不同身份參與羊水栓塞原位情景模擬教學(xué)的效果及運用
肖靜 周志強(qiáng) 曹雪芹 錢巍 張志發(fā) 羅放
[摘要] 目的 探討在原位模擬教學(xué)中以不同身份參與教學(xué)的麻醉醫(yī)生對圍術(shù)期羊水栓塞的識別和處理能力及效果。方法 于2019年3月在我院參加麻醉科住院醫(yī)師規(guī)范化培訓(xùn)的二年級、三年級住院醫(yī)師,以及進(jìn)修醫(yī)生中招募29名學(xué)員參加模擬教學(xué),綜合教學(xué)前理論考核成績和個人意愿分組分工,其中病例操作組12人,觀察評價組17人。病例操作組學(xué)員參加Simman 3G模擬人的羊水栓塞原位情景模擬病例運行,觀察評價組學(xué)員作為觀察者對操作組學(xué)員團(tuán)隊的操作對照教學(xué)目標(biāo)評價表進(jìn)行評價。比較兩組操作前理論考核成績、教學(xué)滿意度反饋評價、模擬教學(xué)效果反饋評價、學(xué)習(xí)后理論知識復(fù)測成績。 結(jié)果 以不同身份體驗開展模擬教學(xué),兩組學(xué)員在教學(xué)后理論成績均明顯高于教學(xué)前,差異有統(tǒng)計學(xué)意義(P<0.05),但組間差異無統(tǒng)計學(xué)意義。100.0%的學(xué)員對原位情景模擬教學(xué)表示滿意,對教學(xué)方法表示認(rèn)可;96.3%的學(xué)員認(rèn)為該教學(xué)方法達(dá)到或超過預(yù)期效果;100.0%的學(xué)員認(rèn)為該教學(xué)方法可以加深理論知識和處理流程的掌握、提高處理突發(fā)事件的溝通能力和團(tuán)隊合作能力。 結(jié)論 原位情景模擬羊水栓塞的教學(xué)方法是一種可行、有效的教學(xué)方法,觀察評價者同樣能夠通過直觀地感受病例、分析病例,參與教學(xué)評價,收獲很好的教學(xué)效果。
[關(guān)鍵詞] 原位情景模擬教學(xué);羊水栓塞;不同身份參與;Simman 3G
[中圖分類號] G642;R47-4 ? ? ? ? ?[文獻(xiàn)標(biāo)識碼] B ? ? ? ? ?[文章編號] 1673-9701(2020)30-0009-05
Effects and applications of in-situ scenario simulation teaching of amniotic fluid embolism participates with different identities
XIAO Jing ? ZHOU Zhiqiang ? CAO Xueqin ? QIAN Wei ? ZHANG Zhifa ? LUO Fang
Department of Anesthesiology, Tongji Hospital, Tongji Medical College of Hust Tongji Medical College Huazhong University of Science & Technology, Wuhan ? 430030, China
[Abstract] Objective To investigate the recognitions, treatment abilities and effects of anesthesiologists who participated in in-situ scenario simulation teaching of perioperative amniotic fluid embolism with different identities. Methods In March 2019, a total of 29 students were recruited from the second-year and third-year residents and refresher doctors who participated in the standardized training of anesthesiology residents admitted to our hospital to participate in the simulation teaching, and the theoretical assessment scores and personal wishes before the teaching were divided into the case operators group(n=12) and the observation evaluators group(n=17). Students in the case operators group were organized to participate in Simman 3G simulated amniotic fluid embolism in-situ scenario simulation case operation. Students in observation evaluators group, as observers, were organized to evaluate the operation control teaching objective evaluation table of students in the case operators group. The scores of theoretical examinations before operation, feedback evaluation of teaching satisfaction, feedback evaluation of simulated teaching effect and retest scores of theoretical knowledge after learning were compared between the two groups. Results With different identity experiences, the theoretical scores of the two groups were obviously higher than those before teaching, and the difference was statistically significant(P<0.05), but there was no difference between the two groups. 100.0% of the students were satisfied with the in-situ scenario simulation teaching and the teaching method was approved. 96.3% of the students thought that the teaching method achieved or exceeded the expected effect. 100.0% of the students thought that this teaching method could deepen the mastery of theoretical knowledge and processing flow, and improve the communication ability and teamwork ability in dealing with emergencies. Conclusion In-situ scenario simulation of amniotic fluid embolism is a feasible and effective teaching method, and observers and evaluators also feel cases intuitively, analyze cases, participate in teaching evaluation, and gain good teaching results.
