膿腫分枝桿菌肺病治療效果及其影響因素分析
張麗娜 李軒 鄧群益 劉國輝
【摘要】 目的 分析膿腫分枝桿菌肺病治療效果及其影響因素。方法 回顧性分析91例膿腫分枝桿菌肺病患者的臨床資料, 根據治療結果分為治愈組(49例)和未愈組(42例)。觀察患者的臨床特征、治療與隨訪情況、死亡情況及影響因素。結果 ①臨床特征:在基礎疾病上診斷為膿腫分枝桿菌肺病患者52例(57.1%);影像特征:肺部CT掃描顯示13例(14.3%)病灶在1個肺野內, 78例(85.7%)累及2個及以上肺野。形態表現:26例(28.6%)伴空洞, 36例(39.6%)伴支氣管擴張, 22例(24.2%)伴胸膜增厚, 7例(7.7%)伴肺毀損。藥物敏感試驗顯示膿腫分枝桿菌對一、二線常用抗結核藥物的耐藥率均>95%, 異煙肼、對氨基水楊酸、鏈霉素、卷曲霉素、利福平、左氧氟沙星和乙胺丁醇耐藥率為98.9%, 利福布汀和丙硫異煙胺耐藥率為97.8%。②治療及隨訪情況:60例(65.9%)患者規則治療并完成療程, 31例(34.1%)
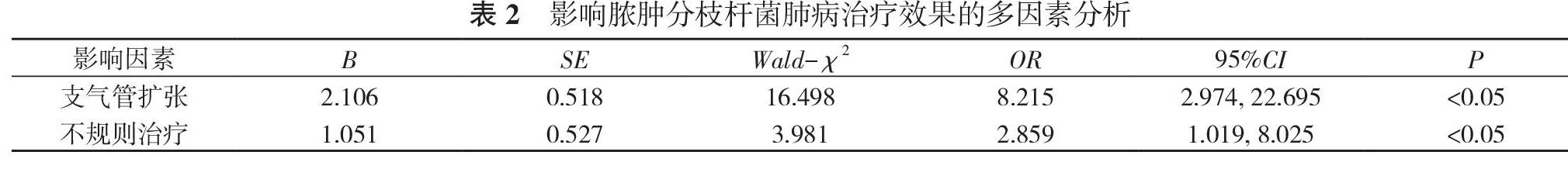
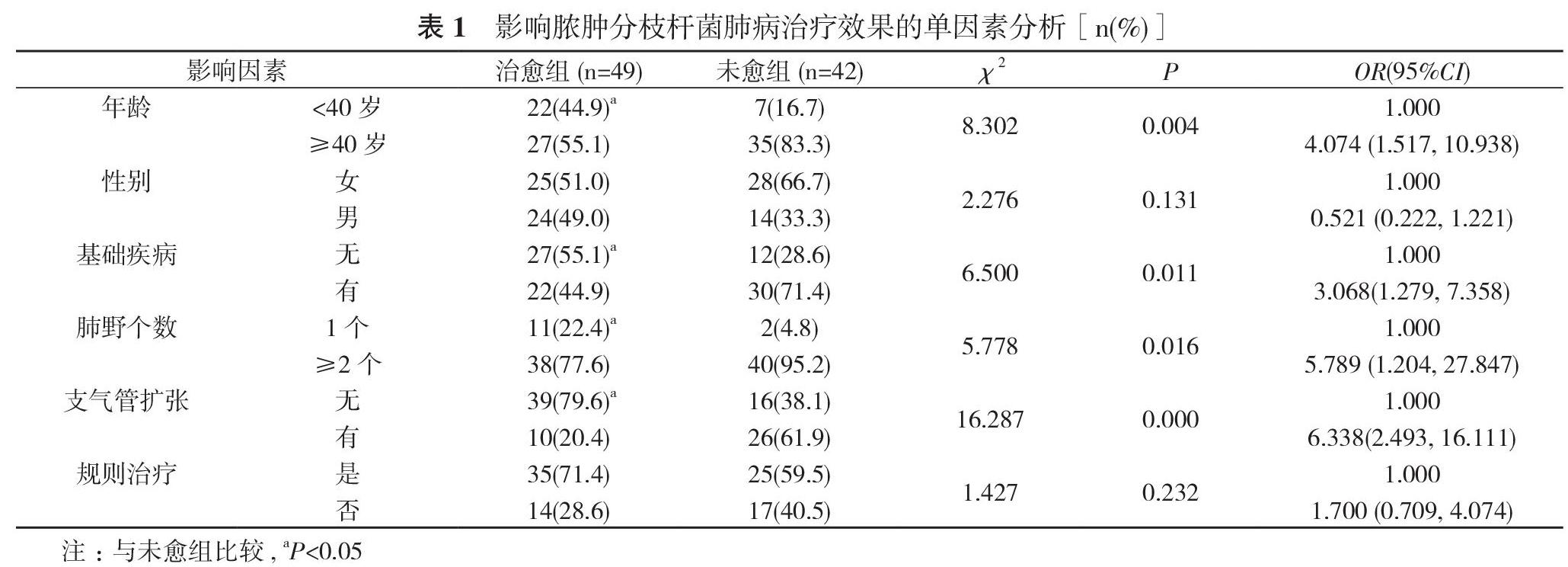
患者存在不規則治療情況。③死亡情況:未愈組患者中死亡1例(1.1%), 死亡原因為感染性休克。④治療效果的影響因素分析:單因素分析顯示:兩組年齡、基礎疾病、肺野個數、支氣管擴張因素比較, 差異有統計學意義(P<0.05)。多因素分析顯示:支氣管擴張[OR=8.215, 95%CI=(2.974, 22.695), P<0.05]、不規則治療[OR=2.859, 95%CI=(1.019, 8.025), P<0.05]是影響治療效果的不利因素。結論 膿腫分枝桿菌耐藥率高, 治愈率低, 支氣管擴張和不規則治療是影響治愈的不利因素。
【關鍵詞】 膿腫分枝桿菌;膿腫分枝桿菌肺病;治療效果;影響因素
DOI:10.14163/j.cnki.11-5547/r.2020.02.006
Study on therapeutic effect of Mycobacterium abscessus pulmonary disease and its affecting factors? ?ZHANG Li-na, LI Xuan, DENG Qun-yi, et al. Shenzhen Third Peoples Hospital, Shenzhen 518000, China
【Abstract】 Objective? ?To analyze the therapeutic effect of Mycobacterium abscessus pulmonary disease and its affecting factors. Methods? ?The clinical data of 91 patients with Mycobacterium abscessus pulmonary disease were analyzed retrospectively. According to the treatment results, they were divided into cured group
(49 cases) and non-cured group (42 cases). The clinical characteristics, treatment and follow-up, death condition and influencing factors were observed. Results? ?