海藻多糖對H2O2誘導人胚肺成纖維細胞MRC-5氧化損傷的影響及其機制
劉驊漫,劉學,賈新華,張心月,張偉
(1山東中醫藥大學,濟南250014;2山東省胸科醫院;3山東中醫藥大學附屬醫院)
海藻多糖對H2O2誘導人胚肺成纖維細胞MRC-5氧化損傷的影響及其機制
劉驊漫1,3,劉學1,2,賈新華3,張心月1,張偉3
(1山東中醫藥大學,濟南250014;2山東省胸科醫院;3山東中醫藥大學附屬醫院)
目的探討海藻多糖對H2O2誘導人胚肺成纖維細胞MRC-5氧化損傷的影響及機制。方法將體外培養的人胚肺成纖維細胞MRC-5隨機分為空白組、H2O2組、海藻多糖組、海藻多糖+H2O2組、H2O2+海藻多糖組。空白組正常培養,H2O2組給予H2O2處理,海藻多糖組給予海藻多糖處理,海藻多糖+H2O2組先給予海藻多糖干預1 h、再給予H2O2處理,H2O2+海藻多糖組先給予H2O2干預1 h、再給予海藻多糖處理。各組H2O2濃度均為600 μmol/L,海藻多糖濃度均為0.312 5 mg/mL。各組均于干預0、24、48、72 h時采用MTT法檢測細胞增殖抑制率;處理24 h時檢測丙二醛(MDA)、超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)、活性氧(ROS)表達,采用免疫熒光法檢測核轉錄因子E2相關因子2(Nrf2)蛋白表達,采用RT-PCR法檢測Nrf2、Kelch樣ECH聯合蛋白1(Keap1)、NADP(H)醌氧化還原酶1(NQO1)、血紅素氧合酶1(HO-1)、CGLC mRNA表達。結果培養24、48、72 h時,H2O2組、海藻多糖+H2O2組、H2O2+海藻多糖組細胞增殖抑制率均高于空白組及海藻多糖組,海藻多糖+H2O2組、H2O2+海藻多糖組均低于H2O2組,組間比較P均<0.05。與空白組及海藻多糖組比較,H2O2組、海藻多糖+H2O2組、H2O2+海藻多糖組MDA、ROS表達增加,SOD表達降低;與H2O2組比較,海藻多糖+H2O2組、H2O2+海藻多糖組MDA、ROS表達降低,SOD表達增加,組間比較P均<0.05。與空白組及海藻多糖組比較,H2O2組、海藻多糖+H2O2組、H2O2+海藻多糖組Nrf2 mRNA和蛋白相對表達量均降低,海藻多糖+H2O2組、H2O2+海藻多糖組均較H2O2組升高,組間比較P均<0.05。與空白組及海藻多糖組比較,H2O2組、海藻多糖+H2O2組、H2O2+海藻多糖組Keap1 mRNA相對表達量均升高,NQO1、CGLC、HO-1 mRNA相對表達量均降低;與H2O2組比較,海藻多糖+H2O2組、H2O2+海藻多糖組Keap1 mRNA相對表達量均降低,NQO1、CGLC、HO-1 mRNA相對表達量均升高;組間比較P均<0.05。結論海藻多糖可抑制H2O2誘導人胚肺成纖維細胞MRC-5的氧化應激損傷,上調 Nrf2表達、激活Nrf2/Keap1/抗氧化反應序列元件信號通路可能是其作用機制。
肺纖維化;人胚肺成纖維細胞MRC-5;海藻多糖;過氧化氫;氧化損傷;核轉錄因子E2相關因子2
Abstract:ObjectiveTo investigate the effects of seaweed polysaccharides on H2O2-induced oxidative damage of human embryonic lung fibroblasts MRC-5 and its mechanism.MethodsMRC-5 cells cultured in vitro were randomly divided into the blank group, H2O2group, seaweed polysaccharide group, seaweed polysaccharide+H2O2group, and H2O2+seaweed polysaccharide group. Cells in the blank group were cultured normally, cells in the H2O2group were treated with H2O2, cells in the seaweed polysaccharide group were treated with seaweed polysaccharide, cells in the seaweed polysaccharide+H2O2group were treated with seaweed polysaccharide for 1 h, then followed by H2O2, and cells in the H2O2+seaweed polysaccharide group were treated with H2O2for 1 h, then followed by H2O2. The concentration of H2O2in each group was 600 umol/L, and the concentration of seaweed polysaccharide was 0.3125 mg/mL. At 0, 24, 48 and 72 h after treatment, the cell proliferation inhibitory rate in