[Key words] In-situ scenario simulation teaching; Amniotic fluid embolism; Participation with different identities; Simman 3G
羊水栓塞(Amniotic fluid embolism,AFE)是妊娠期特有的罕見并發(fā)癥,可以導(dǎo)致母兒死亡等災(zāi)難性后果,其發(fā)病率為(1.9~6.1)/10萬,死亡率可達(dá)19%~86%[1]。麻醉科作為急危重癥患者搶救的平臺科室,是急危重癥產(chǎn)婦搶救醫(yī)療團(tuán)隊的重要一員。由于羊水栓塞病例散發(fā)、少發(fā),臨床醫(yī)生很難通過實踐積累足夠豐富的經(jīng)驗來應(yīng)對[2],麻醉醫(yī)生更難積累足夠經(jīng)驗。然而,臨床工作要求麻醉醫(yī)生必須熟知這類罕見并發(fā)癥。臨床研究發(fā)現(xiàn),有經(jīng)驗的麻醉醫(yī)生可能在改善羊水栓塞產(chǎn)婦預(yù)后中發(fā)揮重要作用[3]。
有研究[4-5]報道,情景模擬訓(xùn)練可以提高臨床醫(yī)務(wù)人員技能、臨床思維以及非技術(shù)性技能,如團(tuán)隊合作等,從而改善患者的預(yù)后。且這種教學(xué)方法已在產(chǎn)科、麻醉、手術(shù)、口腔、急救創(chuàng)傷、護(hù)理等多科室多層面廣泛開展,效果顯著[6-9]。而原位模擬(In situ simulation),是將訓(xùn)練空間從模擬仿真實驗室到真實的臨床工作空間的一種情景模擬演練。其通過提供真實的環(huán)境,熟悉的同事團(tuán)隊,學(xué)習(xí)者代入感強(qiáng),更易進(jìn)入演練的角色,也更容易發(fā)現(xiàn)日常工作中的流程、設(shè)備、操作及協(xié)作的缺陷[10-11]。
本研究采用Simman 3G模擬人系統(tǒng)在手術(shù)間內(nèi)進(jìn)行圍術(shù)期羊水栓塞的原位模擬教學(xué),學(xué)員以不同身份,病例操作者和觀察評價者兩種身份體驗情景教學(xué),評價其對學(xué)生成績的影響及其在教學(xué)中的效果,現(xiàn)報道如下。
1 資料與方法
1.1 一般資料
選取于2019年3月在我院參加麻醉科住院醫(yī)師規(guī)范化培訓(xùn)的二年級、三年級住院醫(yī)師,以及進(jìn)修醫(yī)生中招募有意向參與模擬教學(xué)的學(xué)員。根據(jù)報名順序共納入學(xué)員29人,其中住院醫(yī)師20人,進(jìn)修醫(yī)生9人。培訓(xùn)前,通過問卷星自制調(diào)查試卷,對報名學(xué)員進(jìn)行圍術(shù)期危機(jī)事件的理論考核,根據(jù)理論考核成績分配為實力相對均衡的三組分批參與病例運行,由組內(nèi)學(xué)員自行組建4人操作小組為病例操作組,其余學(xué)員為觀察評價組。實際參與病例操作者12人,觀察評價者17人。
1.2 方法
