重癥肺炎患者PCT、CRP、APACHEⅡ評(píng)分與病原菌及預(yù)后的關(guān)系
唐瑋欣 余雪濤 陳蘭春 丘自挺 李展?jié)h
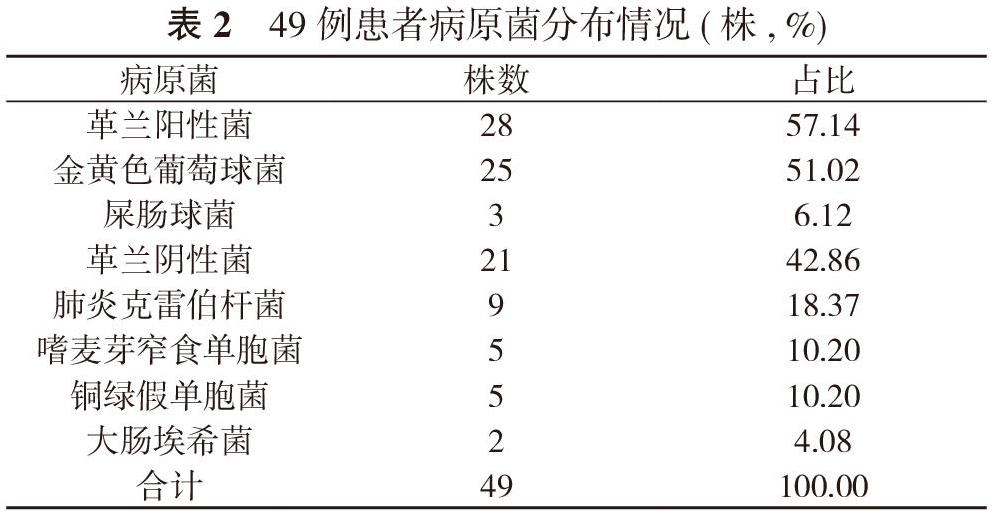
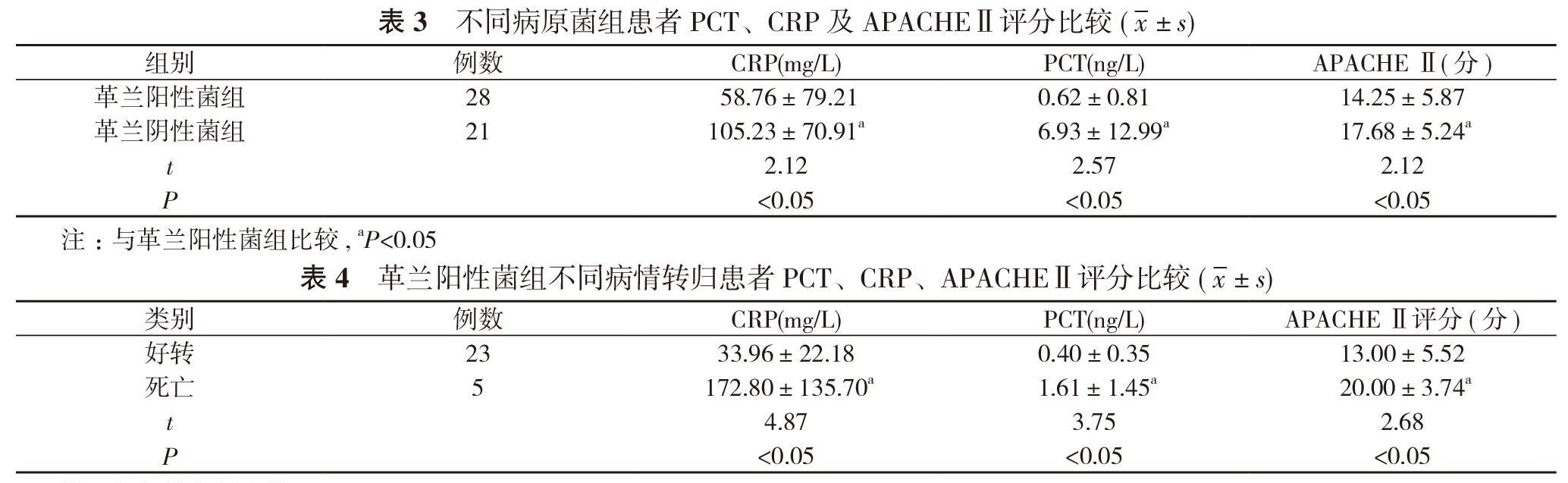
【摘要】 目的 探討不同病原菌感染的重癥肺炎患者降鈣素原(PCT)、C反應(yīng)蛋白(CRP)、急性生理與慢性健康狀況Ⅱ(APACHEⅡ)評(píng)分的差異, 以及其與預(yù)后的關(guān)系。方法 49例重癥肺炎且痰培養(yǎng)陽(yáng)性患者, 按照痰培養(yǎng)結(jié)果分為革蘭陰性菌組(21例)及革蘭陽(yáng)性菌組(28例)。觀察患者病原菌分布情況, 比較革蘭陰性菌組、革蘭陽(yáng)性菌組患者PCT、CRP、APACHEⅡ評(píng)分;比較兩組不同病情轉(zhuǎn)歸患者PCT、CRP、APACHEⅡ評(píng)分。結(jié)果 49例重癥肺炎患者中, 革蘭陽(yáng)性菌占57.14%(28/49), 以金黃色葡萄球菌為主;革蘭陰性菌陽(yáng)性占42.86%(21/49), 以肺炎克雷伯桿菌、嗜麥芽窄食單胞菌、銅綠假單胞菌為主。革蘭陰性菌組患者PCT(105.23±70.91)mg/L、CRP(6.93±12.99)ng/L及APACHEⅡ評(píng)分(17.68±5.24)分均高于革蘭陽(yáng)性菌組的(58.76±79.21)mg/L、(0.62±0.81)ng/L、(14.25±5.87)分, 差異有統(tǒng)計(jì)學(xué)意義(P<0.05)。革蘭陽(yáng)性菌組、革蘭陰性菌組死亡患者的PCT、CRP及APACHEⅡ評(píng)分均高于好轉(zhuǎn)患者, 差異有統(tǒng)計(jì)學(xué)意義(P<0.05)。結(jié)論 PCT、CRP及APACHEⅡ評(píng)分有助于區(qū)分革蘭陰性菌感染與革蘭陽(yáng)性菌感染;PCT、CRP及APACHEⅡ評(píng)分對(duì)重癥肺炎預(yù)后的判定有重要的臨床價(jià)值。
【關(guān)鍵詞】 重癥肺炎;預(yù)后;C反應(yīng)蛋白;降鈣素原;急性生理與慢性健康狀況Ⅱ評(píng)分
【Abstract】 Objective? ?To discuss the difference of procalcitonin (PCT), C-reactive protein (CRP), acute physiological and chronic health evaluation Ⅱ (APACHEⅡ) score in patients with severe pneumonia infected by different pathogens, and their correlation to prognosis. Methods? ?A total of 49 patients with severe pneumonia were divided into gram-negative bacteria group (21 cases) and gram-positive bacteria group (28 cases)?according to the results of sputum culture. The distribution of pathogenic bacteria was observed, and PCT, CRP and APACHEⅡ score were compared between gram-negative group and gram-positive group. The PCT, CRP, APACHEⅡ scores were compared between the two groups with different outcomes. Results? ?In 49 patients with severe