番木瓜鎂離子轉運蛋白家族基因鑒定及轉錄特征分析
周平 岳晶晶 顏少賓 郭瑞 金光
摘要:鎂離子轉運蛋白(Magnesium transporter,MGT)是植物體內鎂離子吸收運輸的重要轉運子。為系統研究番木瓜MGT家族(CpMGTs)特征,鑒定了基因家族成員并分析其蛋白特征和基因轉錄模式。結果表明番木瓜基因組含5個CpMGT家族成員(CpMGTa-CpMGTe),氨基酸數387~491個,分子量43.95~54.84 KD,定位于細胞核、細胞質、葉綠體、過氧化物酶體等亞細胞結構。基于轉錄組測序,發現CpMGTs的表達具有組織特異性,成熟葉、幼花與根器官中優勢表達的CpMGT不同。根、花器官中CpMGTc表達具有性別差異性;CpMGTb和CpMGTd跨季節轉錄變化在雌雄番木瓜幼花中也存在特定差別。這些發現揭示CpMGTs表達模式及性別差異性表達特征,為研究基因功能奠定基礎。
關鍵詞:番木瓜;鎂離子轉運蛋白;表達;性別
中圖分類號:S667.9? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?文獻標識碼:A? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? 文章編號:2095-5774(2023)01-0001-06
Identification and Transcriptional Characteristics Analyses of Magnesium
Transporters Gene Family in Carica papaya
Zhou Ping1,Yue Jingjing2,Yan Shaobin1,Guo Rui1,Jin Guang1*
(1Fruit Research Institute,Fujian Academy of Agricultural Sciences / Research Centre for Engineering Technology of Fujian Deciduous Fruits,Fuzhou,Fujian 350013,China;
2Center for Genomics and Biotechnology / Fujian Provincial Key Laboratory of Haixia Applied Plant Systems Biology / Key Laboratory of Genetics,Breeding and Multiple Utilization of Crops,Ministry of Education,Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University,Fuzhou,Fujian 350002,China)
Abstract:Magnesium Transporter (MGT) was charactered as an important transporter of magnesium absorption and transportation in plant. To investigate characteristics of papaya (Carica papaya) magnesium transporters (CpMGTs),their gene family members were identified,and their protein characteristics and gene transcriptional patterns were analyzed. The results showed that five CpMGT members (CpMGTa-CpMGTe) with 387-491 amino acids and molecular weight of 43.95-54.84 KD,which were predicted to be located in nucleus,cytoplasm,chloroplast,peroxisome and other subcellular strucures,existde in papaya genome. According to the transcriptomic sequencing and analyses,tissue-specific expressional patterns of CpMGTs were observed in different organs,and the predominantly expressed CpMGT members were distinct among mature leaves,young flowers and roots. CpMGTs transcriptional profiles had showed specific sexual differences,i.e. CpMGTc displayed sex-biased gene expression in roots and flowers,while CpMGTb and CpMGTd showed their seasonal change tendencies of gene transcription in distinct manner between male and female papayas. All these findings charactered the expressional patterns and the special sex bias in CpMGTs transcription,laying the foundation for functional study of CpMGTs.
