目標性功能訓練對腦出血術后患者神經功能、認知功能、肢體運動功能和生活質量的影響
徐萍
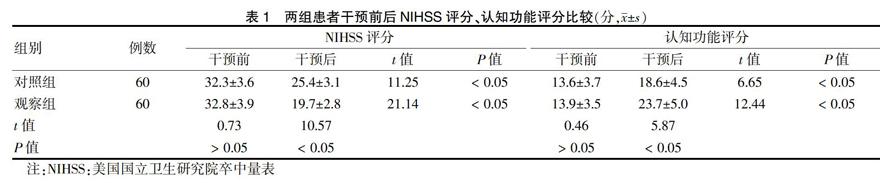
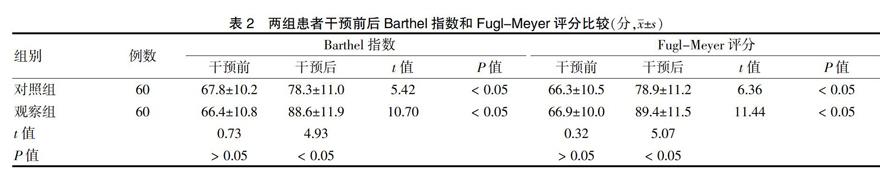

[摘要] 目的 探討目標性功能訓練對腦出血術后患者神經功能、認知功能、肢體運動功能和生活質量的影響。方法 選取浙江省永康市第一人民醫院2016年1月~2018年1月收治的腦出血患者120例,根據隨機紙片法進行分組,對照組(60例)患者采用常規性康復訓練,觀察組(60例)患者采用目標性功能訓練。實施訓練干預前后,兩組患者進行美國國立衛生研究卒中量表(NIHSS)評分、認知功能評分、Barthel指數、Fugl-Meyer評分、生活質量、日常活動能力(ADL)評分和療效評價。 結果 干預前,兩組NIHSS評分、認知功能評分、Barthel指數、Fugl-Meyer評分、生活質量和ADL評分比較,差異無統計學意義(P > 0.05);干預后,兩組NIHSS評分均低于干預前,認知功能評分、Barthel指數、Fugl-Meyer評分、生活質量和ADL評分均高于干預前,且觀察組NIHSS評分低于對照組,認知功能評分、Barthel指數、Fugl-Meyer評分、生活質量和ADL評分高于對照組,差異有統計學意義(P < 0.05)。觀察組臨床治療總有效率高于對照組,差異有統計學意義(P < 0.05)。 結論 目標性功能訓練在腦出血患者中實施,神經功能、認知功能、肢體運動功能和生活質量均可獲得改善,從而提高預后水平,值得臨床推廣應用。
[關鍵詞] 目標性功能訓練;腦出血;神經功能;認知功能;肢體運動功能;生活質量
[中圖分類號] R743.34 ? ? ? ? ?[文獻標識碼] A ? ? ? ? ?[文章編號] 1673-7210(2019)06(c)-0177-04
Influence of targeted functional training on the neural function, cognitive function, body movement function and life quality of hematencephalon patients after operation
XU Ping
Medical Examination Center, the First People′s Hospital in Yongkang City, Zhejiang Province, Yongkang ? 321300, China
[Abstract] Objective To approach the influence of targeted functional training on the neural function, cognitive function, body movement function and life quality of hematencephalon patients after operation. Methods A total of 120 patients with hematencephalon in the First People′s Hospital in Yongkang City of Zhejiang Province from January 2016 to January 2018 was selected, and they were grouped by random paper method, patients in control group (60 cases) were given regular rehabilitation training, and patients in observation group (60 cases) were given targeted functional training. The NIHSS score, cognitive function score, Barthel index, Fugl-Meyer score, life quality, ADL score and therapeutic effect of two groups before and after training intervention were evaluated. Results Before intervention, there was no statistically significant difference in the NIHSS score, cognitive function score, Barthel index, Fugl-Meyer score, life quality and ADL score between the two groups (P > 0.05). After intervention, the NIHSS scores of the two groups were lower than before intervention, the cognitive function score, Barthel index, Fugl-Meyer score, life quality and ADL score were higher than before intervention, and the NIHSS score of observation group was lower than that of control group, the cognitive function score, Barthel index, Fugl-Meyer score, life quality and ADL score of observation group were higher than those of control group, the differences were statistically significant (P < 0.05). The total clinical efficiency of observation group was higher than that of control group, the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.05). Conclusion The implementation of targeted functional training in hematencephalon patients, could improve the neural function, cognitive function, body movement function and life quality, increase prognostic level, it is worthy of clinical application.