①Clinical features: 52 cases (57.1%) were diagnosed as Mycobacterium abscessus pulmonary disease based on underlying disease. Image feature: CT scan showed that 13 cases (14.3%) were in 1 lung field, 78 cases (85.7%) involved 2 or more lung fields. Morphological manifestation: 26 cases (28.6%) were accompanied with cavity, 36 cases (39.6%) with bronchiectasis, 22 cases (24.2%) with pleural thickening and 7 cases (7.7%) with lung damage. Drug susceptibility tests showed that Mycobacterium abscessus resistance to first and second-line commonly used anti-tuberculosis drugs was> 95%. The drug resistance rate of isoniazid, p-aminosalicylic acid, streptomycin, capreomycin, rifampicin, levofloxacin and ethambutol was 98.9%, and rifabutin and propylthioisoniazid was 97.8%. ②Treatment and follow-up:
60 patients (65.9%) had regular treatment and completed the course of treatment, and 31 patients (34.1%) had irregular treatment. ③Death: 1 patient (1.1%) died in non-cured group, and the cause of death was septic shock. ④Influencing factors analysis: univariate analysis showed that there were statistically significant differences in age, underlying disease, number of lung fields, and bronchiectasis in the two groups (P<0.05). Multivariate analysis showed that bronchiectasis [OR=8.215, 95%CI=(2.974, 22.695), P<0.05] and irregular treatment [OR=2.859, 95%CI=(1.019, 8.025), P<0.05] were the adverse factors affecting the treatment effect. Conclusion? ?Mycobacterium abscessus has high drug resistance rate and low cure rate. Bronchiectasis and irregular treatment are the adverse factors affecting the cure.
【Key words】 Mycobacterium abscessus; Mycobacterium abscessus pulmonary disease; Therapeutic effect; Affecting factors
近年來, 非結核分枝桿菌肺病發病率呈逐漸升高趨
勢[1], 在多種與肺部感染有關的非結核分枝桿菌中, 膿腫分枝桿菌(mycobacterium abcessus, MAB)是華南地區最常見的致病菌[2], 而膿腫分枝桿菌肺病(mycobacterium abscessus pulmonary disease, MAB-PD)的治療效果并不理想。為進一步了解膿腫分枝桿菌肺病目前的治療情況, 本次研究分析膿腫分枝桿菌肺病治療效果及影響因素, 現報告如下。

