近紅外光對重型顱腦損傷患者無創腦監測的臨床意義
黃純 周和平 王紹波 錢志余 施正生
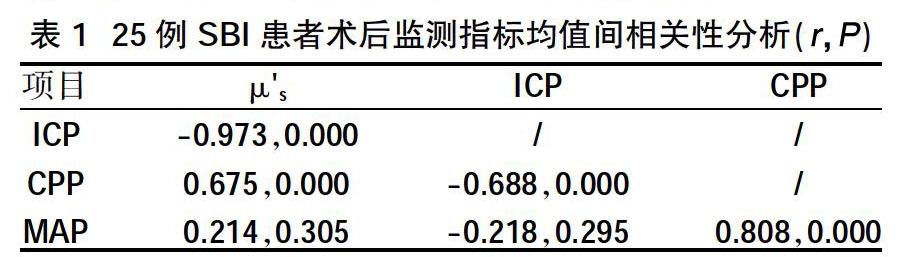
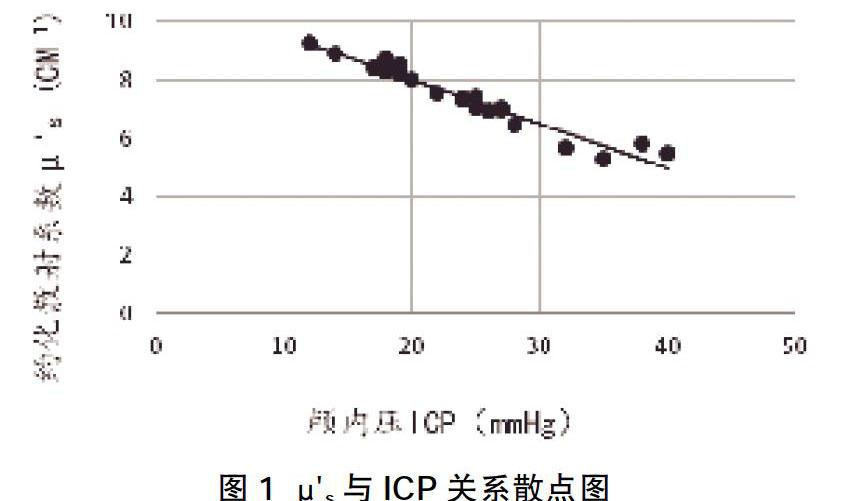
摘 ? 要:目的 ?探討近紅外光譜技術(NIRS)在重型顱腦損傷患者治療過程中實時無創腦監測的可行性。方法 ?采用回顧性病例研究分析2017年12月~2018年6月我院神經外科收治的25例重型顱腦損傷患者臨床資料,使用強生codman顱內壓監護儀及美國ISS公司的NIR Tissure Oximeter系統近紅外光譜分析儀持續監測術后7 d相關指標(約化散射系數、顱內壓、腦灌注壓、平均動脈壓),分析各指標間的相關性;按照患者預后GOS評分分為五組:第1組(1分,4例);第2組(2分,9例);第3組(3分,4例);第4組(4分,4例);第5組(5分,4例),分別比較各組術后第1~7天的μ's。結果 ?μ's與ICP呈顯著負相關(r=-0.973,P<0.05),μ's與CPP呈顯著正相關(r=0.675,P<0.05);μ's與MAP無明顯相關性(r=0.214,P>0.05);不同預后患者,其約化散射系數測量值差異具有統計學意義(P<0.05);從數值上分析,預后較好組,其約化散射系數相對較大;患者術后時間效應分析,對不同組別進行兩兩比較分析,約化散射系數測量值差異具有統計學意義(P<0.05);隨著術后時間的推移,約化散射系數呈上升趨勢;時間與組別交互作用,差異無統計學意義(P>0.05)。結論 ?近紅外光譜技術在無創腦監測領域有著重要的價值,與有創顱內壓監測結果具有良好的一致性,為評估患者預后提供可靠的依據。
關鍵詞:近紅外光譜技術;約化散射系數μ's; 腦灌注;顱內壓;平均動脈壓;
中圖分類號:R651.1+5 ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?文獻標識碼:A ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-1959.2018.24.016
文章編號:1006-1959(2018)24-0063-04
Abstract:Objective ?To explore the feasibility of near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) for real-time non-invasive brain monitoring in patients with severe craniocerebral injury. Methods ?A retrospective case study was conducted to analyze the clinical data of 25 patients with severe craniocerebral injury admitted to our hospital from December 2017 to June 2018. The Johnson & Johnson codman intracranial pressure monitor and the NIR Tissure Oximeter system of ISS USA were used. Near-infrared spectroscopy analyzer continuously monitored the relevant indicators (reduced scattering coefficient, intracranial pressure, cerebral perfusion pressure, mean arterial pressure) at 7 d postoperatively, and analyzed the correlation among the indicators. According to the prognosis GOS score, the patients were divided into five groups: Group 1 (1 point, 4 cases); Group 2 (2 points, 9 cases); Group 3 (3 points, 4 cases); Group 4 (4 points, 4 cases); Group 5 (5 points) , 4 cases), respectively, compared the μ's from the 1st to the 7th day after surgery. Results ?μ's was significantly negatively correlated with ICP (r=-0.973, P<0.05). There was a significant positive correlation between μ's and CPP (r=0.675, P<0.05). There was no significant correlation between μ's ?and MAP (r=0.214, P>0.05); the difference of the measured scattering coefficient of the patients with different prognosis was statistically significant (P<0.05); from the numerical analysis, the prognosis group was relatively large, and the reduced scattering coefficient was relatively large; The postoperative time effect analysis of the patients was carried out by comparing the two groups. The difference of the measured values of the reduced scattering coefficient was statistically significant (P<0.05). With the postoperative time, the reduced scattering coefficient showed an upward trend. Time and group interaction, the difference was not statistically significant (P>0.05). Conclusion ?Near-infrared spectroscopy has important value in the field of non-invasive brain monitoring. It has good consistency with the results of invasive intracranial pressure monitoring, and provides a reliable basis for evaluating the prognosis of patients.

