轉錄中介體復合物的研究進展
王雯 劉坤
摘要:轉錄中介體復合物(Mediator complex)廣泛存在于真核生物中,在進化上高度保守,是一個具有模塊化組織的大復合物,參與轉錄因子與RNA聚合酶Ⅱ之間的信息傳遞。中介體復合物的主要功能是通過其特定亞基與不同信號通路激發的轉錄因子相互作用,調節下游基因的表達。此外,中介體復合物還與各種輔因子相互作用,參與轉錄延伸、mRNA輸出及選擇性剪切等過程,從而調控細胞的各種生理功能。中介體復合物與疾病的密切聯系使得將中介體作為靶標研究疾病的治療方法成為可能。以中介體復合物的結構為基礎,重點介紹了中介體復合物在基因表達調控中的分子機制及功能,以期為后續研究提供參考。
關鍵詞:中介體復合物(Mediator complex);結構;分子機制;功能
中圖分類號:Q71? ? ? ? ?文獻標識碼:A
文章編號:0439-8114(2020)03-0005-08
DOI:10.14088/j.cnki.issn0439-8114.2020.03.001
Resarch progress of transcription mediator complex
WANG Wen,LIU Kun
(School of Life Sciences,Tianjin University,Tianjin 300072,China)
Abstract: The mediator complex, a highly conserved large complex with modular tissue, is widely distributed in eukaryotes and is involved in the transmission of information between transcription factors and RNA polymerase II. The main function of the mediator complex is to regulate the expression of downstream genes by interacting with transcription factors stimulated by different signaling pathways. In addition, the mediator complex interacts with various cofactors to participate in processes such as transcriptional elongation, mRNA export, and selective splicing, thereby controlling various physiological functions of the cell. The close relationship between mediator complexes and disease makes it possible to study the treatment of disease with mediator as a target. Based on the structure of the mediator complex, the molecular mechanism and function of the mediator complex in the regulation of gene expression were introduced, in order to provide reference for the following research.
Key words: mediator complex; structure; molecular mechanism; function
中介體復合物(Mediator complex)最早在酵母中被發現,此后陸續在果蠅和小鼠的細胞中發現了酵母中介體復合物的同源蛋白[1,2]。2004年,科學家對已發現的中介體復合物各亞基采用了統一的命名法,突出了所有真核生物中中介體復合物的保守性。中介體復合物作為最大的銜接蛋白之一,由30個不同亞基組成,不同模塊之間可以發生各種構象變化,可以與3 000個潛在的轉錄因子相互作用,幾乎參與細胞中的所有基因轉錄,因此理解這種大分子機制是分子生物學中的巨大挑戰之一。中介體復合物在轉錄中具有突出的作用,不僅穩定起始復合物,還參與DNA折疊和染色質相關的DNA重塑等[3]。近年來中介體復合物的功能及對疾病的影響備受關注,它在酵母、植物和人體的多種信號轉導途徑中發揮重要作用。本文重點論述中介體復合物的亞基組成和結構,試圖歸納其參與的轉錄調節過程及功能,以期為研究中介體復合物提供理論依據。
1? 中介體的組成和結構
中介體復合物是一個由多亞基組成的生物大分子,在哺乳動物中大小約2 MDa。由于其具有異質性、內在靈活性,并且尺寸較大,存在亞基多,純化產率較低,中介體復合物的研究一度受到技術和方法限制[4]。近年來,通過體外生化試驗和冷凍電鏡技術等先進手段,中介體的研究取得了較大的突破,中介體復合物的組成結構得到了體外重建[4-7]。