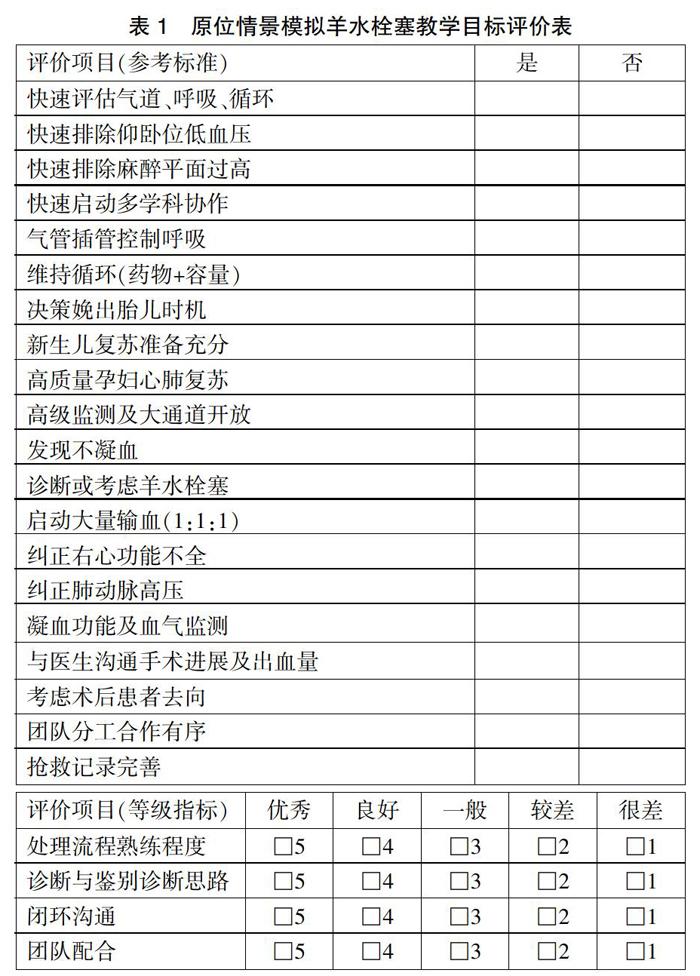
病例操作組學(xué)員參加Simman 3G綜合模擬人(挪威Laerdal公司出品)羊水栓塞病例的原位情景模擬。病例運行時間為10 min。觀察評價組學(xué)員作為觀察者對操作組學(xué)員團(tuán)隊的操作對照教學(xué)目標(biāo)評價表進(jìn)行評價,見表1。病例運行結(jié)束后該組所有學(xué)員均由一位導(dǎo)師進(jìn)行Debriefing,對學(xué)員進(jìn)行反饋。三組學(xué)員分三個時段分別單獨進(jìn)行病例運行和反饋。三次病例運行均由同一個教學(xué)團(tuán)隊同品質(zhì)完成,每次教學(xué)相對獨立,不同時間段的學(xué)員信息零溝通。教學(xué)場地為華中科技大學(xué)同濟(jì)醫(yī)學(xué)院附屬同濟(jì)醫(yī)院麻醉科手術(shù)室。
1.3 觀察指標(biāo)
包括操作前理論考核成績、操作中教學(xué)目標(biāo)完成評價(老師對操作評價和學(xué)員對操作評價)、教學(xué)滿意度反饋評價、模擬教學(xué)效果反饋評價、學(xué)習(xí)后理論知識復(fù)測成績。教學(xué)目標(biāo)根據(jù)教學(xué)主題,由教學(xué)導(dǎo)師團(tuán)隊,針對教學(xué)對象設(shè)置,并對教學(xué)目標(biāo)進(jìn)行細(xì)化,見表1,用于教學(xué)中目標(biāo)完成評價。教學(xué)滿意度評價包括教學(xué)準(zhǔn)備工作、培訓(xùn)講師、教學(xué)內(nèi)容、整體滿意度評價。而教學(xué)效果評價除了學(xué)習(xí)后理論知識復(fù)測考核,還包括學(xué)員參與模擬教學(xué)后的主觀評價和感受。
1.4 統(tǒng)計學(xué)方法
采用SPSS23.0統(tǒng)計學(xué)軟件進(jìn)行數(shù)據(jù)分析。計量資料以均數(shù)±標(biāo)準(zhǔn)差(x±s)表示,組間比較采用t檢驗。P<0.05為差異有統(tǒng)計學(xué)意義。
2 結(jié)果
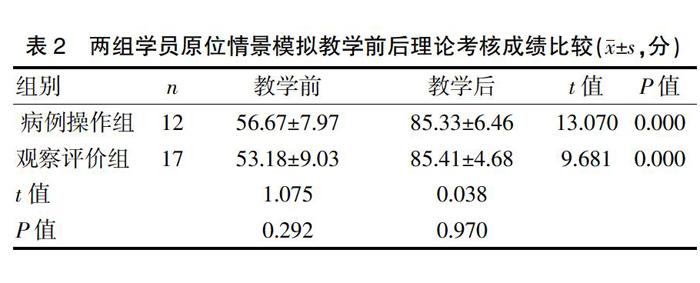
2.1 兩組學(xué)員原位情景模擬教學(xué)前后學(xué)員理論考核成績比較
為保障情景模擬教學(xué)質(zhì)量,實際操作人數(shù)不宜過多,每輪操作者為4人,共有病例操作者12人,余者為觀察評價者,共17人。兩組學(xué)員教學(xué)前的理論考核成績比較,差異無統(tǒng)計學(xué)意義(P>0.05),兩組學(xué)員教學(xué)后理論考核成績比較,差異無統(tǒng)計學(xué)意義(P>0.05)。經(jīng)情景模擬教學(xué)后,整體學(xué)員的理論成績較教學(xué)前顯著提高。見表2。
2.2原位情景模擬教學(xué)目標(biāo)評價結(jié)果
