探討慢性乙型肝炎患者血清不同HBV-DNA載量與炎性因子、肝功能酶學(xué)指標(biāo)的關(guān)系
孫華寶
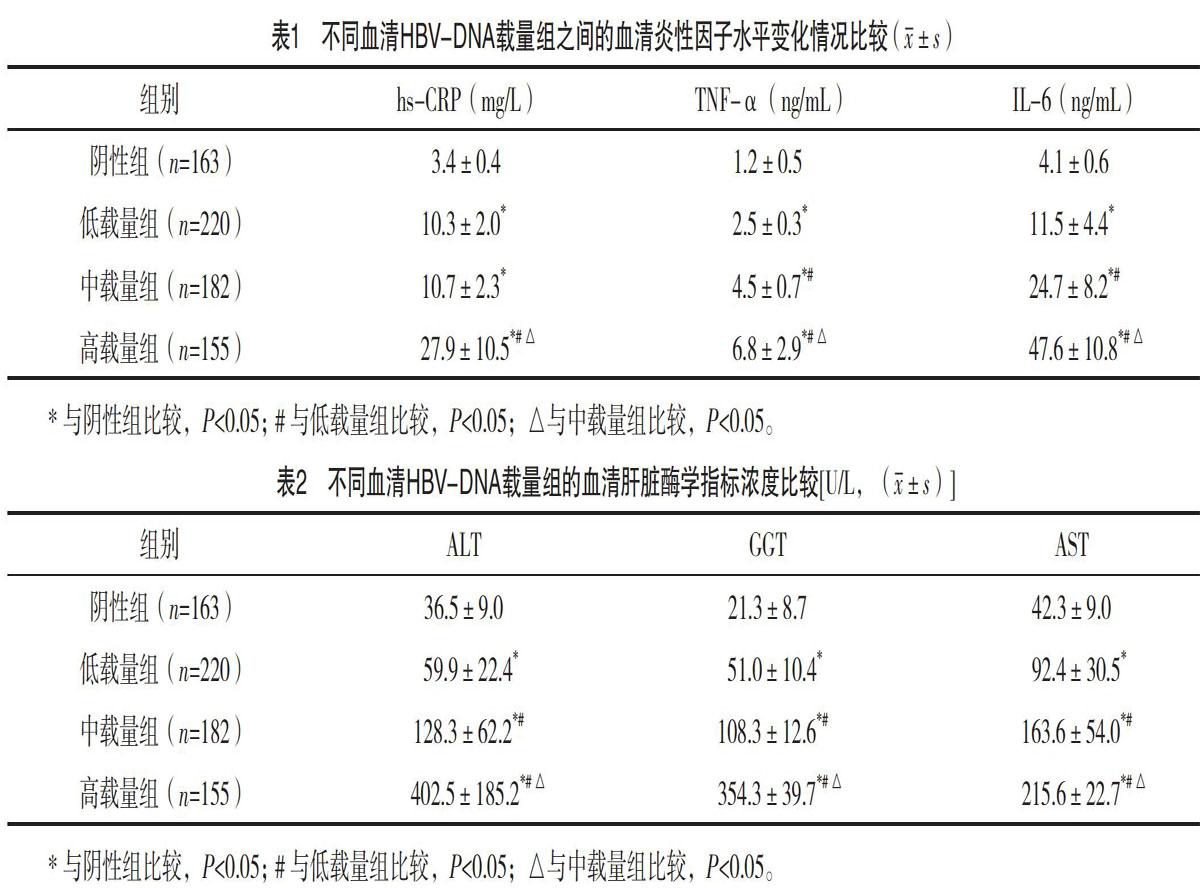
【摘要】 目的:研究慢性乙型肝炎患者血清不同HBV-DNA載量與炎性因子、肝功能酶學(xué)指標(biāo)的關(guān)系。方法:回顧性分析2018年1月-2019年4月本院收治的720例慢性乙型肝炎患者,依據(jù)實(shí)時熒光定量PCR技術(shù)檢查血清HBV-DNA載量,按照血清不同HBV-DNA載量表達(dá)將其劃分為4組,包括高載量組155例、中載量組182例、低載量組220例以及陰性組163例,比較各組之間的腫瘤壞死因子α(TNF-α)、白介素-6(IL-6)、肝功能相關(guān)酶(ALT、GGT、AST)以及超敏C反應(yīng)蛋白(hs-CRP)差異與相關(guān)性。結(jié)果:低、中、高載量組hs-CRP、TNF-α與IL-6水平均高于陰性組,中、高載量組TNF-α與IL-6水平均高于低載量組,高載量組hs-CRP、TNF-α與IL-6水平均高于中載量組,差異均有統(tǒng)計學(xué)意義(P<0.05)。低、中、高載量組ALT、GGT、AST濃度均高于陰性組,中、高載量組ALT、GGT、AST濃度均高于低載量組,高載量組ALT、GGT、AST濃度均高于中載量組,差異均有統(tǒng)計學(xué)意義(P<0.05)。TNF-α、IL-6與ALT呈正相關(guān)(P<0.05),hs-CRP與ALT無相(P>0.05)。結(jié)論:在慢性乙型肝炎發(fā)病過程中炎性因子起著關(guān)鍵性作用,因此臨床應(yīng)當(dāng)結(jié)合檢測血清炎性因子與肝臟酶學(xué)來評估患者體內(nèi)的免疫狀況,為后續(xù)制定安全有效的治療方案提供可靠依據(jù)。
【關(guān)鍵詞】 慢性乙型肝炎 HBV-DNA載量 炎性因子 肝臟酶學(xué)指標(biāo) 超敏C反應(yīng)蛋白
[Abstract] Objective: To investigate the relationship between serum HBV-DNA load and inflammatory factors and liver function enzymes in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Method: Retrospective analysis of 720 patients with chronic hepatitis B admitted to our hospital from January 2018 to April 2019. Serum HBV-DNA load was detected by real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR, the serum was divided into four groups according to different HBV-DNA load expressions, there were 155 cases in the high-load group, 182 cases in the medium-load group, 220 cases in the low-load group and 163 cases in the negative group. The differences and correlations of tumor necrosis factor-α(TNF-α), interleukin-6 (IL-6), liver function related enzymes (ALT, GGT, AST) and high sensitivity c-reactive protein (hs-CRP) were compared among the four groups. Result: