護理干預對2型糖尿病患者自我護理能力及生活質量的影響
王斌
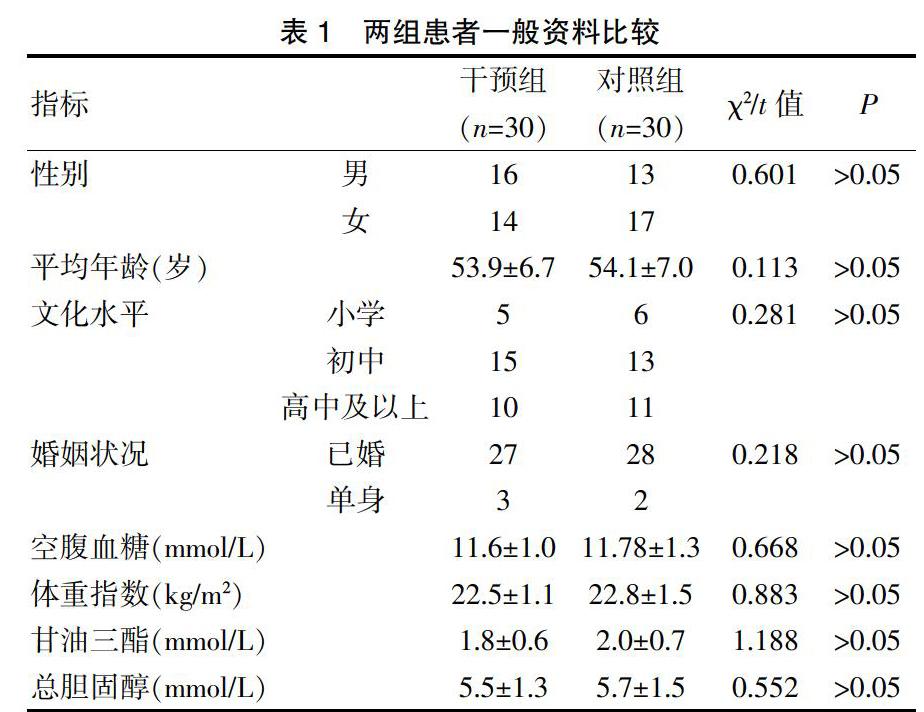
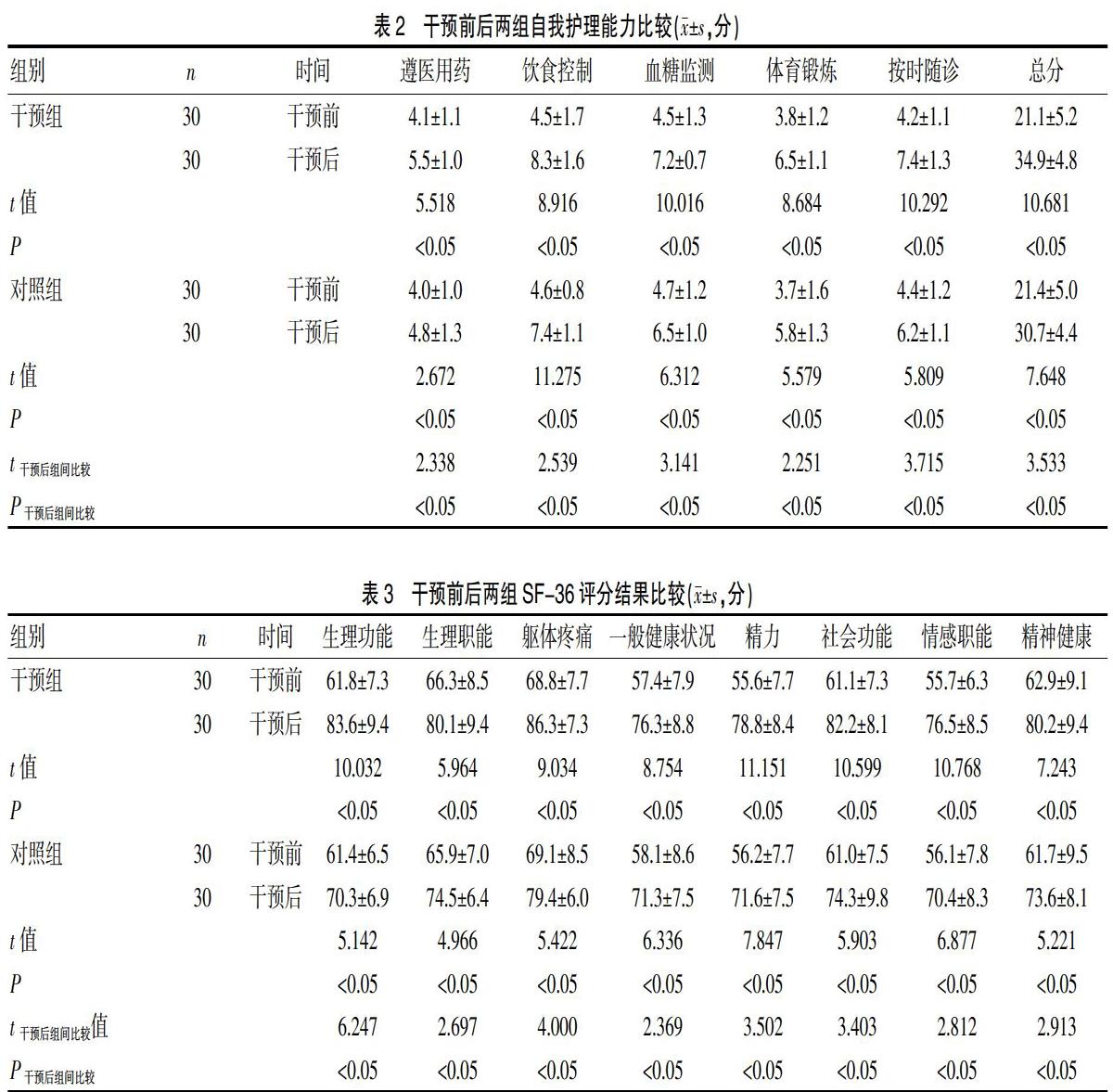
[摘要] 目的 探討護理干預對2型糖尿病患者自我護理能力及生活質量的影響。 方法 選擇2018年7~12月在我院診斷治療的2型糖尿病患者60例為研究對象,隨機分為干預組與對照組,各30例。對照組給予常規處理,干預組給予針對性護理干預。分別于干預前及干預后1個月采用自我管理量表對患者自我護理能力進行評價,采用SF-36量表對患者生活質量進行評價,比較兩組干預前及干預后1個月自我護理能力、生活質量。 結果 干預后兩組自我護理能力均顯著提高,與干預前比較,差異有統計學意義(P<0.05);干預后,干預組自我護理能力顯著高于對照組,差異有統計學意義(P<0.05)。干預后,兩組SF-36各維度得分均顯著高于干預前,差異有統計學意義(P<0.05);干預后,干預組SF-36評分顯著高于對照組,差異有統計學意義(P<0.05)。 結論 護理干預能夠顯著提高2型糖尿病患者的自我護理能力,改善患者生活質量。
[關鍵詞] 護理干預;2型糖尿病;自我護理能力;生活質量
[中圖分類號] R473.5? ? ? ? ? [文獻標識碼] B? ? ? ? ? [文章編號] 1673-9701(2019)33-0146-04
[Abstract] Objective To explore the effect of nursing intervention on self-nursing ability and quality of life in patients with type 2 diabetes. Methods A total of 60 patients with type 2 diabetes diagnosed and treated in our hospital from July to December 2018 were enrolled in the study. They were randomly divided into intervention group and control group, with 30 cases in each group. The control group was given routine treatment and the intervention group was given targeted nursing intervention. The self-management scale was used to evaluate self-nursing ability, and the SF-36 scale was used to evaluate the patient's quality of life before and after 1 month of the intervention. The self-nursing ability and quality of life before and after the intervention were compared between the two groups. Results After the intervention, the self-nurising ability of the two groups was significantly improved, and the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05). After the intervention, the self-care ability of the intervention group was significantly higher than that of the control group, and the difference was statistically significant(P<0.05). After the intervention, the scores of SF-36 in each dimension were significantly higher than those before intervention, and the difference was statistically significant(P<0.05). After the intervention, the SF-36 score of the intervention group was significantly higher than that of the control group, and the difference was statistically significant(P<0.05). Conclusion Nursing intervention can significantly improve the self-nursing ability of patients with type 2 diabetes and improve their quality of life.