根據(jù)教學(xué)目標(biāo)設(shè)定具體的操作評價項目,由導(dǎo)師團(tuán)隊及觀察者共同進(jìn)行整體評價。共收到教學(xué)目標(biāo)評價表25份(導(dǎo)師評價8份和學(xué)員評價17份)。第二組的病例操作表現(xiàn)相對較弱,而各組病例運行中認(rèn)為在“診斷與鑒別診斷的思路”一項上表現(xiàn)明顯不足。根據(jù)教學(xué)目標(biāo)評價表的結(jié)果,可以有針對性地進(jìn)行反饋。見表3。
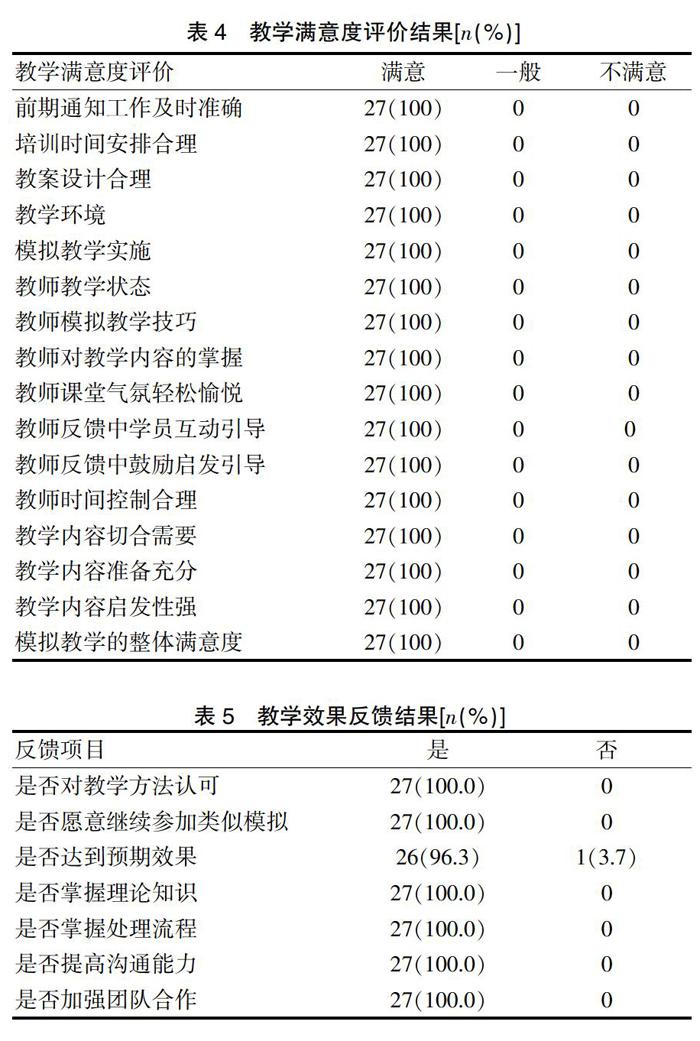
2.3原位情景模擬教學(xué)滿意度評價結(jié)果
從教學(xué)準(zhǔn)備工作(前期準(zhǔn)備;培訓(xùn)時間安排;教案設(shè)計;教學(xué)環(huán)境;教學(xué)實施)、培訓(xùn)講師(教學(xué)狀態(tài);模擬教學(xué)技巧;教師對教學(xué)內(nèi)容的掌握;課堂氣氛;反饋過程中互動;反饋過程中鼓勵學(xué)員參與,啟發(fā)學(xué)員思考;時間控制)、教學(xué)內(nèi)容(與臨床工作及個人需求緊密聯(lián)系;教學(xué)內(nèi)容準(zhǔn)備充分,邏輯嚴(yán)密;教學(xué)內(nèi)容啟發(fā)性強(qiáng))和整體滿意度四大方面16個細(xì)節(jié)進(jìn)行教學(xué)滿意度的評價。29位學(xué)員實際回收評價表27份,回收率93.1%,各項滿意度評價指標(biāo),包括整體滿意度均達(dá)到100%。見表4。
2.4 教學(xué)效果反饋結(jié)果
教學(xué)結(jié)束后,對教學(xué)效果進(jìn)行反饋,共收到反饋表27份,回收率93.1%,見表5。參與反饋的學(xué)員中,100.0%的學(xué)員對原位情景模擬教學(xué)方法表示認(rèn)可,并愿意繼續(xù)參加類似模擬訓(xùn)練;96.3%的學(xué)員認(rèn)為該教學(xué)方法達(dá)到或超過預(yù)期效果,1名操作者表示培訓(xùn)效果低于預(yù)期,理由是作為操作者時間比較緊張,未能很好進(jìn)入角色,影響了培訓(xùn)效果;100.0%的學(xué)員認(rèn)為該教學(xué)方法可以加深理論知識和處理流程的掌握、提高處理突發(fā)事件的溝通能力和團(tuán)隊合作能力。進(jìn)一步對模擬教學(xué)效果的首要影響因素進(jìn)行分析,55.56%的學(xué)員(15/27)認(rèn)識到團(tuán)隊合作影響模擬教學(xué)效果;22.22%的學(xué)員(6/27)認(rèn)為理論知識儲備不足影響模擬教學(xué)效果。見表6。
3 討論