each group was determined by MTT assay. The levels of malondialdehyde (MDA), superoxide dismutase (SOD), and reactive oxygen species (ROS) were measured at 24 h. NF-E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) protein was detected by immunofluorescence assay. The expression levels of Nrf2, Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 (Keap1), NADP (H) quinone oxidoreductase 1 (NQO1), heme oxygenase 1 (HO-1), and CGLC mRNA were detected by RT-PCR.ResultsThe cell inhibition rates of the H2O2group, seaweed polysaccharide +H2O2group, and H2O2+ seaweed polysaccharide group were higher than those of the blank group and seaweed polysaccharide group at 24, 48 and 72 h, and those of the seaweed polysaccharide+H2O2group and H2O2+seaweed polysaccharide group were lower than that of the H2O2group (allP<0.05). Compared with the blank group and the seaweed polysaccharide group, the levels of MDA and ROS in the H2O2group, the seaweed polysaccharide+H2O2group, and the H2O2+seaweed polysaccharide group increased, and the SOD level decreased. Compared with the H2O2group, the MDA and ROS levels decreased and the SOD level increased in the seaweed polysaccharide+H2O2group and the H2O2+seaweed polysaccharide group (allP<0.05). Compared with the blank group and the seaweed polysaccharide group, the expression of Nrf2 mRNA and protein in the H2O2group, the seaweed polysaccharide+H2O2group, and the H2O2+seaweed polysaccharide group decreased, and the seaweed polysaccharide+H2O2group and H2O2+seaweed polysaccharide group were higher than the H2O2group (allP<0.05). Compared with the blank group and the seaweed polysaccharide group, the relative expression of Keap1 mRNA in the H2O2group, the seaweed polysaccharide+H2O2group, and the H2O2+seaweed polysaccharide group increased, and the relative expression of NQO1, CGLC, and HO-1 mRNA decreased. Compared with the H2O2group, the relative expression of Keap1 mRNA in the polysaccharide+H2O2group and H2O2+seaweed polysaccharide group decreased, and the relative expression of NQO1, CGLC, and HO-1 mRNA increased (allP<0.05).ConclusionSeaweed polysaccharide could inhibit the oxidative stress injury of MRC-5 induced by H2O2through up-regulating the expression of Nrf2 and activating Nrf2-Keap1-ARE signaling pathway.
