核苷(酸)類藥物治療HBeAg陽性CHB患者血清HBsAg水平變化Meta分析*
張海月,王魯文,劉菲菲,龔作炯
每年約有65萬人死于HBV感染所致的肝功能衰竭、肝硬化和肝細胞癌(HCC)。抗病毒治療藥物主要有干擾素(interferon,IFN)和核苷(酸)類【nucleos(t)ide analogues,NAs】藥物兩類。研究表明,長期給予NAs抗病毒治療能夠降低CHB患者肝臟相關并發癥,改善臨床結局[1-3]。但NAs治療并不能清除HBV感染,需要長時間的治療以維持病毒復制的抑制。另外,尋找能預測NAs停藥的臨床指標和生物學標志都是亟待解決的問題[4,5]。HBsAg是HBV S基因表達的一種病毒包膜蛋白。HBsAg的合成量遠遠大于病毒裝配所需的量,因此一部分HBsAg以含有病毒核酸的Dane顆粒形式存在,大量過剩的HBsAg被裝配成不含病毒核酸的球形或管形顆粒,從肝細胞釋放入血,以無感染性顆粒的形式存在[6]。HBsAg是反應病毒持續存在的一項穩定的血清學標志,在已獲得病毒學應答的CHB患者血清HBsAg仍持續可被檢測到,而HBsAg的消失可預示有轉錄活性的HBV cccDNA的清除[7-9]。因此,HBsAg持久消失是CHB患者抗病毒理想的治療終點。長效干擾素抗病毒治療患者可在有限的治療時間內實現HBsAg的消失,但發生率較低[10,11]。長期應用NAs治療患者血清HBsAg消失的幾率更小,造成停藥時間不能確定。因此,尋找NAs抗病毒治療過程中預測HBsAg消失的指標非常重要。研究顯示,在抗病毒治療過程中,血清HBsAg水平動態變化對獲得穩定的遠期療效有一定的預測作用。干擾素抗病毒治療12~24周后,血清HBsAg可持續下降,且發生病毒學應答患者血清HBsAg下降較為明顯[12-14]。HBsAg水平變化可用于IFN抗病毒治療療效的預測,而在NAs抗病毒治療過程中,血清HBsAg變化緩慢,對NAs抗病毒療效的預測作用尚未達成一致的意見。研究表明,在NAs抗病毒治療過程中,HBsAg快速下降提示患者最終可能發生HBsAg清除,HBsAg下降≥1 lg IU/mL反映宿主對HBV感染免疫控制能力的提高[15]。本文采用Meta分析法評估了NAs抗病毒治療過程中CHB患者血清HBsAg水平變化是否對HBeAg血清學轉換或/和HBsAg消失有一定的預測價值。
1 資料與方法