1.1? 酵母中介體復合物的組成和結構
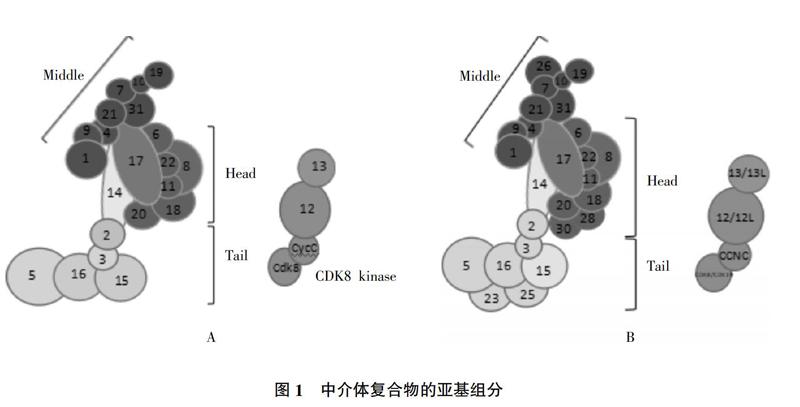
酵母中介體復合物(Mediator of RNA polymerase II transcription subunit,MED)由25個亞基組成(圖1A),大小約1.4 MDa,其中MED1、MED4、MED7、MED9、MED10、MED19、MED21和MED31構成中介體的頭部模塊,MED6、MED8、MED11、MED14、MED17、MED18、MED20及MED22構成中部模塊,頭部模塊和中部模塊是中介體復合物的核心,與RNA聚合酶Ⅱ(RNA polymerase Ⅱ,Pol Ⅱ)相互作用參與轉錄過程[8]。酵母中介體15個核心亞基復合物的晶體結構已被報道(不含MED1)[5]。MED2、MED3、MED5、MED15和MED16組成尾部模塊,主要通過與轉錄因子相互作用以調控轉錄,MED12、MED13、CycC同CDK8構成細胞周期素依賴性激酶8(Cyclin-dependent kinase 8,CDK8)模塊,該模塊與中介體的其余部分可逆性結合以調節轉錄過程[4,9,10]。MED14連接中介體頭部、中部和尾部模塊[11,12]。在體外對頭部和中部模塊進行重組時發現,頭部和中部模塊可以彼此穩定結合,但得到的復合物在轉錄中是無活性的,在此基礎上加入MED14可恢復轉錄活性并顯著增強復合物與Pol Ⅱ的相互作用。同時還發現MED14添加到復合物中顯著增強了與Pol Ⅱ的相互作用[4]。
1.2? 哺乳動物中介體復合物的組成和結構
哺乳動物中的中介體復合物由30個蛋白亞基組成,與酵母中介體類似可以分成不同的模塊。從單細胞生物到后生動物的進化過程中,中介體的組成和結構高度保守[4](圖1B),酵母中介體復合物的亞基模塊與哺乳動物的亞基模塊存在廣泛同源性。在后生動物中介體中,MED24、MED27和MED29分別與酵母中的MED5、MED3和MED2直系同源[10]。但隨著生物的進化,轉錄的基因數目和復雜性不斷增加,導致中介體復合物的亞基數也在增加。例如人中介體亞基MED23、MED25、MED26、MED28和MED30在酵母中介體復合物中不存在,本文中這5個組分的模塊分配方式是預測的結果。
1.3? 中介體復合物的構象變化及三維結構
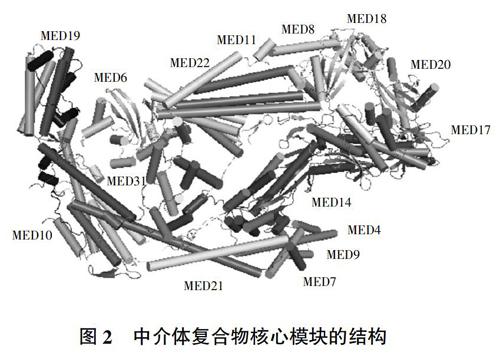
中介體復合物在轉錄中的作用涉及多種機制,其中構象改變在功能調節中發揮關鍵作用[13]。中介體的較大體積和表面積有助于與多種分子及蛋白發生相互作用,使其構象發生變化,已經證明中介體復合物能夠與多種轉錄因子結合,并與轉錄起始復合物(Preinitiation complex,PIC)相互作用形成前延伸復合物(Pre-elongation complex,PEC)[14],中介體復合物的結構變化可能導致PEC的結構和功能發生改變。研究發現中介體復合物的不同亞基與轉錄因子p53相互作用會導致構象發生不同的變化,并顯著影響PIC的活性[15]。此外,在其他轉錄因子結合中介體時也觀察到類似的構象變化,說明轉錄因子可能通過改變中介體復合物的構象去調節PIC活性,從而調節下游基因表達[16]。中介體復合物與Pol Ⅱ相互作用時,核心模塊(core Mediator,cMED)發揮主要作用,cMED的結構(圖2)包含15個亞基,不含MED1,原因可能是在結晶過程中發生了解離[5]。該結構揭示了頭部模塊和中部模塊的亞基結構,也顯示了兩個模塊間的相互作用方式,為功能的研究提供了分子機制和理論基礎。
2? 中介體復合物在基因表達調控中的分子機制及功能
中介體復合物幾乎參與了所有的基因轉錄,而基因的轉錄調控是一個非常復雜的過程,先前研究的轉錄控制模型對基因調控原理提供了重要的見解,揭示了中介體如何將上游眾多信號通路的信息正確地傳遞至基因啟動子上的轉錄裝置,從而精確地控制下游基因的表達[17],以下結合近年來對中介體的研究,對中介體復合物在基因表達調控中的分子機制及功能作詳細描述。
2.1? 增強子招募中介體
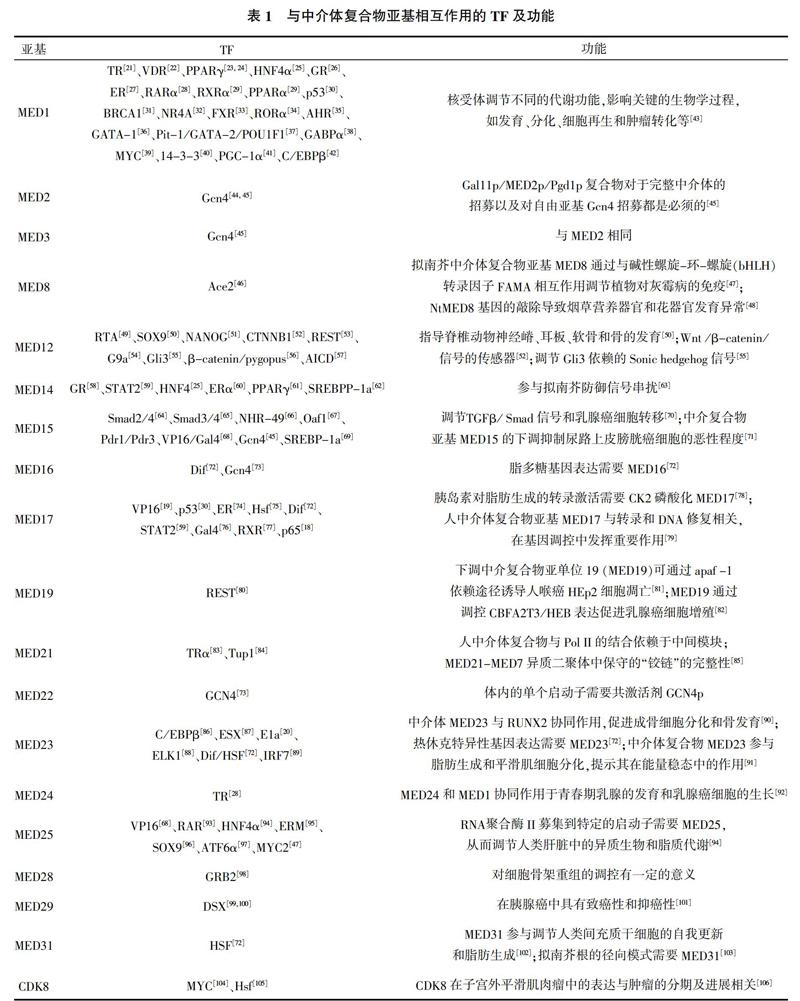
中介體在轉錄激活中起作用的關鍵是被增強子招募,然后與不同啟動子相對應的轉錄起始復合物(Preinitiation complex,PIC)相互作用,以調節轉錄。中介體復合物并不與DNA直接結合,而是與轉錄因子(Transcription factors,TFs)相互作用招募至增強子處。不同亞基與對應TF的這種相互作用是靶基因活化的必要條件,所以特定亞基的缺失可以在不同程度上阻止對應TF調節的基因表達,酵母和低等后生動物的遺傳研究已經證明了這一點,并在哺乳動物中也有發現[18]。例如,亞基MED1是核受體的共同靶標,研究發現敲除小鼠胚胎成纖維細胞中的MED1會導致核受體依賴性基因表達缺陷,而與其他亞基相互作用的TF的激活未受到負面影響[19],敲除小鼠細胞中MED23會致使轉錄因子ELK-1或E1A的失活,但并不影響轉錄因子VP16和p53的活化[20]。中介體復合物主要通過尾部模塊與IF相互作用[8],其他的亞基也有參與,中介體亞基與不同轉錄因子相互作用及相關功能詳見表1。