Keywords: pulmonary fibrosis; human embryonic lung fibroblasts MRC-5; seaweed polysaccharide; H2O2; oxidative damage; nuclear transcription factor E2-related factor 2
肺纖維化是肺間質性疾病的最終結局,氧化應激誘導的細胞氧化/抗氧化失衡是其形成及進展的主要原因之一。肺纖維化主要表現為肺功能進行性下降。目前尚無確切有效的治療藥物。中藥海藻味咸性寒,歸脾、肝、腎經,具有消痰散結、利水消腫之功效,起主要作用的成分為海藻多糖。海藻多糖具有抗氧化作用,目前多被作為食品抗氧化劑,其作為藥物用于疾病抗氧化的研究較少。2014年10月~2015年6月,本研究探討了海藻多糖對H2O2誘導人胚肺成纖維細胞MRC-5氧化損傷的影響及其機制。
1 材料與方法
1.1 材料 細胞:人胚肺成纖維細胞MRC-5購自南京凱基生物工程有限公司。主要試劑:海藻多糖(含量>99%)購自美國Sigma公司,MEM培養基、DMSO均購自美國Gibco公司,FBS購自美國 ExCell公司;RT-PCR試劑盒購自美國 Thermo Fisher公司,丙二醛(MDA)、超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)、活性氧(ROS)、總蛋白提取試劑盒及核轉錄因子E2相關因子2(Nrf2)一抗均購自南京凱基生物工程有限公司。Nrf2、Kelch樣ECH聯合蛋白1(Keap1)、NADP(H)醌氧化還原酶1(NQO1)、血紅素氧合酶1(HO-1)、CGLC、GAPDH引物均由南京凱基生物工程有限公司合成。
1.2 細胞培養及分組處理 將MRC-5細胞置于含10% FBS、100 IU/mL青霉素、100 IU/mL鏈霉素的DMEM培養液中,在37 ℃、5% CO2培養箱中培養,隔天換液。當培養瓶中細胞覆蓋面積達80%~90%時,加入0.25%胰蛋白酶,按1∶3傳代培養。取第4代細胞,隨機分為空白組、H2O2組、海藻多糖組、海藻多糖+H2O2組、H2O2+海藻多糖組。空白組正常培養,H2O2組給予終濃度為600 μmol/L H2O2處理,海藻多糖組給予終濃度為0.312 5 mg/mL海藻多糖處理,海藻多糖+H2O2組給予0.312 5 mg/mL海藻多糖干預1 h后再給予600 μmol/L H2O2處理,H2O2+海藻多糖組給予600 μmol/L H2O2干預1 h后再給予0.312 5 mg/mL海藻多糖處理。
1.3 細胞增殖抑制率檢測 采用MTT法。取1.2中處理24 h的各組細胞,以密度為5×104個/mL接種于96孔細胞培養板,每組設3個復孔,分別在孵育0、24、48、72 h時每孔加入20 μL MTT,繼續培養4 h;棄去所有液體,每孔加入DMSO 150 μL,置于搖床上輕輕搖勻10 min;酶標儀讀取波長490 nm處各孔吸光度(A)值,計算細胞增殖抑制率。細胞增殖抑制率=(A空白組-A觀察組)/A空白組×100%。
1.4 MDA、SOD、ROS表達檢測 取1.2中處理24 h的各組細胞,采用硫代巴比妥酸法檢測MDA表達,采用氯化硝基氮藍四唑光還原法檢測SOD表達,采用DCFH-DA探針檢測ROS表達(以A值表示)。具體步驟均嚴格參照試劑盒說明書操作。
1.5 Nrf2 mRNA和蛋白表達檢測 ①Nrf2 mRNA:采用RT-PCR法。取1.2中處理24 h的各組細胞,提取細胞總RNA,逆轉錄為cDNA后置于PCR儀中,42 ℃、1 h,70 ℃、10 min,冰浴5 min;將樣本稀釋10倍,依次向0.2 mL PCR管加入2×Master Mix(SYBR Green) 10 μL、模板(進行10倍稀釋后的cDNA)1 μL、引物混合物2 μL(含正、反向引物各10 μmol/L)、無RNase的雙蒸水7 μL,總量20 μL。以GAPDH為內參,計算Nrf2 mRNA相對表達量。Nrf2引物:F:TCCGGGTGTGTTTGTTCCAA,R:CGCCCGCGAGATAAAGAGTT;產物長度88 bp。GAPDH引物:F:TCCTGGCTCAGCCTCAAATG,R:CGTTAAACACCTCCCTCCCC;產物長度108 bp。②Nrf2蛋白:采用免疫熒光法。將MRC-5細胞置于預先放有載玻片的24孔培養板中培養,分組及處理同1.2。處理24 h時取出細胞爬片室溫下自然晾干,浸入4%多聚甲醛中,室溫固定30 min或4 ℃過夜,PBS洗滌3 min×3次;血清封閉,滴加Nrf2一抗,37 ℃恒溫箱中濕盒孵育2 h,PBS洗滌3 min×3次;滴加FITC二抗,37 ℃恒溫箱中濕盒避光孵育1 h,PBS洗滌3 min×3次;滴加DAPI染液,封片,熒光顯微鏡觀察。取3個高表達視野拍照留存,檢測熒光強度,計算Nrf2蛋白相對表達量。