Simman 3G模擬人由于其仿真性高、反饋性好,能夠有效開展臨床基本技能培訓(xùn)[9,12-14]。然而模擬人只能按照設(shè)定的程序開展簡單的人機(jī)對話,還不能滿足綜合臨床勝任力的提高,如臨床思維能力、溝通交流能力、應(yīng)急能力以及團(tuán)隊、學(xué)科間協(xié)作能力等,因此需要帶入情境中。情景模擬教學(xué)是連接臨床教學(xué)與臨床實踐之間的橋梁,可以訓(xùn)練學(xué)員的臨床操作技能、臨床思維能力,培養(yǎng)高效協(xié)調(diào)的團(tuán)隊合作能力,并對學(xué)員及其團(tuán)隊的能力進(jìn)行綜合考核和評估[4-9]。基于Simman 3G的情景模擬教學(xué)已經(jīng)成為現(xiàn)代臨床教學(xué)的重要手段。而原位情景模擬,教學(xué)場景從仿真實驗室走向現(xiàn)實,其教學(xué)內(nèi)容更豐富、形式更新穎生動、場景更逼真,能給學(xué)員們更感性、更直觀的認(rèn)識,更能滿足學(xué)員們對臨床病例多次反復(fù)操作實踐的要求,同時也可以對學(xué)員及團(tuán)隊進(jìn)行系統(tǒng)性的考核和評估[10-11]。
開展情景模擬教學(xué),首先需要設(shè)置臨床案例,確定本次教學(xué)的目標(biāo),并設(shè)置教學(xué)情景,然后通過病例運行,讓學(xué)員們參與病例體驗,在病例運行中發(fā)現(xiàn)問題、思考問題、分析可能的答案去解決問題、并獲取團(tuán)隊的協(xié)作;因此,本次原位情景模擬教學(xué),針對教學(xué)對象的臨床工作、理論知識的能力及需求,設(shè)置教學(xué)主題為手術(shù)室內(nèi)羊水栓塞快速識別、臨床決策與危機(jī)管理;確定本次教學(xué)目標(biāo)為:①快速識別羊水栓塞;②掌握羊水栓塞的臨床決策和危機(jī)管理;③加強(qiáng)團(tuán)隊協(xié)作能力、培養(yǎng)急救意識、提高臨床勝任力,根據(jù)教學(xué)主題和教學(xué)目標(biāo)編寫教案,通過預(yù)演最后實現(xiàn)病例運行。而后在Debriefing引導(dǎo)性反饋的環(huán)節(jié)中,學(xué)員們通過導(dǎo)師獲得有效反饋,這是情景模擬教學(xué)的最重要也是最關(guān)鍵的教學(xué)環(huán)節(jié)[15-17]。而導(dǎo)師根據(jù)教學(xué)目標(biāo)評價表的結(jié)果,引導(dǎo)學(xué)員用言語表達(dá)自己的感受,回顧所做的事情,進(jìn)行自我反思和自我發(fā)現(xiàn),使學(xué)員獲得知識點的連接和頓悟,達(dá)到臨床流程和決策的融會貫通和恰當(dāng)把握的目的,最終形成和發(fā)展能應(yīng)變復(fù)雜情況的臨床思維能力。
本研究結(jié)果顯示,在手術(shù)室內(nèi)開展羊水栓塞病例的原位情景模擬,通過提供熟悉的環(huán)境、同事、團(tuán)隊,因其訓(xùn)練空間真實,學(xué)習(xí)者代入感強(qiáng),更易進(jìn)入演練的角色,100.0%的學(xué)員對本次教學(xué)滿意,100.0%的學(xué)員對原位情景模擬教學(xué)的教學(xué)方法表示認(rèn)可,96.3%的學(xué)員認(rèn)為該教學(xué)方法達(dá)到或超過預(yù)期效果。同時由教學(xué)目標(biāo)評價表(表3)可知,操作者確實在處理流程、診斷及鑒別、閉環(huán)溝通及團(tuán)隊配合中存在不同程度的不足。