Key words:Papaya;Magnesium transporter;Expression;Sexes
鎂是植物必需元素,其以鎂離子形式被攝取后利用于植物生長發育及重要生理代謝反應。研究表明鎂離子是構成葉綠素的重要組分;也是數百種生理代謝酶的激活劑,參與植物新陳代謝[1]。缺鎂嚴重影響葉綠素合成,干擾光合產物分配與韌皮部運輸,抑制植株生長及產量[2,3]。植物中的鎂離子轉運蛋白(Magnesium Transporter,MGT)被認為是最重要的鎂離子轉運載體。最早在擬南芥中鑒定報道10個MGT家族成員[4]。此后系統分析水稻、玉米、甘蔗、番茄、油菜、梨等作物發現植物MGTs家族可聚類為五大分支[5-10]。不同家族成員功能偏向各不相同,如控制根系對Mg2+的吸收[11,12]、拮抗抑制金屬毒害[13]、參與配子發育[10,14,15]、維持葉肉葉綠體Mg2+平衡及光合反應[16-18]。
番木瓜(Carica papaya L.)原產熱帶美洲,在我國福建、臺灣、廣東、云南、海南等地有產業化栽培。番木瓜是有性別的水果作物,其性別類型可分為雌性、雄性和兩性。雌株、雄株和兩性株分別開雌花、雄花和完全花。不同性別類型植株間常存在形態、生理代謝和遺傳學差異[19]。目前發現番木瓜CpMGT1具有Mg2+轉運活性[20],但未報道該物種其它MGT成員情況。
為系統研究番木瓜鎂離子轉運蛋白(CpMGT)基因家族轉錄表達特征,鑒定全基因組范圍內的鎂離子轉運蛋白,并分別在雌雄番木瓜植株上檢測CpMGTs表達,首次發現部分CpMGT成員表達具有性別差異性。這些發現為深入研究番木瓜鎂離子轉運蛋白功能奠定基礎。
1? 材料與方法
1.1? CpMGTs鑒定與表征預測
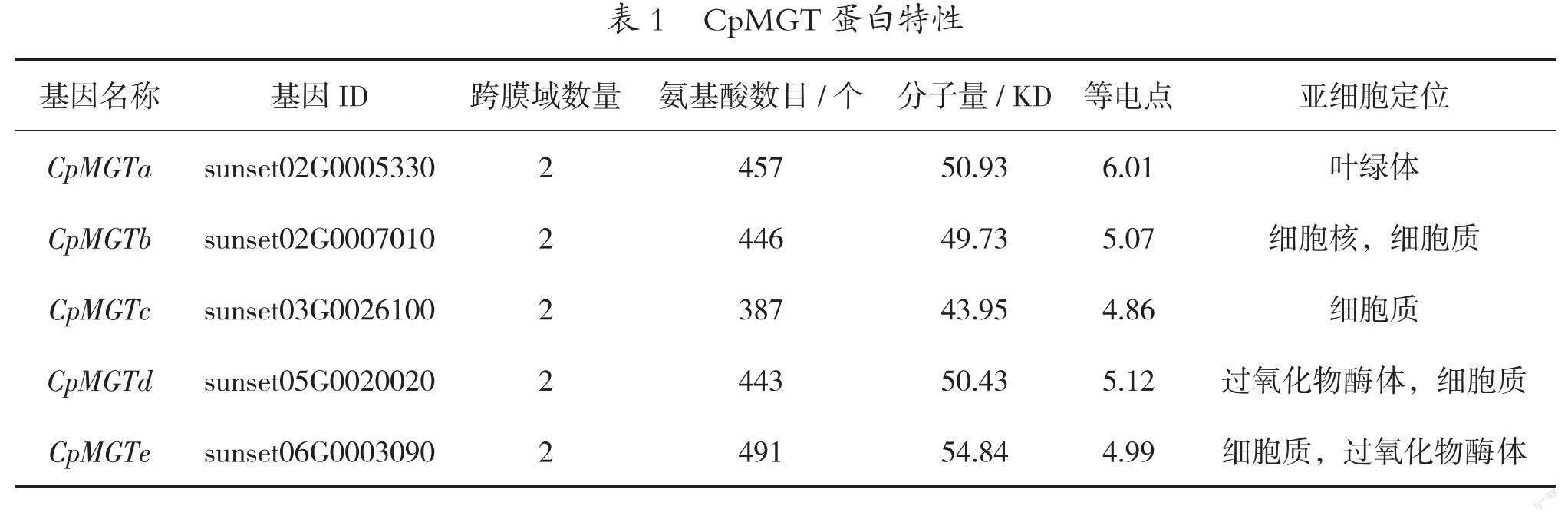
以擬南芥、水稻MGT序列[4,5]為參考,BLASP比對Sunset番木瓜基因組轉錄本翻譯蛋白數據集[21],篩選比對結果E-value值小于E-10且相似度大于70%的編碼蛋白為CpMGTs。Protparam[22]計算CpMGTs氨基酸數、相對分子質量以及理論等電點,TMHMM[23]預測CpMGTs跨膜區及跨膜數,YLoc+[24]預測CpMGTs亞細胞定位。
1.2? 試驗植物材料