2.2? 中介體復合物與PIC相互作用促進PIC的形成
中介體被招募到增強子區域后,為協助PIC裝配,被傳送至在核啟動子形成的PIC處[107,108]。增強子結合IF后招募共轉錄激活因子以修飾和重塑染色質,用于改變染色質結構并使其更易獲得其他因子,其中中介體就是共轉錄激活因子之一,然后招募更多的共激活因子組裝PIC,包括Pol Ⅱ(含12個亞基)、通用轉錄因子(General transcription factors,GTFs)、轉錄起始因子(Transcription initiation factor,TIF)ⅡA、TIFⅡB、TIFⅡD、TIFⅡE、TIFⅡF和TIFⅡH[109]。中介體復合物能夠與PIC直接相互作用,不同于被增強子招募時中介體包含所有模塊,與核心啟動子相互作用時不含Cdk8激酶模塊,頭部和中部模塊發揮主要作用。招募后的Pol Ⅱ、TFs和中介體復合物參與構成轉錄起始的全酶,Pol Ⅱ的羧基末端結構域(Carboxyl terminal domain,CTD)區域是中介體復合物與之結合的重要位點,包括解旋酶活性和激酶活性等多種酶活性的TF IIH,能夠幫助打開DNA雙鏈,磷酸化Pol Ⅱ CTD,以促使轉錄起始。經典理論認為中介體復合物在全酶中的作用是短暫的,在Pol Ⅱ完成轉錄起始并即將轉錄延伸時,中介體復合物將與Pol Ⅱ分離,分離的過程與CTD的磷酸化有關。有報道稱CTD的磷酸化與中介體復合物的Cdk8激酶模塊有關,并認為Cdk8激酶模塊通過磷酸化CTD抑制轉錄過程[110]。這一定程度上與中介體復合物和PIC相互作用時不包含Cdk8激酶模塊的結論一致。
2.3? 中介體復合物的“招募后”功能
越來越多的證據表明,中介體不僅在招募Pol Ⅱ裝配PIC中起關鍵作用,也參與招募后的諸多功能,以使靶基因的轉錄從多方面得到調控,達到精確的效果。
中介體復合物參與轉錄延伸。構成核心正相關因子(Positive transcriptional elongation factor b,P-TEFb)的cyclinT1/Cdk9異二聚體通常被認為是刺激RNA聚合酶Ⅱ延伸的轉錄活性形式,大約一半的細胞P-TEFb存在于具有7SK snRNA和HEXIM1蛋白的無活性復合物中,剩余的一半與溴結構域蛋白Brd4相互作用,與Brd4的結合使P-TEFb 具有轉錄活性。哺乳動物Brd4屬于BET家族,基于其他BET蛋白在轉錄中的作用,Brd4被認為可能也參與了轉錄,人轉錄介體復合物被報道含有Brd4或Brd4類似蛋白[111,112]。除此之外,有研究發現中介體復合物與P-TEFb有直接的物理相互作用[113]。在酵母中還發現中介體復合物能與延伸因子TFIIS相互作用,進一步影響延伸因子DSlF,從而調節轉錄延伸過程[114]。
中介體復合物參與mRNA的輸出。成熟的mRNA形成之后,需要通過核孔復合物(Nuclear pore complexes,NPCs)輸出到細胞質中,保守的轉錄偶聯輸出(Conserved transcription-coupled export,TREX2)復合物與NPC結合并參與轉錄和mRNA輸出[115,116]。最近的一項研究發現在酵母中中介體與TREX2復合物之間有直接相互作用,這表明由中介體協調的轉錄調節與NPC介導的mRNA輸出有關[117]。通過一系列試驗進一步揭示了TREX2復合物直接與中介體的中間模塊相互作用。TREX2復合物與中介體的相互作用被認為參與轉錄和mRNA轉運的復雜調節[118]。
中介體復合物在選擇性剪切過程中起重要作用[119];中介體是酵母基因組中負責高級染色質折疊的關鍵復合物之一;中介體復合物與轉錄記憶有關,已在酵母和人體中證實了這種功能[118]。中介體參與轉錄絕大部分過程,上述只是其中小部分,更多的功能需要被發現和補充。
3? 小結與展望
中介體復合物在酵母中的組成和結構研究已經相對成熟,但核心結構中不包括MED1,這個結果并未得到清晰的解釋。隨著生物的不斷進化,中介體復合物的復雜性也提高,在高級的物種例如人體中,中介體的結構尚未解析,組成成分及分布需要進一步確定。中介體復合物幾乎參與真核細胞的所有轉錄過程,中介體功能的異常與許多癌癥有關,例如MED29調節胰腺癌的關鍵細胞功能,包括致癌和抑制腫瘤的功能[101],MED15在睪丸生殖細胞腫瘤中差異表達[120]等。中介體亞基已經被作為治療癌癥的靶標,其中中介體復合物亞基MED15的敲低抑制了泌尿道上皮膀胱癌細胞的惡性腫瘤;MED1作為ER關鍵的共激活因子,在ER依賴的基因表達和雌激素依賴的乳腺癌生長過程中起到關鍵性作用,而且參與了另一類內分泌治療藥物Tamoxifen的耐藥形成過程,與乳腺癌患者的不良預后有著高度相關;siRNA介導的CDK8沉默抑制乳腺癌細胞的增殖和生長[121]。還有研究表明中介體復合物與真菌感染等有關,有望成為更多疾病的治療靶標。目前對它與癌癥等疾病的研究大多數處于理論階段,將其應用于臨床研究更加迫切。