教學(xué)目標(biāo)評價既是評價學(xué)員臨床勝任力的指標(biāo),也是導(dǎo)師有針對性開展Debriefing的依據(jù),而通過本次原位情景模擬教學(xué),100.0%的學(xué)員認(rèn)為加深理論知識和處理流程的掌握、提高處理突發(fā)事件的溝通能力和團(tuán)隊合作能力,教學(xué)后理論成績顯著提高,可見該教學(xué)方法可行。
情景模擬的另一個教學(xué)特點就是小班教學(xué),每次參與病例運行的學(xué)員3~5人。在本研究中,根據(jù)病例需求,每次參與病例運行的學(xué)員有4人。目前國內(nèi)的情景模擬教學(xué)模式多數(shù)是采用攝像頭直播、遠(yuǎn)程學(xué)習(xí)的方法,場下學(xué)員可以討論參與學(xué)習(xí),其效果如何尚未可知。本研究中采用觀察評價者直接進(jìn)入模擬情景中現(xiàn)場觀察體驗的方式進(jìn)行,并要求觀察者對照教學(xué)目標(biāo)評價表對體驗者團(tuán)隊進(jìn)行評價。本研究結(jié)果顯示,模擬教學(xué)后,病例操作組和觀察評價組的理論成績較模擬教學(xué)前均有顯著提高(P=0.000),而兩組教學(xué)后的理論成績并無差異。這表明,雖然沒有參加實際情景病例操作,但觀察原位模擬病例的運行和評價,同樣有很好的教學(xué)效果。這可能與觀察者能夠進(jìn)入原位模擬的情境,同樣能夠直觀地感受病例、分析病例,并作為評價者參與其中,同樣深度參與病例發(fā)生發(fā)展有關(guān)。
在教學(xué)活動中,結(jié)合教學(xué)反饋結(jié)果,參與教學(xué)的導(dǎo)師團(tuán)隊也進(jìn)行教學(xué)反思。原位模擬教學(xué)是一種較好的教學(xué)方法,但任何成熟的教學(xué)方法需要在教學(xué)中不斷完善,尤其是情景模擬教學(xué),在計算機(jī)程序、信號輸出、模擬人操作、助理人員等方面均可能出現(xiàn)突發(fā)狀況。需要對病例進(jìn)行充分預(yù)演,不斷完善教案,以應(yīng)對各種狀況。
綜上所述,開展羊水栓塞病例的原位情景模擬是一種可行、有效的方法。在模擬教學(xué)資源有限的情況下,在病例操作者之外設(shè)置原位觀察評價者身份,同樣能夠直觀地感受病例、分析病例,參與教學(xué)評價,收獲很好的教學(xué)效果,部分解決模擬教學(xué)資源不足的矛盾。該教學(xué)方法不僅對麻醉醫(yī)生有效,而且可以推廣至整個參與搶救的團(tuán)隊,包括手術(shù)室、產(chǎn)科、急診、新生兒科,提高一線醫(yī)生的臨床勝任力,提高醫(yī)療安全。
[參考文獻(xiàn)]
[1] Shamshirsaz AA,Clark SL. Amniotic fluid embolism[J]. Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am, 2016,43(4):779-790.