The levels of hs-CRP, TNF-α and IL-6 in the low, medium and high load group were higher than those in the negative group, the levels of TNF-α and IL-6 in the middle and high load group were higher than those in the low load group, hs-CRP, TNF-α and IL-6 levels in the high load group were higher than those in the medium load group, the differences were statistically significant (P<0.05). The ALT, GGT and AST concentrations in the low, medium and high load groups were higher than those in the negative group, ALT, GGT and AST concentrations in the medium and high load groups were higher than those in the low load group, ALT, GGT and AST concentrations in the high load group were higher than those in the medium load group, the differences were statistically significant (P<0.05). There were positive correlations between TNF-α, IL-6 and ALT (P<0.05), but no correlation between hs-CRP and ALT (P>0.05). Conclusion: Inflammatory factors play a key role in the pathogenesis of chronic hepatitis B, so clinical should be combined with the detection of serum inflammatory factors and liver enzymes to evaluate the immune status of patients, to provide a reliable basis for the subsequent development of safe and effective treatment programs.[Keywords] Chronic hepatitis B HBV-DNA loads Inflammatory factor Liver enzyme index High sensitive C-reactive proteinFirst-authors address: Ninth Hospital of Nanchang City, Nanchang 330002, China
乙型病毒性肝炎(viral hepatitis type B, HBV)作為臨床上常見的感染性疾病,已被我國列入乙類傳染病中,具有流行性廣泛且發(fā)病率高等特征,會危害到人們的身心健康[1]。部分慢性HBV感染早期無明顯癥狀,但隨著發(fā)展會轉(zhuǎn)化為慢性乙型肝炎和肝硬化,嚴(yán)重可致癌,在整個病變過程中,離不開免疫反應(yīng)介導(dǎo)的炎性因子,而細(xì)胞因子活化、繁殖和滅亡能夠?qū)ζ溥M(jìn)行調(diào)控[2]。現(xiàn)階段臨床診斷肝細(xì)胞損傷主要是依靠肝功能相關(guān)酶檢測,能夠?qū)Ω渭?xì)胞損傷程度進(jìn)行評估,并且能夠評價乙肝的治療效果及預(yù)后。……