1.1 檢索策略 應用計算機檢索2006年1月1日~2016年12月31日PubMed,EMBASE和Cochrane Central Register數據庫中關于血清HBsAg水平與接受NAs抗病毒治療的CHB患者HBeAg血清學轉換關系的臨床研究論文,并檢索相應的參考文獻。文獻檢索策略見表1。
1.2 納入與排除標準 納入標準:①研究類型:RCT文獻;②研究對象為核苷(酸)類治療HBeAg陽性的慢性乙型肝炎患者;③試驗組:HBsAg應答組(1年內,HBsAg下降>1 lg IU/mL),對照組為非HBsAg應答組。排除標準:描述性研究,試驗設計存在診斷標準及評價指標不統一、樣本資料交待不清楚等問題、合并HAV、HCV、HDV、HEV及HIV等感染者、有肝細胞癌者。結局指標:①HBeAg血清學轉換率;②HBsAg消失率;③HBsAg基線水平。
1.3 數據提取與統計學分析 兩名研究者依照Cochrane Handbook進行文獻質量評價。計數資料采用風險比(odds ratio,OR)作為系統評價指標,計量資料則以均數差(mean difference,MD)表示,區間估計采用 95%可信區間(confidence interval,CI),應用Rev 5.2軟件,首先對納入數據進行異質性分析。當P>0.10,I2<50%時,表示數據間無異質性,采用固定效應模型進行Meta分析;當P<0.10,I2>50%表示存在異質性,先分析異質性來源。當無法找到特定的統計學異質性來源時,則采用隨機效應模型分析。采用漏斗圖評估發表偏倚。當P<0.05時,表示兩組間差異有統計學意義。
2 結果
2.1 納入文獻的特點及質量分析 初始檢索到209篇相關文獻,排除重復、非RCT文獻以及非NAs初治患者的文獻,最終有10篇[16-25]被納入。納入研究的特點見表2,納入研究的質量評價見表3。
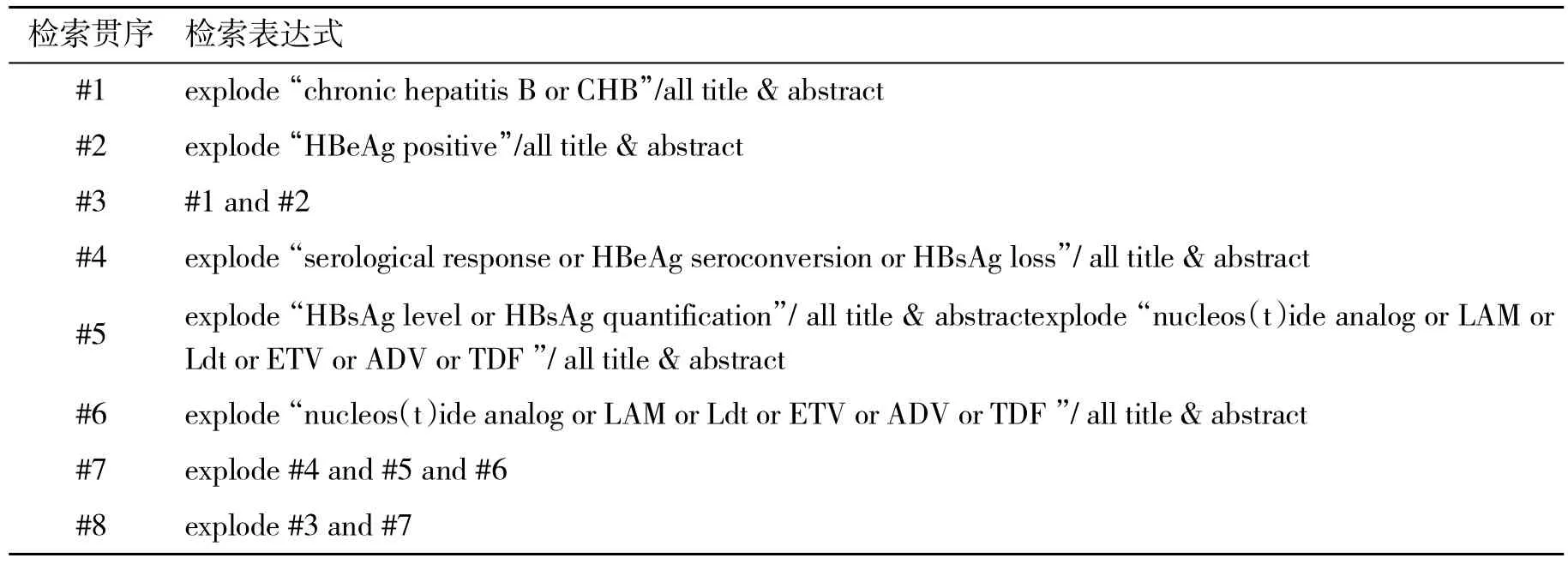
表1 文獻檢索策略

表2 納入研究的一般特征
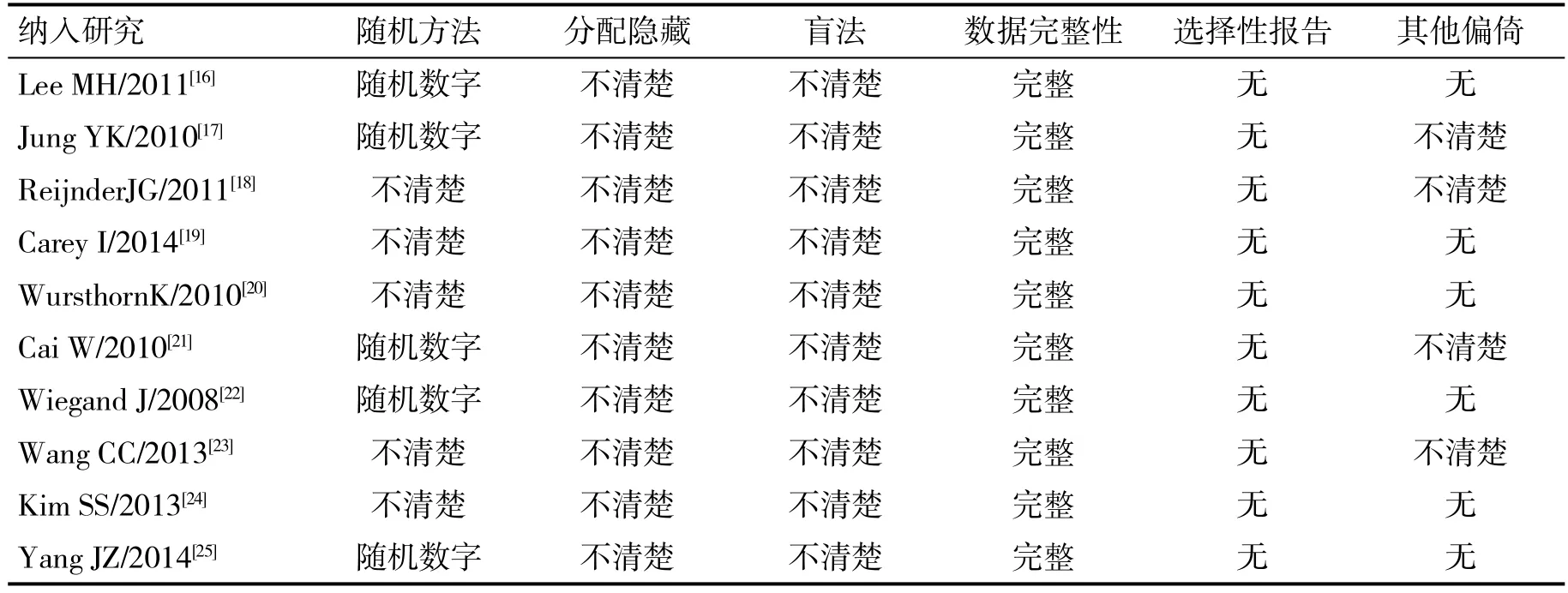
表3 納入研究的質量評價情況