參考文獻:
[1] BOUBE M,FAUCHER C,JOULIA L,et al. Drosophila homologs of transcriptional mediator complex subunits are required for adult cell and segment identity specification[J].Genes Dev,2000, 14(22):2906-2917.
[2] JIANG Y W,VESCHAMBRE P,ERDJUMENT-BROMAGE H,et al. Mammalian mediator of transcriptional regulation and its possible role as an end-point of signal transduction pathways[J].Proc Natl Acad Sci USA,1998,95(15):8538-8543.
[3] SIERECKI E. The Mediator complex and the role of protein-protein interactions in the gene regulation machinery[J].Semin Cell Dev Biol,2018,(in press).
[4] CEVHER M A,SHI Y,LI D,et al. Reconstitution of active human core Mediator complex reveals a critical role of the MED14 subunit[J].Nature structural & molecular biology,2014,21(12):1028-1034.
[5] NOZAWA K,SCHNEIDER T R,CRAMER P. Core Mediator structure at 3.4 ?魡 extends model of transcription initiation complex[J].Nature,2017,545(7653):248-251.
[6] WANG X,SUN Q,DING Z,et al. Redefining the modular organization of the core Mediator complex[J].Cell Res,2014,24(7):796-808.
[7] TSAI K L,SATO C T,SATO S,et al. Subunit architecture and functional modular rearrangements of the transcriptional mediator complex[J].Cell,2014,157(2):1430-1444.
[8] SOUTOURINA J. Transcription regulation by the Mediator complex[J].Nature reviews molecular cell biology,2017,19(4):262-274.
[9] PLASCHKA C,LARIVI?魬RE L,WENZECK L, et al. Architecture of the RNA polymerase II-Mediator core initiation complex[J].Nature,2015,518(7539):376-380.
[10] SOUTOURINA J. Transcription regulation by the Mediator complex[J].Nature reviews molecular cell biology,2017,19(4):262-274.
[11] TSAI K,YU X,GOPALAN S,et al. Mediator structure and rearrangements required for holoenzyme formation[J].Nature,2017,544(7649):196-201.
[12] ROBINSON P J,TRNKA M J,PELLARIN R,et al. Molecular architecture of the yeast Mediator complex[J].eLife,2015,4.e08719.
[13] ROBINSON P J,TRNKA M J,BUSHNELL D A,et al. Structure of a complete Mediator-RNA polymerase II Pre-Initiation complex[J].Cell,2016,166(6):1411-1422.
[14] LARIVIERE L,SEIZL M,CRAMER P. A structural perspective on Mediator function[J].Curr Opin Cell Biol,2012,24(3):305-313.