以福建農林大學中華園試驗設施大棚所種兩年生‘中黃番木瓜(Carica papaya var. Zhonghuang)為試驗材料。‘中黃番木瓜系實生繁殖,播種的‘中黃種子由福建農林大學基因組與生物技術中心通過多代人工授粉全同胞雜交獲得,以保證后代群體中的雄株、雌株個體遺傳背景接近一致[19]。
1.3? CpMGTs基因表達特征分析
1.3.1? 花、葉、根CpMGTs轉錄表達特征分析
分析雌雄異株‘中黃番木瓜雄株、雌株幼花(采集未見雌雄蕊原基分化的極早期花,花徑小于2 mm)、成熟葉及根組織CpMGTs表達特征。試驗測試幼花、葉、根樣本各3個生物學重復。取自1株番木瓜植株的樣品為1個生物學重復,試驗共采集3株雄株和3株雌株樣本進行轉錄組測序。所得測序數據,參照報道方法[25]比對番木瓜Sunset參考基因組[21],‘DEseq2篩選多重校驗校正后P < 0.05且表達變化倍數大于2或者小于1/2的基因為兩組差異表達基因。
最終本文所用CpMGTs基因表達水平以樣本轉錄組分析所得的FPKM(Fragments Per Kilobase per Million,每百萬讀段中來自于某基因每千堿基長度的讀段數)數值衡量。
1.3.2? 春、夏、冬三季CpMGTs轉錄表達分析
于2019年4月17日、8月13日和2020年1月3日采集相同‘中黃番木瓜試驗植株春、夏、冬三季幼花,轉錄組測序分析CpMGTs基因表達。試驗步驟及方法同1.3.1。
2? 結果與分析
2.1 CpMGTs鑒定與理化特性預測
同源相似性比對共鑒定獲得5個CpMGT,依據其編碼基因所處染色體位置依次命名為CpMGTa-CpMGTe(表1)。所得CpMGTs均含2個跨膜結構,蛋白氨基酸數387~491個,分子量43.95~54.84 KD,等電點4.86~6.01,預測蛋白定位于細胞核、細胞質、葉綠體、過氧化物酶體等不同的亞細胞結構。
2.2 CpMGTs轉錄表達特征分析
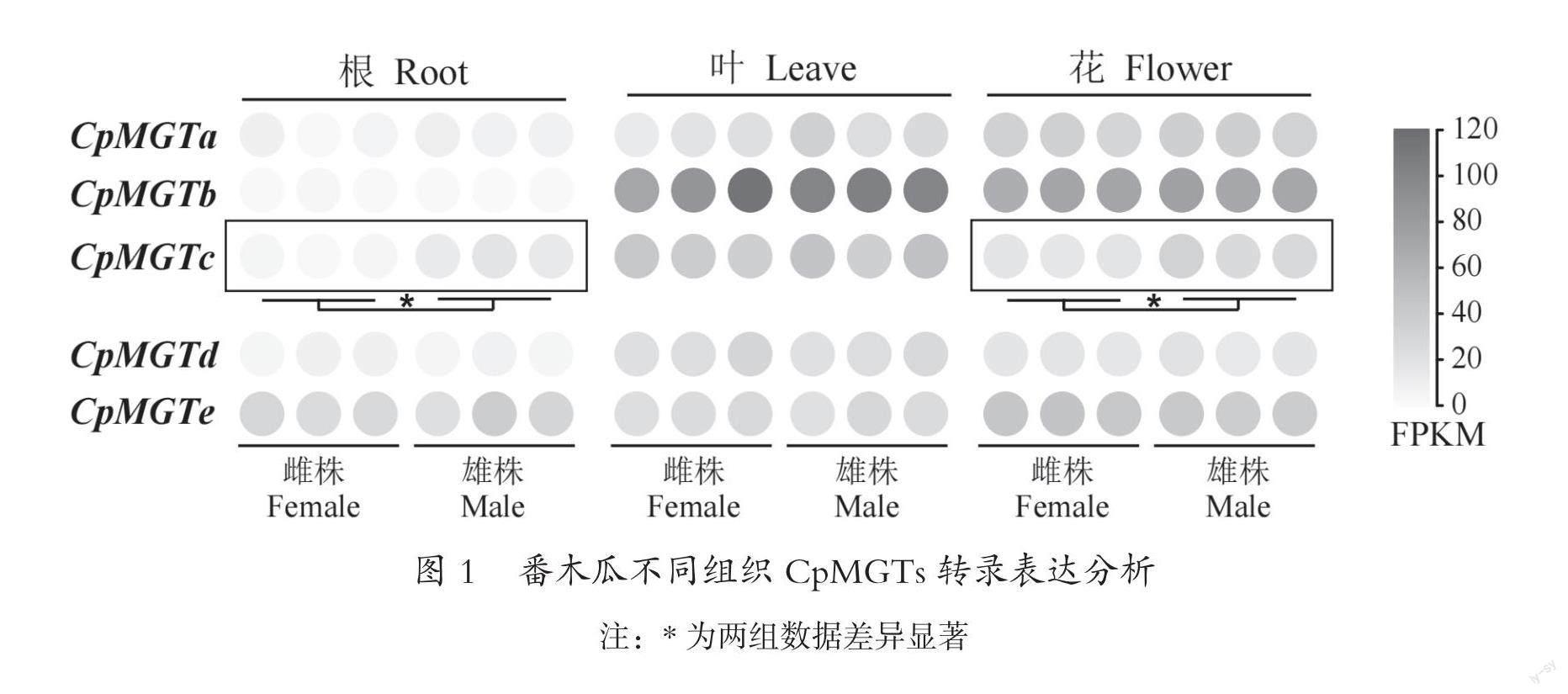
轉錄譜分析番木瓜花、葉、根器官CpMGTs表達(圖1),發現地上部分和地下部分CpMGTs表達模式存在特定差異。番木瓜葉、花中CpMGTs表達水平整體高于根器官中基因表達。其中,CpMGTb在葉和花中優勢表達,表達水平高于其他家族成員;而CpMGTe在根中表達相對較強。
比較不同性別番木瓜CpMGTs在所檢測的器官中的轉錄表達水平,發現CpMGTc轉錄具有性別差異性,即雄株番木瓜根器官、花器官中的CpMGTc mRNA轉錄豐度顯著高于雌株;而其他家族成員無此現象。