1.6 Keap1、NQO1、CGLC、HO-1 mRNA表達檢測 采用RT-PCR法,具體步驟參照1.5①。 Keap1引物:F:GTCCCCTACAGCCAAGGTCC,R:ACTCAGTGGAGGCGTACATC;產物長度175 bp。NQO1引物:F:GGTTTGGAGTCCCTGCCATT,R:ACCAGTGGTGATGGAAAGCA;產物長度134 bp。CGLC引物:F:GAGGTCAAACCCAACCCAGT,R:AAGGTACTGAAGCGAG-
GGTG;產物長度92 bp。HO-1引物:F:TCCTGGCTCAGCCTCAAATG,R:CGTTAAACACCTCCCTCCCC;產物長度108 bp。以GAPDH為內參,計算Keap1、NQO1、CGLC、HO-1 mRNA相對表達量。
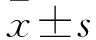
2 結果
2.1 各組細胞增殖抑制率比較 見表1。
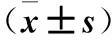
表1 各組細胞增殖抑制率比較
注:與空白組同時間點比較,*P<0.05;與H2O2組同時間點比較,△P<0.05;與海藻多糖組同時間點比較,#P<0.05。
2.2 各組MDA、SOD、ROS表達比較 見表2。
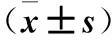
表2 各組MDA、SOD、ROS表達比較
注:與空白組比較,*P<0.05;與H2O2組比較,△P<0.05;與海藻多糖組比較,#P<0.05。
2.3 各組Nrf2 mRNA和蛋白表達比較 見表3。
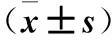
表3 各組Nrf2 mRNA和蛋白相對表達量比較
注:與空白組比較,*P<0.05;與H2O2組比較,△P<0.05;與海藻多糖組比較,#P<0.05。
2.4 各組Keap1、NQO1、CGLC、HO-1 mRNA表達比較 見表4。
表4 各組Keap1、NQO1、CGLC、HO-1 mRNA相對表達量比較
注:與空白組比較,*P<0.05;與H2O2組比較,△P<0.05;與海藻多糖組比較,#P<0.05。
3 討論
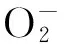
Nrf2是細胞氧化應激反應的關鍵因子,在氧化應激應答中發揮核心調控作用。Nrf2可與抗氧化反應序列元件(ARE)結合,發揮內源性抗氧化作用;誘導機體產生Ⅱ相解毒酶及抗氧化酶,增強對ROS的清除能力,減輕細胞氧化損傷,維持細胞內氧化還原平衡狀態。當細胞被親電子物質或氧化劑等攻擊處于氧化應激狀態時,Nrf2與Keap1解偶聯后跨膜轉運入核,激活Nrf2/Keap1/ARE信號通路。Nrf2/Keap1/ARE信號通路是目前機體最主要的內源性抗氧化信號通路,在機體抗氧化損傷中發揮至關重要的作用[11]。本研究免疫熒光觀察發現,空白組Nrf2主要在細胞質內表達,細胞質內熒光反應明顯增強;當細胞受到H2O2刺激時,機體產生氧化應激反應,細胞質內Nrf2向細胞核內轉移,細胞核內Nrf2熒光反應增強,用海藻多糖對細胞進行預刺激后再進行H2O2誘導,細胞質內Nrf2較正常細胞內明顯增多。與單用H2O2刺激組相比,海藻多糖+H2O2組、海藻多糖組、H2O2+海藻多糖組各項抗氧化指標CGLC、HO-1、NQO1、Nrf2 mRNA相對表達量均明顯增高,海藻多糖組高于海藻多糖+H2O2組和H2O2+海藻多糖組;海藻多糖+H2O2組、海藻多糖組、H2O2+海藻多糖組Keap1 mRNA表達量下降,H2O2+海藻多糖組和海藻多糖+H2O2組高于海藻多糖組,提示海藻多糖抗氧化作用機制可能與Nrf2/Keap1/ARE信號通路激活有關。
綜上所述,海藻多糖可抑制人胚肺成纖維細胞MRC-5的氧化應激損傷,上調 Nrf2表達、激活Nrf2/Keap1/ARE信號通路可能是其作用機制。
[1] Katzanstein AL, Myers JL. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: clinical relevance of pathologic classification[J]. Am J Respir Crit Care Med, 1998,157(4):1301-1315.