[Key words] Nursing intervention; Type 2 diabetes; Self-care ability; Quality of life
中國是全球糖尿病患病人數最多的國家,過去30年,中國糖尿病患病率急劇增加,從1980年的不到1%,到2013年的10.9%,老年人、男性、城市居民、經濟發達地區居民、超重、肥胖者是高發人群[1,2]。環境因素,包括患者飲食模式、生活方式是糖尿病重要的危險因素。因此,患者良好的自我護理能力有利于患者執行健康飲食模式,改善生活方式,進而提高糖尿病控制水平,提高生活質量[3,4]。護理干預是基于一定科學理論,在護理診斷的指導下,按事先預定的干預方法從事的一系列護理活動[5,6]。患者的健康決定干預類型,干預措施有助于幫助患者達到預定目標,促進康復,預防并發癥發生。本研究對2型糖尿病患者實施護理干預,觀察患者自我護理能力及生活質量的改善情況,以期為臨床護理提供參考。
綜上所述,護理干預能夠顯著提高2型糖尿病患者的自我護理能力,改善患者生活質量。
[參考文獻]
[1] 張波,楊文英. 中國糖尿病流行病學及預防展望[J].中華糖尿病雜志,2019,11(1):7-10.
[2] 朱大龍. 十年磨一劍:中國糖尿病研究進展及思考(Ⅰ)[J]. 中華糖尿病雜志,2019,11(1):1-6.
[3] 趙子煜,高志娟,陸嘉燕,等. 目視健康管理對2型糖尿病患者自我管理能力及行為的影響研究[J]. 中國全科醫學,2019,22(13):1603-1607.
[4] 王思琛,張正平,胡麗莖,等. 2型糖尿病職場工作者的自我效能與情緒困擾的相關性[J]. 護理研究,2019,33(7):1240-1243.
[5] 盧璐璐,陳瓊妮,羅碧華. 正念干預應用于糖尿病患者管理的研究進展[J]. 中國護理管理,2019,19(1):128-132.
[6] 劉宇飛,李閨臣,華珊珊,等. 問題解決療法在國外糖尿病病人中的研究進展[J].護理研究,2019,33(7):1153-1157.
[7] 葛均波,徐永健. 內科學[M]. 第8版. 北京:人民衛生出版社, 2013:733.
[8] 李超群. 糖尿病患者自我管理量表的漢化及信效度評價[D]. 河北大學,2018.
[9] Ware JE,Sherbourne CD. The MOS 36-item short-from health survery(SF-36):Conceptual framework and item selection[J]. Medical Care,1992,(30):473.
[10] 蘆燕,蘆莉. 飲食護理干預對糖尿病腎病病人飲食治療依從性及營養狀況的影響[J]. 首都食品與醫藥,2019, 26(2):135.
[11] 林偉,梅陽陽,林麗娜. 延續護理干預對糖尿病足患者自我管理能力的影響[J]. 廣西中醫藥大學學報,2019, 22(1):91-94.
[12] 盧璐璐,陳瓊妮,羅碧華. 正念干預應用于糖尿病患者管理的研究進展[J]. 中國護理管理,2019,19(1):128-132.
[13] 施燕麗. 護理干預用于ICU內高血壓合并糖尿病患者效果分析[J].糖尿病新世界,2019,22(5):125-126.
[14] 韓云梅. 整體護理干預在妊娠期糖尿病患者中的應用觀察[J]. 中國藥物與臨床,2019,19(3):519-521.
[15] 韓雪. 全程護理干預對冠心病合并糖尿病患者的效果觀察[J]. 糖尿病新世界,2019,22(5):142-143.
(收稿日期:2019-08-07)