pneumonia, gram-positive bacteria accounted for 57.14% (28/49), mainly Staphylococcus aureus; gram-negative bacteria accounted for 42.86% (21/49), mainly Klebsiella pneumoniae, Stenotrophomonas maltophilia and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. PCT (105.23±70.91) mg/L, CRP (6.93±12.99) ng/L and APACHEⅡ score (17.68±5.24) points in gram-negative group was higher than (58.76±79.21) mg/L, (0.62±0.81) ng/L and (14.25±5.87) points in gram-positive group. Their difference was statistically significant (P<0.05). The PCT, CRP and APACHE Ⅱ score of the dead patients in the gram-positive bacteria group and the gram-negative bacteria group were higher than those of the improved patients, their difference was statistically significant (P<0.05). Conclusion? ?PCT, CRP and APACHE Ⅱ score are helpful to distinguish gram-negative bacterial infection from gram-positive bacterial infection, and PCT, CRP and APACHE Ⅱ scores have important clinical value in the prognosis of severe pneumonia.
【Key words】 Severe pneumonia; Prognosis; C-reactive protein; Procalcitonin; Acute physiology and chronic health evaluation Ⅱ score
重癥肺炎是重癥醫(yī)學(xué)科臨床常見(jiàn)的呼吸系統(tǒng)疾病, 有發(fā)病時(shí)間短、進(jìn)展快的特點(diǎn), 是常見(jiàn)死亡原因之一[1], 重癥肺炎患者治療的關(guān)鍵在于及時(shí)明確診斷、積極治療[2]。感染的重要檢測(cè)指標(biāo)通常為C反應(yīng)蛋白(C-reactive protein, CRP)及降鈣素原(procalcitonin, PCT), 而APACHEⅡ是常用的危重病病情評(píng)價(jià)系統(tǒng)之一[3]。本研究探討不同病原菌感染的重癥肺炎患者PCT、CRP、APACHEⅡ評(píng)分的差異, 以及PCT、CRP、APACHEⅡ水平與預(yù)后的關(guān)系。現(xiàn)報(bào)告如下。
1 資料與方法
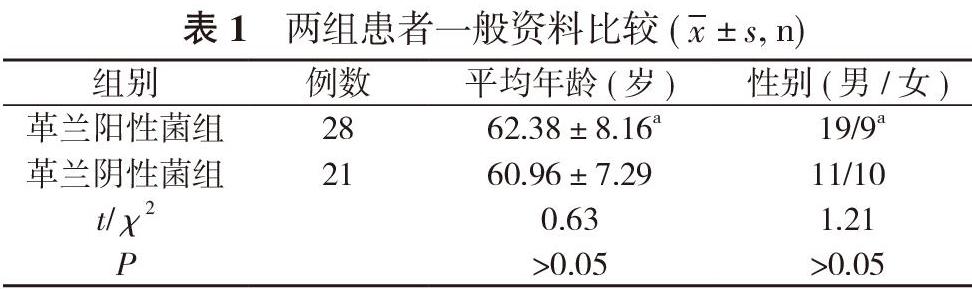
1. 1 一般資料 選取2015年10月~2016年10月醫(yī)院重癥加強(qiáng)護(hù)理病房(ICU)收治的49例重癥肺炎且痰培養(yǎng)陽(yáng)性患者, 其中男30例, 女19例;年齡41~80歲。將患者按照痰培養(yǎng)結(jié)果分為革蘭陰性菌組(21例)及革蘭陽(yáng)性菌組(28例)。革蘭陽(yáng)性菌組患者平均年齡(62.38±8.16)歲;男19例, 女