[2] 余晶,鮑中英,徐玉敏,等.花青素抗氧化損傷及細胞凋亡的作用研究[J]中西醫結合肝病雜志,2009,19(1):24-26,31.
[3] 胡婷婷.海藻多糖的生物活性研究進展[J].科技視窗,2012(36):17.
[4] Liu D, Sheng J, Li Z, et al. Antioxidant activity of polysaccharide fractions extracted from Athyrium multidentatum (Doll.) Ching[J]. Int J Biol Macromol, 2013(56):1-5.
[5] 秦華.海藻多糖對博來霉素誘導的大鼠肺間質纖維化模型的干預作用研究[J].齊魯藥事,2008,27(9):554-557.
[6] Ananthi S, Raghavendran HR, Sunil AG, et al. In vitroantioxidant and in vivo anti-inflammatory potential of crudepolysaccharide from Turbinaria ornate(Marine Brown Alga)[J]. Food Chem Toxicol, 2010,48(1):187-192.
[7] 馮珍鴿,王力,吳永沛,等.褐藻中巖藻聚糖的化學成分及其對超氧離子的抑制作用[J].食品研究與開發,2010,31(3):66-68.
[8] Wang J, Zhang QB, Zhang ZS, et al. Antioxidant activity of sulfated polysacchari defractions extracted from Laminaria japonica[J]. Int J Biol Macromol, 2008,42(2):127-132.
[9] Deshmukh P, Unni S, Krishnappa G, et al. The Keap1-Nrf2 pathway: promising therapeutic target to counteract ROS-mediated damage in cancers and neurodegenerative diseases[J]. Biophys Rev, 2017,9(1):41-56.
[10] 李研,叢建波,田曉華,等.海藻多糖抑制白細胞呼吸暴發作用研究[J].生物化學與生物理進展,1996,26(2):162-164.
[11] Yu X, Kensler T. Nrf2 as a target for cancer chemoprevention[J]. Mutat Res, 2005,591(1-2):93-102.
Antioxidation of seaweed polysaccharides on H2O2-induced oxidative damage of human embryonic lung fibroblasts MRC-5
LIUHuaman1,LIUXue,JIAXinhua,ZHANGXinyue,ZHANGWei
(1ShandongUniversityofTraditionalChineseMedicine,Jinan250014,China)
國家自然科學基金資助項目(81273704);“泰山學者”建設工程(ts20110819)。
劉驊漫(1986-),女,主治醫師,研究方向為呼吸系統疾病的中西醫結合診斷及治療。E-mail: liuhuaman@126.com
張偉(1963-),男,主任醫師,研究方向為呼吸系統疾病的中西醫結合診斷及治療。E-mail: huxizhijia@126.com
10.3969/j.issn.1002-266X.2017.32.005
R56
A
1002-266X(2017)32-0017-04
2017-04-14)