[15] MEYER K D,LIN S C,BERNECKY C,et al. p53 activates transcription by directing structural shifts in Mediator[J].Nat Struct Mol Biol,2010,17(6):753-760.
[16] LIN J J,LEHMANN L W,BONORA G,et al. Mediator coordinates PIC assembly with recruitment of CHD1[J].Genes Dev,2011,25(20):2198-2209.
[17] POSS Z C,EBMEIER C C,TAATJES D J. The Mediator complex and transcription regulation[J].Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol,2013,48(6):575-608.
[18] VAN ESSEN D,ENGIST B,NATOLI G,et al. Two modes of transcriptional activation at native promoters by NF-kappaB p65[J].PLoS Biol,2009,7(3):e73.
[19] ITO M,YUAN C X,MALIK S,et al. Identity between TRAP and SMCC complexes indicates novel pathways for the function of nuclear receptors and diverse mammalian activators[J].Mol Cell,1999,3(3):361-370.
[20] STEVENS J L,CANTIN G T,WANG G,et al. Transcription control by E1A and MAP kinase pathway via Sur2 mediator subunit[J].Science,2002,296(5568):755-758.
[21] FONDELL J D,GE H,ROEDER R G. Ligand induction of a transcriptionally active thyroid hormone receptor coactivator complex[J].Proc Natl Acad Sci USA,1996,93(16):8329-8333.
[22] RACHEZ C,LEMON B D,SULDAN Z,et al. Ligand-dependent transcription activation by nuclear receptors requires the DRIP complex[J].Nature,1999,398-824.
[23] GE K,CHO Y W,GUO H,et al. Alternative mechanisms by which mediator subunit MED1/TRAP220 regulates peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma-stimulated adipogenesis and target gene expression[J].Mol Cell Biol,2008,28(3):1081-1091.
[24] GE K,GUERMAH M,YUAN C,et al. Transcription coactivator TRAP220 is required for PPARγ2-stimulated adipogenesis[J]. Nature,2002,417-563.
[25] MALIK S,WALLBERG A E,KANG Y K,et al. TRAP/SMCC/mediator-dependent transcriptional activation from DNA and chromatin templates by orphan nuclear receptor hepatocyte nuclear factor 4[J].Mol Cell Biol,2002,22(15):5626-5637.
[26] HITTELMAN A B,BURAKOV D,INIGUEZ-LLUHI J A,et al. Differential regulation of glucocorticoid receptor transcriptional activation via AF-1-associated proteins[J].EMBO J,1999,18(19):5380-5388.
[27] KANG Y K,GUERMAH M,YUAN C X,et al. The TRAP/Mediator coactivator complex interacts directly with estrogen receptors? alpha and beta through the TRAP220 subunit and directly enhances estrogen receptor function in vitro[J].Proc Natl Acad Sci USA,2002,99(5):2642-2647.
[28] YUAN C X,ITO M,FONDELL J D,et al. The TRAP220 component of a thyroid hormone receptor-associated protein (TRAP) coactivator complex interacts directly with nuclear receptors in a ligand-dependent fashion[J].Proc Natl Acad Sci USA,1998, 95(14):7939-7944.
[29] ZHU Y,QI C,JAIN S,et al. Isolation and characterization of PBP,a protein that interacts with peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor[J].J Biol Chem,1997,272(41):25500-25506.
[30] MEYER K D,LIN S C,BERNECKY C,et al. p53 activates transcription by directing structural shifts in Mediator[J].Nat Struct Mol Biol,2010,17(6):753-760.
[31] WADA O,OISHI H,TAKADA I,et al. BRCA1 function mediates a TRAP/DRIP complex through direct interaction with TRAP220[J].Oncogene,2004,23(35):6000-6005.
[32] WANSA K D,MUSCAT G E. TRAP220 is modulated by the antineoplastic agent 6-Mercaptopurine,and mediates the activation of the NR4A subgroup of nuclear receptors[J].J Mol Endocrinol,2005,34(3):835-848.
[33] PINEDA T I,FREEDMAN L P,GARABEDIAN M J. Identification of DRIP205 as a coactivator for the Farnesoid X receptor[J].J Biol Chem,2004,279(35):36184-36191.
[34] ATKINS G B,HU X,GUENTHER M G,et al. Coactivators for the orphan nuclear receptor RORalpha[J].Mol Endocrinol,1999, 13(9):1550-1557.
[35] WANG S,GE K,ROEDER R G,et al. Role of mediator in transcriptional activation by the aryl hydrocarbon receptor[J].J Biol Chem,2004,279(14):13593-13600.
[36] STUMPF M,WASKOW C,KROTSCHEL M,et al. The mediator complex functions as a coactivator for GATA-1 in erythropoiesis via? subunit Med1/TRAP220[J].Proc Natl Acad Sci USA,2006,103(49):18504-18509.
[37] GORDON D F,TUCKER E A,TUNDWAL K,et al. MED220/thyroid receptor-associated protein 220 functions as a transcriptional coactivator with Pit-1 and GATA-2 on the thyrotropin-beta promoter in thyrotropes[J].Mol Endocrinol,2006, 20(5):1073-1089.
[38] UDAYAKUMAR T S,BELAKAVADI M,CHOI K H,et al. Regulation of Aurora-A kinase gene expression via GABP recruitment of TRAP220/MED1[J].J Biol Chem,2006,281(21):14691-14699.