2.2 HBsAg應答與無HBsAg應答患者血清HBeAg血清學轉換率比較 在5項研究[16-18,21,23],包括154例患者,Meta分析顯示,在28例HBsAg應答患者中有18例(64.3%)發生HBeAg血清學轉換,126例非HBsAg應答患者中25例(19.8%)發生HBeAg血清學轉換,差異顯著[OR=6.03,95%CI為(2.55,14.19),P<0.0001,圖1];發表偏倚漏斗圖見圖 2。數據并非嚴格對稱性分布,提示可能存在發表性偏倚。敏感性分析顯示,無論去掉哪一項研究,HBsAg應答組HBeAg血清學轉換率仍顯著高于非HBsAg應答組。
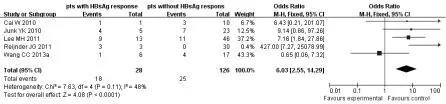
圖1 HBsAg應答組與非HBsAg應答組HBeAg血清學轉換率比較
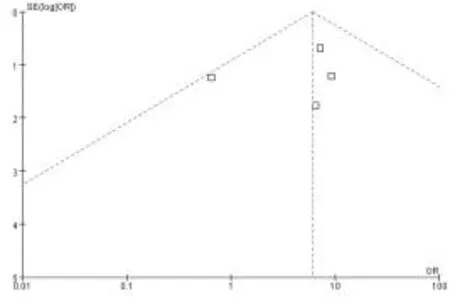
圖2 HBsAg應答組與非HBsAg應答組 HBeAg血清學轉換率發表偏倚漏斗圖
2.3 HBsAg應答組與無HBsAg應答組HBsAg消失率比較 在6項研究[18-23],隨訪300例患者,在59例HBsAg應答患者中有18例(30.5%)發生了HBsAg消失,而在241例非HBsAg應答患者中,只有1例(0.4%)發生了HBsAg消失,差異顯著(OR=34.44,95%CI 為 9.07~130.77,P<0.00001)。發表偏倚漏斗圖顯示數據大致呈對稱性分布,未發現明顯的發表偏倚。
2.4 HBeAg血清學轉換組與HBeAg未轉換組HBsAg 基線水平比較 在 3 篇文獻[16,24,25],包括 143例患者,Meta分析結果顯示,HBeAg血清學轉換組與HBeAg未轉換組HBsAg基線水平【(3.4±0.6)lg IU/mL 對(3.7±0.4)lg IU/mL】相比,無明顯差異[MD=-0.23,95%CI為(-0.83,0.36),P=0.44]。
3 討論
本文評估了HBsAg動態變化對NAs治療HBeAg陽性慢性乙型肝炎患者發生血清學應答的預測價值。結果顯示,發生HBsAg應答即HBsAg早期(1年內)快速下降≥1 lg IU/mL預示有發生HBsAg清除的可能,且與無HBsAg應答者比,出現HBeAg血清學轉換率更高(64.3%對19.8%,P<0.0001),提示NAs治療HBeAg陽性的CHB患者,HBsAg早期快速下降對HBeAg血清學轉換及HBsAg消失都有預測作用。