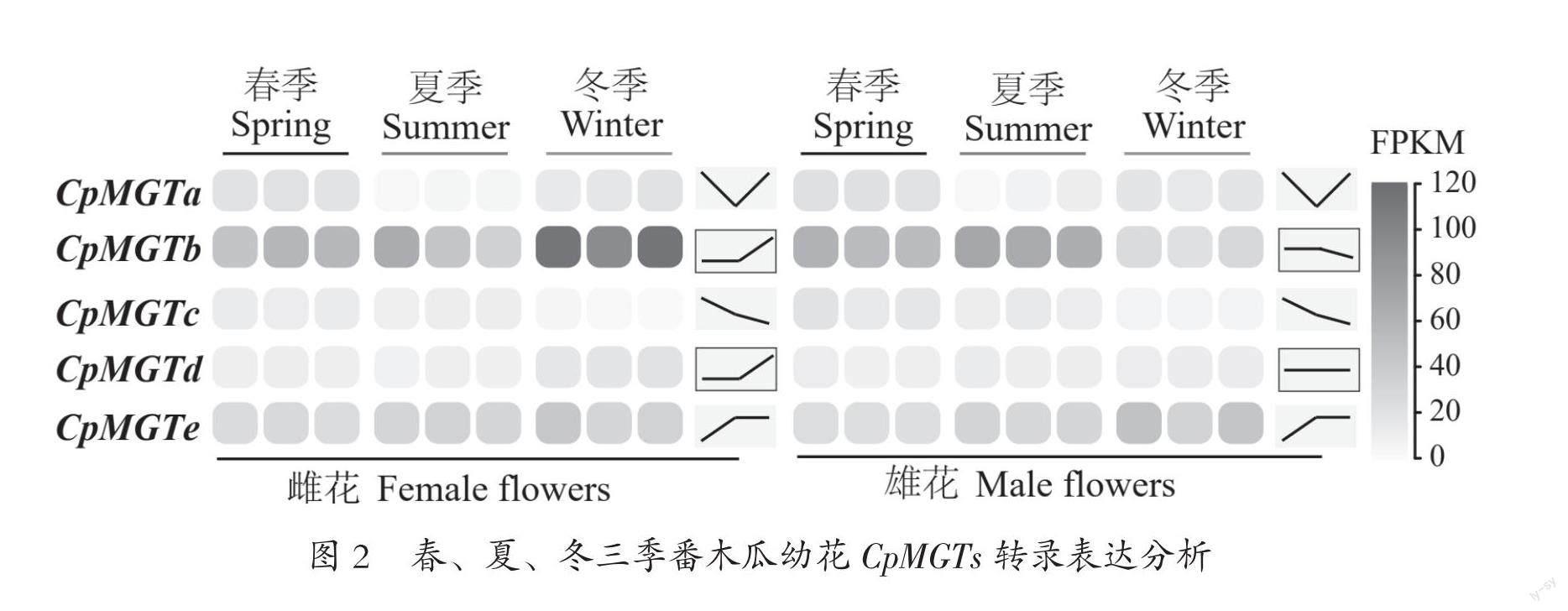
追蹤調查雌雄異株番木瓜CpMGTs春、夏、冬三季轉錄表達動態(圖2),觀測到的CpMGTa(先降后升)、CpMGTc(持續下降)、CpMGTe(先升后穩)基因轉錄變化趨勢在雌雄株幼花間無差異。但CpMGTb和CpMGTd轉錄在不同性別番木瓜幼花中存在特定差別。轉錄譜分析結果表明:冬季雌花CpMGTb轉錄上升,雄花CpMGTb轉錄減弱;冬季雌花CpMGTd表達水平高于春、夏兩季,而雄花CpMGTd三季表達水平接近。
3? 討論
MGT是古老的基因,從水生原始藻類至其后的陸生植物一直存在。研究認為由MGT介導的鎂吸收和鎂利用在植物生長發育和生命活動過程中發揮了重要的作用[26]。基于同源相似性比對方法,本研究在番木瓜基因組中共鑒定出5個高置信度CpMGT。預測這些CpMGTs編碼蛋白性質具有差異,且定位于不同的細胞結構組分(細胞核、細胞質、葉綠體、過氧化物酶體),這表明CpMGTs很可能是以協作的方式參與細胞內外鎂離子的平衡過程。進一步的轉錄譜分析結果發現番木瓜地上部分和地下部分CpMGTs表達模式具有明顯的差異,CpMGTb和CpMGTe分別是地上部分葉、花和地下根器官中相對優勢表達的CpMGT,可能在對應器官的鎂離子攝取、運輸過程中發揮主要作用。
本研究還發現番木瓜植株中部分CpMGTs表達具有性別差異性。與多種果樹不同,番木瓜具有性別,其性別是由性染色體組合遺傳決定,XX雌性,XY雄性[21]。試驗所用‘中黃番木瓜系多代人工授粉全同胞雜交得到的雌雄異株品種,其雌雄株后代除XY性染色體非重組性別決定區段外,常染色體和假常染色體基因組序列基本一致[19]。本研究使用遺傳背景接近的雌雄植株材料檢測CpMGTs表達仍能發現性別差異性轉錄,說明番木瓜性別差異對常染色體上的CpMGT表達能產生特定影響。持續追蹤三季CpMGTs轉錄表達,觀測到兩個CpMGT在不同季節雌、雄株幼花樣本中的轉錄表達變化趨勢不同,亦暗示番木瓜性別分化可能會對CpMGTs運輸鎂離子能力形成影響,這是否會造成不同性別番木瓜鎂積累與鎂利用的差異值得后續研究進一步關注。
參考文獻:
[1]Chen Z,Peng W,Li J,et al. Functional dissection and transport mechanism of magnesium in plants[J]. Seminars in Cell & Developmental Biology,2018(74):142-152.
[2]Huang J,Xu J,Ye X,et al. Magnesium deficiency affects secondary lignification of the vascular system in Citrus sinensis seedlings[J]. Trees,2019,33(1):171-182.
[3]Zhang B,Cakmak I,Feng J,et al. Magnesium deficiency reduced the yield and seed germination in wax gourd by affecting the carbohydrate translocation[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science,2020(11):797.
[4]Li L,Tutone A,Drummond R,et al. A novel family of magnesium transport genes in Arabidopsis[J]. The Plant Cell,2001,13(12):2761-2775.
[5]Saito T,Kobayashi NI,Tanoi K,et al. Expression and functional analysis of the CorA-MRS2-ALR-type magnesium transporter family in rice[J]. Plant and Cell Physiology,2013,54(10):1673-1683.
[6]Li H,Du H,Huang K,et al. Identification,and functional and expression analyses of the CorA/MRS2/MGT-type magnesium transporter family in maize[J]. Plant and Cell Physiology,2016,57(6):1153-1168.