[39] LIU X,VORONTCHIKHINA M,WANG Y L,et al. STAGA recruits Mediator to the MYC oncoprotein to stimulate transcription and cell proliferation[J].Mol Cell Biol,2008,28(1):108-121.
[40] ZILLIACUS J,HOLTER E,WAKUI H,et al. Regulation of glucocorticoid receptor activity by 14--3-3-dependent intracellular relocalization of the corepressor RIP140[J].Mol Endocrinol,2001, 15(4):501-511.
[41] WALLBERG A E,YAMAMURA S,MALIK S,et al. Coordination of p300-mediated chromatin remodeling and TRAP/mediator function through coactivator PGC-1alpha[J].Mol Cell,2003, 12(5):1137-1149.
[42] LI H,GADE P,NALLAR S C,et al. The Med1 subunit of transcriptional mediator plays a central role in regulating CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein-beta-driven transcription in response to interferon-gamma[J].J Biol Chem,2008,283(19):13077-13086.
[43] JIA Y,VISWAKARMA N,REDDY J K. Med1 subunit of the mediator complex in nuclear receptor-regulated energy metabolism,liver regeneration,and hepatocarcinogenesis[J].Gene Expr,2014,16(2):63-75.
[44] NATARAJAN K,JACKSON B M,ZHOU H,et al. Transcriptional activation by Gcn4p involves independent interactions with the SWI/SNF complex and the SRB/mediator[J].Mol Cell,1999,4(4):657-664.
[45] ZHANG F,SUMIBCAY L,HINNEBUSCH A G,et al. A triad of subunits from the Gal11/tail domain of Srb mediator is an in vivo target of transcriptional activator Gcn4p[J].Mol Cell Biol,2004,24(15):6871-6886.
[46] MEHTA S,MIKLOS I,SIPICZKI M,et al. The Med8 mediator subunit interacts with the Rpb4 subunit of RNA polymerase II and Ace2 transcriptional activator in Schizosaccharomyces pombe[J].FEBS Lett,2009,583(19):3115-3120.
[47] LI X,YANG R,CHEN H. The Arabidopsis thaliana Mediator subunit MED8 regulates plant immunity to Botrytis Cinerea through interacting with the basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) transcription factor FAMA[J].PLoS One,2018,13(3):e193458.
[48] WANG F,WEI H,TONG Z,et al. Knockdown of NtMed8, a Med8-like gene,causes abnormal development of vegetative? and floral organs in tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L.)[J].Plant Cell Rep,2011,30(11):2117-2129.
[49] GWACK Y,BAEK H J,NAKAMURA H,et al. Principal role of TRAP/mediator and SWI/SNF complexes in Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus RTA-mediated lytic reactivation[J].Mol Cell Biol,2003,23(6):2055-2067.
[50] RAU M J,FISCHER S,NEUMANN C J. Zebrafish Trap230/Med12 is required as a coactivator for Sox9-dependent neural crest,cartilage and ear development[J].Dev Biol,2006,296(1):83-93.
[51] TUTTER A V,KOWALSKI M P,BALTUS G A,et al. Role for Med12 in Regulation of Nanog and Nanog Target Genes[J].Journal of biological chemistry,2009,284(6):3709-3718.
[52] KIM S,XU X,HECHT A,et al. Mediator is a transducer of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling[J].J Biol Chem,2006,281(20):14066-14075.
[53] DING N,ZHOU H,ESTEVE P,et al. Mediator Links Epigenetic Silencing of Neuronal Gene Expression with X-Linked Mental Retardation[J].Molecular cell,2008,31(3):347-359.
[54] DING N,ZHOU H,ESTEVE P O,et al. Mediator links epigenetic silencing of neuronal gene expression with x-linked mental retardation[J].Mol Cell,2008,31(3):347-359.
[55] ZHOU H,KIM S,ISHII S,et al. Mediator modulates Gli3-dependent Sonic hedgehog signaling[J].Mol Cell Biol,2006,26(23):8667-8682.
[56] CARRERA I,JANODY F,LEEDS N,et al. Pygopus activates Wingless target gene transcription through the mediator complex subunits Med12 and Med13[J].Proc Natl Acad Sci USA,2008,105(18):6644-6649.
[57] XU X,ZHOU H,BOYER T G. Mediator is a transducer of amyloid-precursor-protein-dependent nuclear signalling[J].EMBO Rep,2011,12(3):216-222.
[58] CHEN W,ROGATSKY I,GARABEDIAN M J. MED14 and MED1 differentially regulate target-specific gene activation by the glucocorticoid receptor[J].Mol Endocrinol,2006,20(3):560-572.
[59] LAU J F,NUSINZON I,BURAKOV D,et al. Role of metazoan mediator proteins in interferon-responsive transcription[J].Mol Cell Biol,2003,23(2):620-628.
[60] LEE J E,KIM K,SACCHETTINI J C,et al. DRIP150 coactivation of estrogen receptor alpha in ZR-75 breast cancer cells is independent of LXXLL motifs[J].J Biol Chem,2005,280(10):8819-8830.
[61] GRONTVED L,MADSEN M S,BOERGESEN M,et al. MED14 tethers mediator to the N-terminal domain of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma and is required for full transcriptional activity and adipogenesis[J].Mol Cell Biol,2010,30(9):2155-2169.
