1型糖尿病患者血睪酮與低度炎癥狀態及微血管病變的關系分析
蔡填 王素妍 李桂平 賴玉林
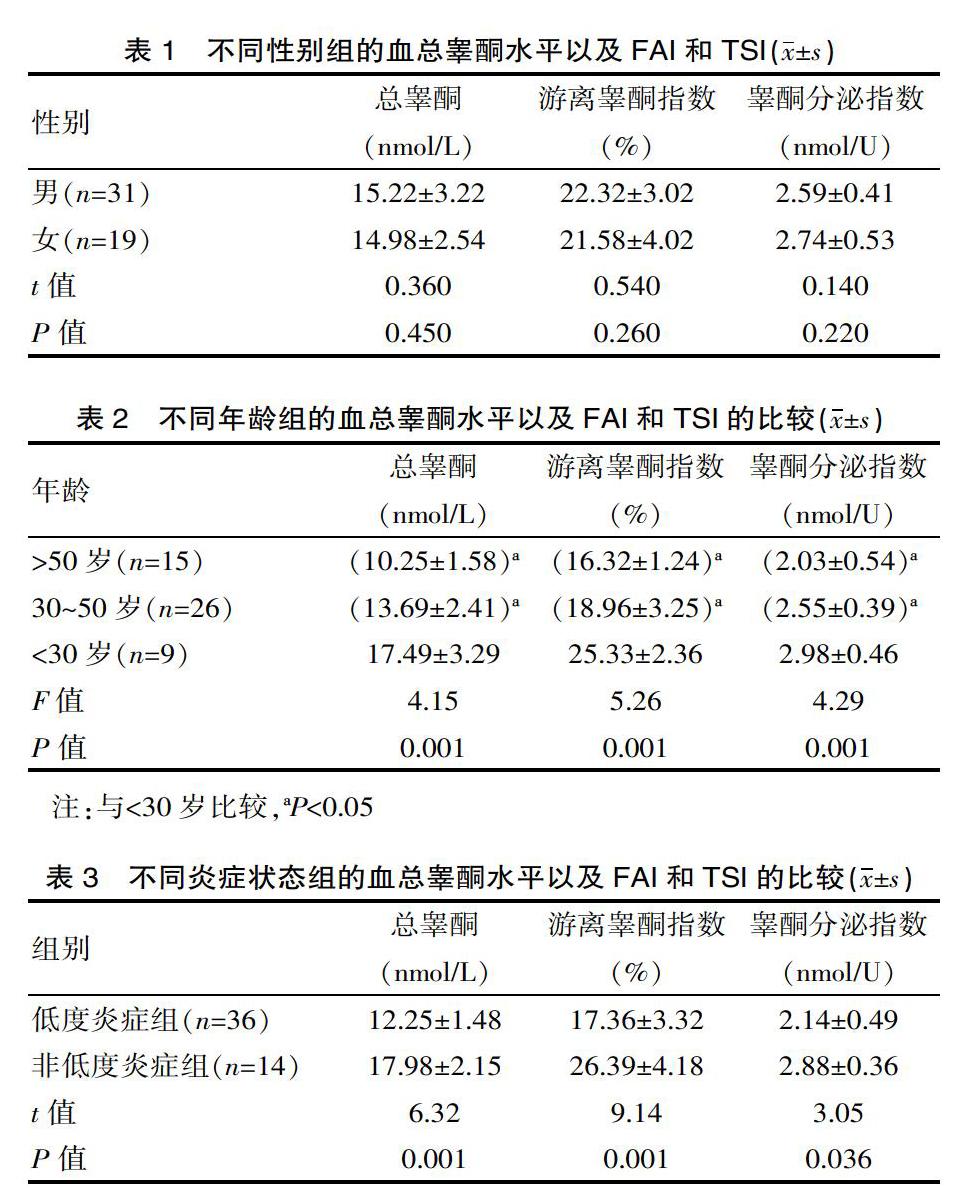

[摘要] 目的 探討I型糖尿病患者血睪酮與臨床指標包括性別、年齡、炎性指標以及微血管病變的關系。 方法 隨機對該院2015年1月—2019年1月間診治的I型糖尿病患者50例,根據患者的性別、年齡、炎性指標CRP、血脂以及是否合并微血管病變(糖尿病腎病、糖尿病周圍神經病變、糖尿病視網膜病變)進行分組,對比各組的血總睪酮水平以及游離睪酮指數(FAI)和睪酮分泌指數(TSI)的差異。 結果 不同性別組的總睪酮水平以及游離睪酮指數和睪酮分泌指數比較差異無統計學意義(P>0.05);年齡段為>50歲組的總睪酮水平降低較為明顯,為(10.25±1.58)nmol/L,其次是30~50歲組,FAI和TSI亦有所降低,兩組與<30歲組比較差異有統計學意義(P<0.05);根據血清CRP水平,將患者分為低度炎癥組(CRP≥2.0 mg/L)和非低度炎癥組, 低度炎癥組的血清總睪酮水平較低,為(12.25±1.48)nmol/L,明顯低于非低度炎癥組(P<0.05),同時兩組患者的FAI和TSI差異有統計學意義(P<0.05);合并微血管病變組的血睪酮水平明顯降低,同時FAI和TSI亦低于無微血管病變組(P<0.05)。結論I型糖尿病患者存在明顯的睪酮代謝紊亂,并與體內的炎癥狀態關系密切,共同促進糖尿病并發癥的發生。
[關鍵詞] I型糖尿病;血睪酮;微血管病變
[中圖分類號] R587.2? ? ? ? ? [文獻標識碼] A? ? ? ? ? [文章編號] 1672-4062(2020)02(b)-0004-03
[Abstract] Objective To investigate the relationship between blood testosterone and clinical indicators including type, age, inflammatory indicators and microangiopathy in patients with type 1 diabetes. Methods From January 2015 to January 2019 Fifty patients with type I diabetes diagnosed and treated in our hospital were randomly divided into two groups according to their gender, age, inflammatory index CRP, blood lipids, and whether they were associated with microangiopathy (diabetic nephropathy, diabetic peripheral neuropathy, and diabetic retinopathy). The total blood testosterone levels and differences in free testosterone index (FAI) and testosterone secretion index (TSI) of the groups were different. Results There was no significant difference in the total testosterone levels, free