NAs抗病毒治療可降低HBV感染者肝細胞癌的發生率[26-29]。然而,停藥時間仍是一個尚未解決的重大問題。理想的治療終點即安全的停藥時間是發生HBsAg清除。抗病毒治療后發生HBsAg血清學轉換的CHB 患者有更好的臨床結局[30,31]。NAs抗病毒治療可以實現HBV DNA顯著降低,但HBsAg下降較IFN-α治療者緩慢[32]。NAs抗病毒治療使HBsAg降低的機制尚不明確,但HBsAg下降反應宿主對病毒的免疫控制有了更高的水平,肝內HBV cccDNA水平也降低[33]。
NAs治療后發生HBeAg血清學轉換與未發生HBeAg血清學轉換患者比,治療前HBsAg基線水平并無明顯差異。研究表明,ETV初治患者基線HBsAg水平是抗病毒24個月后發生HBeAg血清學轉換的獨立預測因素[16]。LdT抗病毒治療24周時HBeAg水平優于其他血清學標志物能預測發生HBeAg血清學轉換[37]。ETV治療82例HBeAg陽性CHB患者超過3年,發生HBeAg血清學轉換者較未發生HBeAg血清學轉換患者有較高的基線HBsAg水平,但HBsAg下降明顯[38]。因此,基線HBsAg水平是否對NAs抗病毒治療后HBeAg血清學轉換或HBsAg消失有預測價值,尚需更多大樣本的研究來驗證。
[1]Chang TT,Gish RG,de Man R,et al.A comparison of entecavir and lamivudine for HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B.N Engl J Med,2006,354:1001-1010.
[2]Lai CL,Shouval D,Lok AS,et al.Entecavir versus lamivudine for patients with HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B.N Engl J Med,2006,354:1011-1020.
[3]Heathcote EJ,Marcellin P,Buti M,et al.Three-year efficacy and safety of tenofovir disoproxil fumarate treatment for chronic hepatitis B.Gastroenterology,2011,140:132-143.