[62] TOTH J I,DATTA S,ATHANIKAR J N,et al. Selective coactivator interactions in gene activation by SREBP-1a and -1c[J].Mol Cell Biol,2004,24(18):8288-8300.
[63] WANG C,DU X,MOU Z. The Mediator Complex Subunits MED14,MED15,and MED16 Are Involved in Defense Signaling Crosstalk in Arabidopsis[J].Front Plant Sci,2016,7:1947.
[64] LIN X,RINALDO L,FAZLY A F,et al. Depletion of Med10 enhances Wnt and suppresses Nodal signaling during zebrafish embryogenesis[J].Dev Biol,2007,303(2):536-548.
[65] KATO Y,HABAS R,KATSUYAMA Y,et al. A component of the ARC/Mediator complex required for TGF beta/Nodal signalling[J].Nature,2002,418(6898):641-646.
[80] DING N,TOMOMORI-SATO C,SATO S,et al. MED19 and MED26 are synergistic functional targets of the RE1 silencing transcription factor in epigenetic silencing of neuronal gene expression[J].J Biol Chem,2009,284(5):2648-2656.
[81] ZHAO Y,MENG Q,GAO X,et al. Down-regulation of mediator complex subunit 19 (Med19) induces apoptosis in human laryngocarcinoma HEp2 cells in an Apaf-1-dependent pathway[J].Am J Transl Res,2017,9(2):755-761.
[82] ZHANG X,FAN Y,LIU B,et al. Med19 promotes breast cancer cell proliferation by regulating CBFA2T3/HEB expression[J].Breast Cancer,2017,24(3):433-441.
[83] NEVADO J,TENBAUM S P,ARANDA A. hSrb7,an essential human Mediator component,acts as a coactivator for the thyroid hormone receptor[J].Mol Cell Endocrinol,2004,222(1-2):41-51.
[84] HALLBERG M,HU G Z,TRONNERSJO S,et al. Functional and physical interactions within the middle domain of the yeast mediator[J].Mol Genet Genomics,2006,276(2):197-210.
[85] SATO S,TOMOMORI-SATO C,TSAI K L,et al. Role for the MED21-MED7 Hinge in Assembly of the Mediator-RNA Polymerase II Holoenzyme[J].J Biol Chem,2016,291(52):26886-26898.
[86] MO X,KOWENZ-LEUTZ E,XU H,et al. Ras induces mediator complex exchange on C/EBP beta[J].Mol Cell,2004,13(2):241-250.
[87] SHIMOGAWA H,KWON Y,MAO Q,et al. A wrench-shaped synthetic molecule that modulates a transcription factor-coactivator interaction[J].J Am Chem Soc,2004,126(11):3461-3471.
[88] WANG G,BALAMOTIS M A,STEVENS J L,et al. Mediator Requirement for Both Recruitment and Postrecruitment Steps in Transcription Initiation[J].Molecular Cell,2005,17(5):683-694.
[89] GRIFFITHS S J,KOEGL M,BOUTELL C,et al. A systematic analysis of host factors reveals a Med23-interferon-lambda regulatory axis against herpes simplex virus type 1 replication[J].PLoS Pathog,2013,9(8):e1003514.
[90] LIU Z,YAO X,YAN G,et al. Mediator MED23 cooperates with RUNX2 to drive osteoblast differentiation and bone development[J].Nat Commun,2016,7:11149.
[91] CHU Y,GOMEZ R L,HUANG P,et al. Liver Med23 ablation improves glucose and lipid metabolism through modulating FOXO1 activity[J].Cell Res,2014,24(10):1250-1265.
[92] HASEGAWA N,SUMITOMO A,FUJITA A,et al. Mediator subunits MED1 and MED24 cooperatively contribute to pubertal mammary gland development and growth of breast carcinoma cells[J].Mol Cell Biol,2012,32(8):1483-1495.
[93] LEE H K,PARK U H,KIM E J,et al. MED25 is distinct from TRAP220/MED1 in cooperating with CBP for retinoid receptor activation[J].EMBO J,2007,26(15):3545-3557.
[94] RANA R,SURAPUREDDI S,KAM W,et al. Med25 is required for RNA polymerase II recruitment to specific promoters,thus regulating xenobiotic and lipid metabolism in human liver[J].Mol Cell Biol,2011,31(3):466-481.
[95] VERGER A,BAERT J L,VERREMAN K,et al. The Mediator complex subunit MED25 is targeted by the N-terminal transactivation? domain of the PEA3 group members[J].Nucleic Acids Res,2013,41(9):4847-4859.
[96] NAKAMURA Y,YAMAMOTO K,HE X,et al. Wwp2 is essential for palatogenesis mediated by the interaction between Sox9 and? mediator subunit 25[J].Nat Commun,2011,2:251.
[97] SELA D,CONKRIGHT J J,CHEN L,et al. Role for human mediator subunit MED25 in recruitment of mediator to promoters by endoplasmic reticulum stress-responsive transcription factor ATF6alpha[J].J Biol Chem,2013,288(36):26179-26187.
[98] WIEDERHOLD T,LEE M F,JAMES M,et al. Magicin,a novel cytoskeletal protein associates with the NF2 tumor suppressor merlin and Grb2[J].Oncogene,2004,23(54):8815-8825.