testosterone index and testosterone secretion index between different gender groups(P>0.05); the total testosterone levels in the age group> 50 years were significantly reduced, which was (10.25±1.58)nmol/L, followed by the 30-50 years old group, FAI and TSI also decreased, the differences between the two groups were statistically significant compared with the <30 year old group (P<0.05); patients were classified as low according to serum CRP levels; the level of serum total testosterone in the low-inflammatory group (CRP≥2.0 mg/L) and the non-low-inflammatory group was low (12.25±1.48) nmol/L, which was significantly lower than the non-low-inflammatory group(P<0.05), and there were statistical differences in FAI and TSI between the two groups of patients (P<0.05); blood testosterone levels in the combined microangiopathy group were significantly reduced, while FAI and TSI were also lower than those in the non-microvascular lesion group(P<0.05). Conclusion Patients with type I diabetes have obvious disorder of testosterone metabolism, which is closely related to the inflammatory state in the body, and jointly promote the occurrence of complications of diabetes.
[Key words] Type I diabetes; Blood testosterone; Microangiopathy
睪酮是一種類固醇激素,在男性睪丸或女性卵巢中分泌,具有維持骨骼和肌肉強度和質量的作用[1]。對于男性糖尿病患者,患者容易出現不同程度的血睪酮水平下降,并出現性功能減退、疲倦、記憶力減退和體重減輕等表現,對于出現此類癥狀的1型糖尿病患者,需要密切監測患者血清睪酮的變化,而對伴有性功能在減退的患者,則需要使用睪酮替代治療[2]。有研究顯示[3],對此類患者使用睪酮替代治療后,可以明顯改善患者的胰島素抵抗以及炎癥反應狀態,提示睪酮在提高糖尿病患者胰島素敏感性中具有獨特的作用。因此,該研究選取2015年1月—2019年1月收治的50例患者,深入探討I型糖尿病患者血睪酮與臨床指標包括性別、年齡、炎性指標以及微血管病變的關系。