[4]Marcellin P,Heathcote EJ,ButiM,etal.Tenofovirdisoproxil fumarate versus adefovir dipivoxil for chronic hepatitis B.N Engl J Med,2008,359:2442-2455.
[5]Thompson AJ,Nguyen T,Iser D,et al.Serum hepatitis B surface antigen and hepatitis B e antigen titers:disease phase influences correlation with viral load and intrahepatic hepatitis B virus markers.Hepatology,2010,51:1933-1944.
[6]Nguyen T,Desmond P,Locarnini S.The role of quantitative hepatitis B serology in the natural history and management of chronic hepatitis B.Hepatol Int,2009,3:5-15.
[7]Raimondo G,Brunetto MR,Pontisso P,et al.Longitudinal evaluation reveals a complex spectrum of virological profiles in hepatitis B virus/hepatitis C virus-coinfected patients.Hepatology,2006,43:100-107.
[8]Werle-Lapostolle B,Bowden S,Locarnini S,et al.Persistence of cccDNA during the natural history of chronic hepatitis B and decline during adefovir dipivoxil therapy.Gastroenterology,2004,126:1750-1758.
[9]Pichoud C,Berby F,Stuyver L.Persistence of viral replication after anti-HBe seroconversion during antiviral therapy for chronic hepatitis B.J Hepatol,2000,32:307-316.
[10]Janssen HL,van Zonneveld M,Senturk H,et al.Pegylated interferon alfa-2b aloneorin combination with lamivudine for HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B:a randomised trial.Lancet,2005,365:123-129.
[11]Lau GK,Piratvisuth T,Luo KX,etal.Peginterferon alfa-2a HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B study group.Peginterferon alfa-2a,lamivudine,and the combination for HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B.N Engl J Med,2005,352:2682-2695.
[12]Gish RG,Lau DT,Schmid P,et al.A pilot study of extended duration peginterferon alfa-2a for patients with hepatitis B e antigen-negative chronic hepatitis B.Am J Gastroenterol,2007,102:2718-2723.
[13]Manesis EK,Hadziyannis ES,Angelopoulou OP,et al.Prediction of treatment-related HBsAg loss in HBeAG-negative chronic hepatitis B:a clue from serum HBsAg levels.Antivir Ther,2007,12:73-82.
[14]Lee JM,Ahn SH,Kim HS,et al.Quantitative hepatitis B surface antigen and hepatitis B e antigen titers in prediction of treatment response to entecavir.Hepatology,2011,53:1486-1493.
[15]Tseng TC,Kao JH.Clinical utility of quantitative HBsAg in natural history and nucleos(t)ide analogue treatment of chronic hepatitis B:new trick of old dog.J Gastroenterol,2013,48(1):13-21.
[16]Lee MH,Lee da M,Kim SS,et al.Correlation of serum hepatitis B surface antigen level with response to entecavir in naive patients with chronic hepatitis B.J Med Virol,2011,83:1178-1186.
[17]Jung YK,Kim JH,Lee YS,et al.Change in serum hepatitis B surface antigen level and its clinical significance in treatment-naive,hepatitis Be antigen-positive patients receiving entecavir.J Clin Gastroenterol,2010,44(9):653-657.
[18]Reijnders JG,Rijckborst V,Sonneveld MJ,et al.Kinetics of hepatitis B surface antigen differ between treatment with peginterferon and entecavir.J Hepatol,2011,54:449-454.
[19]Carey I,Bruce M,Horner M,et al.HBsAg plasma level kinetics:a new role for an old marker as a therapy response predictor in vertically infected children on combination therapy.J Viral Hepat,2015,22:441-452.
[20]Wursthorn K,Jung M,Riva A,et al.Kinetics of hepatitis B surface antigen decline during 3 years of telbivudine treatment in hepatitis B e antigen-positive patients.Hepatology,2010,52:1611-1620.
[21]Cai W,Xie Q,An B,et al.On-treatment serum HBsAg level is predictive of sustained off-treatment virologic response to telbivudine in HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B patients.J Clin Virol,2010,48:22-26.