[7]Wang Y,Hua X,Xu J,et al. Comparative genomics revealed the gene evolution and functional divergence of magnesium transporter families in Saccharum[J]. BMC genomics,2019,20(1):1-18.
[8]Zhang L,Wen A,Wu X,et al. Molecular identification of the magnesium transport gene family in Brassica napus[J]. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry,2019(136):204-214.
[9]Regon P,Chowra U,Awasthi J,et al. Genome-wide analysis of magnesium transporter genes in Solanum lycopersicum[J]. Computational Biology and Chemistry,2019(80):498-511.
[10]Zhao Z,Wang P,Jiao H,et al. Phylogenetic and expression analysis of the magnesium transporter family in pear,and functional verification of PbrMGT7 in pear pollen[J]. The Journal of Horticultural Science and Biotechnology,2018,93(1):51-63.
[11]Mao D,Chen J,Tian L,et al. Arabidopsis transporter MGT6 mediates magnesium uptake and is required for growth under magnesium limitation[J]. The Plant Cell,2014,26(5):2234-2248.
[12]Mao D,Tian L,Li L,et al. AtMGT7:an Arabidopsis gene encoding a low‐affinity magnesium transporter[J]. Journal of integrative plant biology,2008,50(12):1530-1538.
[13]Deng W,Luo K,Li D,et al. Overexpression of an Arabidopsis magnesium transport gene,AtMGT1,in Nicotiana benthamiana confers Al tolerance[J]. Journal of experimental botany,2006,57(15):4235-4243.
[14]Chen J,Li L,Liu Z,et al. Magnesium transporter AtMGT9 is essential for pollen development in Arabidopsis[J]. Cell research,2009,19(7):887-898.
[15]Xu X,Wang B,Lou Y,et al. Magnesium Transporter 5 plays an important role in Mg transport for male gametophyte development in Arabidopsis[J]. The Plant Journal,2015,84(5):925-936.
[16]Sun Y,Yang R,Li L,et al. The magnesium transporter MGT10 is essential for chloroplast development and photosynthesis in Arabidopsis thaliana[J]. Molecular Plant,2017,10(12):1584-1587.
[17]Conn S,Conn V,Tyerman S,et al. Magnesium transporters,MGT2/MRS2-1 and MGT3/MRS2-5,are important for magnesium partitioning within Arabidopsis thaliana mesophyll vacuoles[J]. New Phytologist,2011,190(3):583-594.
[18]Li J,Yokosho K,Liu S,et al. Diel magnesium fluctuations in chloroplasts contribute to photosynthesis in rice[J]. Nature Plants,2020,6(7):848-859.
[19]Zhou P,Zhang X,Fatima M,et al. DNA methylome and transcriptome landscapes revealed differential characteristics of dioecious flowers in papaya[J]. Horticulture Research,2020,7(1):81.
[20]許迎港,鄒智,郭靜遠,等. 番木瓜鎂離子轉運蛋白基因CpMGT1的克隆與功能分析[J]. 熱帶作物學報,2022,43(6):1114-1121.
[21]Yue J,VanBuren R,Liu J,et al. SunUp and Sunset genomes revealed impact of particle bombardment mediated transformation and domestication history in papaya[J]. Nature Genetics,2022,54(5):715-724.
[22]Gasteiger E,Hoogland C,Gattiker A,et al. Protein Identification and Analysis Tools on the Expasy Server:The Proteomics Protocols Handbook[M]. Totowa:Humana Press,2005.
[23]Mller S,Croning MDR and Apweiler R. Evaluation of methods for the prediction of membrane spanning regions[J]. Bioinformatics,2001,17(7):646-653.
[24]Briesemeister S,Rahnenführer J and Kohlbacher O. Going from where to why—interpretable prediction of protein subcellular localization[J]. Bioinformatics,2010,26(9):1232-1238.
[25]周平,林志楷,郭瑞,等. 低溫處理對桃樹葉片基因表達及類黃酮合成代謝的影響[J]. 農業生物技術學報,2021,29(7):1283-1294.
[26]叢悅璽,駱東峰,陳坤明,等. 生物鎂離子轉運體研究進展[J]. 農業生物技術學報,2012,20(7):837-848.
(責任編輯:馮新)