[2] 周瑋,漆洪波.美國母胎醫(yī)學(xué)會羊水栓塞指南(2016)要點解讀[J].中國實用婦科與產(chǎn)科雜志,2016,32(9):864-867.
[3] Fitzpatrick KE,van den Akker T,Bloemenkamp KWM,et al. Risk factors, management, and outcomes of amniotic fluid embolism:A multicountry,population-based cohort and nested case-control study[J]. PLoS Med,2019,16(11):e1002962.
[4] Alfredo Lee Chang,Andrew A Dym,Carla Venegas-Borsellino,et al. Comparison between simulation-based training and lecture-based education in teaching situation awareness. A randomized controlled study[J]. Ann Am Thorac Soc,2017,14(4):529-535.
[5] Jennifer H Hepps,Clifton E Yu,Sharon Calaman.Simulation in medical education for the hospitalist:Moving beyond the mock code[J]. Pediatr Clin North Am,2019,66(4):855-866.
[6] Shah A,Mai CL,Shah R,et al. Simulation-based education and team training[J]. Otolaryngol Clin North Am,2019, 52(6):995-1003.
[7] Robertson JM,Dias RD,Yule S,et al. Operating room team training with simulation:A systematic review[J]. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A,2017,27(5):475-480.
[8] Gavin NR,Satin AJ. Simulation training in obstetrics[J]. Clin Obstet Gynecol,2017,60(4): 802-810.
[9] Roy E,Quinsat VE,Bazin O,et al. High-fidelity Simulation in training dental students for medical life-threatening emergency[J].Eur J Dent Educ,2018,22(2):e261-e268.
[10] Jette Led S?覬rensen,Doris tergaard,Vicki LeBlanc,et al.Design of simulation-based medical education and advantages and disadvantages of in situ simulation versus off-site simulation[J]. BMC Med Educ,2017,17(1):20.
[11] Viji Kurup,Veronica Matei,Jessica Ray. Role of in-situ simulation for training in healthcare:Opportunities and challenges[J]. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol,2017,30(6):755-760.
[12] 戴雯,趙會麗,王登芹,等. Simman 3G模擬人在臨床思維能力培訓(xùn)中的應(yīng)用[J]. 中國高等醫(yī)學(xué)教育,2019,(8):96-97.
[13] 馬杰,徐新娟,王沁. 基于Simman 3G高端模擬人的情景模擬教學(xué)效果評價[J]. 新疆醫(yī)科大學(xué)學(xué)報,2016,39(8):1075-1077.
[14] 程鈞. SimMan 3G 模擬人在臨床技能教學(xué)培訓(xùn)中的應(yīng)用[J]. 中國現(xiàn)代醫(yī)生,2017,55(3):137-139.
[15] Taylor Sawyer,Walter Eppich,Marisa Brett-Fleegler,et al. More than one way to debrief:A critical review of healthcare simulation debriefing[J]. Simul Healthc,2016,11(3):209-217.
[16] Linda A Hunter. Debriefing and feedback in the current healthcare environment[J]. J Perinat Neonatal Nurs,2016, 30(3):174-178.
[17] Cheng A,Eppich W,Grant V,et al. Debriefing for technology enhanced simulation:A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Med Educ,2014,48(7):657-666.
(收稿日期:2020-04-21)