[22]Wiegand J,Wedemeyer H,Finger A,et al.A decline in hepatitis B virus surface antigen(HBsAg) predicts clearance,but does not correlate with quantitative HBeAg or HBV DNA levels.Antivir Ther,2008,13:547-554.
[23]Wang CC,Tseng TC,Wang PC,et al.Baseline hepatitis B surface antigen quantitation can predict virologic response in entecavir-treated chronic hepatitis B patients.J Formos Med Assoc,2014,113:786-793.
[24]Kim SS,Lee D,Lee MH,etal.Association of on-treatment serum hepatitis B surface antigen level with sustained virological response to nucleos(t)ide analog in patients with hepatitis B e-antigen positive chronic hepatitis B.Hepatol Res,2013,43:219-227.
[25]Yang J,Chen J,Ye P,et al.HBsAg as an important predictor of HBeAg seroconversion following antiviral treatment for HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B patients.J Transl Med,2014,12:183.
[26]Marcellin P,Gane E,Buti M,et al.Regression of cirrhosis during treatmentwith tenofovirdisoproxilfumarate forchronic hepatitis B:a 5-year open-labelfollow-up study.Lancet,2013,381:468-475.
[27]Chang TT,Liaw YF,Wu SS,et al.Long-term entecavir therapy results in the reversal of fibrosis/cirrhosis and continued histological improvement in patients with chronic hepatitis B.Hepatology,2010,52:886-893.
[28]Papatheodoridis GV,Lampertico P,Manolakopoulos S,et al.Incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma in chronic hepatitis B patients receiving nucleos (t)ide therapy:a systematic review.J Hepatol,2010,53:348-356.
[29]Hosaka T,Suzuki F,Kobayashi M,et al.Long-term entecavir treatment reduces hepatocellular carcinoma incidence in patients with hepatitis B virus infection.Hepatology,2013,58:98-107.
[30]Chen YC,Sheen IS,Chu CM,et al.Prognosis following spontaneous HBsAg seroclearance in chronic hepatitis B patients with or without concurrent infection. Gastroenterology,2002,123:1084-1089.
[31]Yuen MF,Wong DK,Sablon E,et al.HBsAg seroclearance in chronic hepatitis B in the Chinese:virological,histological,and clinical aspects.Hepatology,2004,39:1694-1701.
[32]Moucari R,Mackiewicz V,Lada O,et al.Early serum HBsAg drop:a strong predictor of sustained virological response to pegylated interferon alfa-2a in HBeAg-negative patients.Hepatology,2009,49:1151-1157.
[33]Manesis EK,Papatheodoridis GV,Tiniakos DG,et al.Hepatitis B surface antigen:relation to hepatitis B replication parameters in HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B.J Hepatol,2011,55:61-68.
[34]Sonneveld MJ,Rijckborst V,Boucher CA,et al.Prediction of sustained response to peginterferon alfa-2b for hepatitis B e antigen-positive chronic hepatitis B using on-treatment hepatitis B surface antigen decline.Hepatology,2010,52:1251-1257.
[35]Jaroszewicz J,Ho H,Markova A,et al.Hepatitis B surface antigen(HBsAg) decrease and serum interferon-inducible protein-10 levels as predictive markers for HBsAg loss during treatment with nucleoside/nucleotide analogues.Antivir Ther,2011,16:915-924.
[36]Brunetto MR,Moriconi F,Bonino F,et al.Hepatitis B virus surface antigen levels:a guide to sustained response to peginterferon alfa-2a in HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B.Hepatology,2009,49:1141-1150.
[37]Wang J,Du LY,Zhu X,et al.The predictive value of early indicators for HBeAg seroconversion in HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B patients with Telbivudine treatment for 104 weeks.Indian J Med Microbiol,2015,33(Suppl 1):20-25.
[38]Shin JW,Jung SW,Park BR,et al.Prediction of response to entecavir therapy in patients with HBeAgpositive chronic hepatitis B based on on-treatment HBsAg,HBeAg and HBV DNA levels.J Viral Hepat,2012,19:724-731.