[99] GARRETT-ENGELE C M,SIEGAL M L,MANOLI D S,et al. intersex,a gene required for female sexual development in Drosophila,is expressed in both sexes and functions together with doublesex to regulate terminal differentiation[J].Development,2002,129(20):4661-4675.
[100] SATO S,TOMOMORI-SATO C,BANKS C A,et al. A mammalian homolog of Drosophila melanogaster transcriptional coactivator intersex is a subunit of the mammalian Mediator complex[J].J Biol Chem,2003,278(50):49671-49674.
[101] KUUSELO R,SAVINAINEN K,SANDSTROM S,et al. MED29,a component of the mediator complex,possesses both oncogenic and tumor suppressive characteristics in pancreatic cancer[J].Int J Cancer,2011,129(11):2553-2565.
[102] BEADLE E P,STRAUB J A,BUNNELL B A,et al. MED31 involved in regulating self-renewal and adipogenesis of human mesenchymal stem cells[J].Mol Biol Rep,2018.45(5):1545-1550.
[103] ZHANG X,ZHOU W,CHEN Q,et al. Mediator subunit MED31 is required for radial patterning of Arabidopsis roots[J].Proc Natl Acad Sci USA,2018,115(24):E5624-E5633.
[104] EBERHARDY S R,FARNHAM P J. Myc recruits P-TEFb to mediate the final step in the transcriptional activation of the cad promoter[J].J Biol Chem,2002,277(42):40156-40162.
[105] PARK J M,WERNER J,KIM J M,et al. Mediator, not holoenzyme,is directly recruited to the heat shock promoter by HSF upon heat shock[J].Mol Cell,2001,8(1):9-19.
[106] YERGIYEV O,GARIB G,SCHOEDEL K,et al. CDK8 Expression in Extrauterine Leiomyosarcoma Correlates With Tumor Stage and Progression[J].Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol,2018,26(3):161-164.
[107] KOLESKE A J,BURATOWSKI S,NONET M, et al. A novel transcription factor reveals a functional link between the RNA polymerase II CTD and TFIID[J].Cell,1992,69(5):883-894.
[108] RANISH J A,YUDKOVSKY N,HAHN S. Intermediates in formation and activity of the RNA polymerase II preinitiation complex:holoenzyme recruitment and a postrecruitment role for the TATA box and TFIIB[J].Genes Dev,1999,13(1):49-63.
[109] EYCHENNE T,NOVIKOVA E,BARRAULT M B,et al. Functional interplay between Mediator and TFIIB in preinitiation complex assembly in relation to promoter architecture[J].Genes Dev,2016,30(18):2119-2132.
[110] AKOULITCHEV S,CHUIKOV S,REINBERG D. TFIIH is negatively regulated by cdk8-containing mediator complexes[J].Nature,2000,407(6800):102-106.
[111] JANG M K,MOCHIZUKI K,ZHOU M,et al. The bromodomain protein Brd4 is a positive regulatory component of P-TEFb and stimulates RNA polymerase II-dependent transcription[J].Molecular cell,2005,19(4):523-534.
[112] YANG Z,YIK J H N,CHEN R,et al. Recruitment of P-TEFb for stimulation of transcriptional elongation by the bromodomain protein Brd4[J].Molecular cell,2005,19(4):535-545.
[113] DONNER A J,EBMEIER C C,TAATJES D J,et al. CDK8 is a positive regulator of transcriptional elongation within the serum response network[J].Nat Struct Mol Biol,2010,17(2):194-201.
[114] GUGLIELMI B,SOUTOURINA J,ESNAULT C,et al. TFIIS elongation factor and Mediator act in conjunction during transcription initiation in vivo[J].Proc Natl Acad Sci USA,2007, 104(41):16062-16067.
[115] BENTLEY D L.Coupling mRNA processing with transcription in time and space[J].Nat Rev Genet,2014,15(3):163-175.
[116] BEN-YISHAY R,ASHKENAZY A J,SHAV-TAL Y. Dynamic encounters of genes and transcripts with the nuclear pore[J].Trends genet,2016,32(7):419-431.
[117] SCHNEIDER M,HELLERSCHMIED D,SCHUBERT T,et al. The nuclear pore-associated TREX-2 complex employs mediator to regulate gene expression[J].Cell,2015,162(5):1016-1028.
[118] SOUTOURINA J. Transcription regulation by the Mediator complex[J].Nature reviews molecular cell biology,2017,19(4):262-274.
[119] 汪? 煒,尹景雯,劉艾潔,等.中介體復合物——真核轉錄調控中的中央控制器[J].中國細胞生物學學報,2011(6):597-607.
[120] KLUMPER N,SYRING I,OFFERMANN A,et al. Differential expression of Mediator complex subunit MED15 in testicular germ cell tumors[J].Diagn Pathol,2015,10:165.
[121] siRNA-mediated silencing of CDK8 inhibits proliferation and growth in breast cancer cells[Retraction][J].Int J Clin Exp Pathol,2018,11(3):1836.
收稿日期:2019-01-06
基金項目:國家自然科學基金項目(31470731)
作者簡介:王? 雯(1993-),女,山西長子人,在讀碩士研究生,研究方向為生物化學與分子生物學,(電話)18202278662(電子信箱)18202278662@163.com。

