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci,2011,(52):190-198.
[8] R?met, M.,Manfruelli, P.,Pearson, A.,Mathey-Prevot,B. &Ezekowitz,R. A. B. Functional genomic analysis of phagocytosis and identification of a Drosophila receptor for E. coli[J].Nature,2002,(416):644-648.
[9] Rines,D. R.,M. A. Gomez-Ferreria,et al. Whole genome functional analysis identifies novel components required for mitotic spindle integrity in human cells[J].Genome Biol,2008,9(2):R44.
[10] Schlabach,M. R.,J. Luo,et al. Cancer proliferation gene discovery through functional genomics[J]. Science,2008,319(5863):620-624.
[11] Kessler,J. D.,K. T. Kahle,et al. A SUMOylation-dependent transcriptional subprogram is required for Myc-driven tumorigenesis[J].Science,2012,335(6066): 348-353.
[12] Garnett,M. J.,J. Mansfeld,et al. UBE2S elongates ubiquitin chains on APC/C substrates to promote mitotic exit[J].Nat Cell Biol,2009,11(11):1363-1369.
[13] Allende-Vega,N.,S. Dayal,et al. p53 is activated in response to disruption of the pre-mRNA splicing machinery[J].Oncogene,2013,32(1):1-14.
[14] Rines,D. R.,M. A. Gomez-Ferreria,et al. Whole genome functional analysis identifies novel components required for mitotic spindle integrity in human cells[J].Genome Biol,2008,9(2):R44.
[15] Kittler,R.,L. Pelletier,et al. Genome-scale RNAi profiling of cell division in human tissue culture cells[J].Nat Cell Biol,2007,9(12):1401-1412.
Study on spliceosome of PRPF8
CAO Di-fei1, JIANG Yang1, HUANG Guo-qing1, XUE Jia-ying1, WU Qiong1, WANG Lei1,SUN Yao1, WANG Dong-kai1, LI Yao1, XING Yan1, LIU Zhao-liang2
(1. Institute of Advanced Technology, Heilongjiang Academy of Sciences, Harbin 150020, China;2. Harbin Medical University, Harbin 150020, China)
In eukaryotes, alternative splicing of mRNA precursors is an important process, which plays an important role in this process. PRPF8 is the core protein of splicing, the mutation of which can cause the death of model cell, and it has an important relationship with the occurrence of the disease.
Pre-mRNA; Splicing; PRPF8
2016-09-12
項目來源:黑龍江省科學院預研項目(CX13H08)
曹滌非(1981-),女,博士,副研究員。
劉兆良(1975-),男,博士,副研究員。
R73-3
A
1674-8646(2016)23-0014-02

