早期腸內營養與延遲腸內營養對重癥急性胰腺炎患者腹內高壓及免疫功能的影響
許守明
241001安徽省蕪湖市,皖南醫學院附屬弋磯山醫院
?
·論著·
早期腸內營養與延遲腸內營養對重癥急性胰腺炎患者腹內高壓及免疫功能的影響
許守明
241001安徽省蕪湖市,皖南醫學院附屬弋磯山醫院
【摘要】目的比較早期腸內營養與延遲腸內營養對重癥急性胰腺炎(SAP)患者腹內高壓及免疫功能的影響。方法選取2013年1月—2014年12月在皖南醫學院附屬弋磯山醫院急診內科就診的SAP患者40例,按照隨機數字表法將其分為觀察組和對照組,各20例。在綜合治療的基礎上,觀察組患者入院48 h后行腸內營養支持治療,對照組患者在入院后5 d予腸內營養支持。兩組腸內營養支持干預療程均為2周。分別記錄兩組治療前后腹內壓(IAP)及腹內高壓發生率;檢測兩組治療前后血清免疫球蛋白(IgG、IgM、IgA)及外周血T淋巴細胞亞群)水平;記錄兩組治療前后血淀粉酶、體質指數(BMI)及視覺模擬評分(VAS)。結果兩組患者治療前IAP比較,差異無統計學意義(P>0.05);治療后,觀察組IAP低于對照組(P<0.05);且兩組患者IAP均低于同組治療前(P<0.05)。兩組患者第1天和第14天腹內高壓發生率比較,差異均無統計學意義(P>0.05);觀察組第7天和第10天腹內高壓發生率低于對照組(P<0.05)。治療前,兩組患者血清免疫球蛋白IgG、IgM、IgA及外周血T淋巴細胞亞群水平比較,差異均無統計學意義(P>0.05);治療后,觀察組血清免疫球蛋白IgG、IgM、IgA及外周血T淋巴細胞亞群水平均高于對照組(P<0.05);兩組治療后血清免疫球蛋白IgG、IgM、IgA及外周血T淋巴細胞亞群水平均高于同組治療前(P<0.05)。治療前,兩組血淀粉酶、BMI及VAS比較,差異均無統計學意義(P>0.05);治療后,觀察組血淀粉酶、BMI及VAS均低于對照組(P<0.05);兩組治療后血淀粉酶、BMI及VAS均較治療前降低(P<0.05)。治療過程中對照組患者有5例發生不良反應,觀察組有3例發生不良反應,兩組不良反應發生率比較,差異無統計學意義(χ2=0.625,P>0.05)。結論早期腸內營養可以明顯降低SAP患者腹內高壓發生率,調節并改善機體的免疫功能,從而改善患者的預后情況。
【關鍵詞】腸道營養;重癥急性胰腺炎;腹內高壓;免疫活性
許守明.早期腸內營養與延遲腸內營養對重癥急性胰腺炎患者腹內高壓及免疫功能的影響[J].中國全科醫學,2016,19(14):1711-1714.[www.chinagp.net]
Xu SM.Influence of early enteral nutrition and delayed enteral nutrition on intra-abdominal hypertension and immune function of patients with severe acute pancreatitis[J].Chinese General Practice,2016,19(14):1711-1714.
急性胰腺炎是指多種病因引起的胰酶激活,以胰腺局部炎性反應為特征的疾病[1]。多數患者的病程具有自限性,而其中20%~30%的患者會發展為重癥急性胰腺炎(SAP),常并發多器官功能衰竭,其病死率高達20%左右[2]。目前研究已經證實,SAP患者發病過程中存在腹內壓升高及免疫功能損害,而腹內高壓的發生率及免疫功能損害的嚴重程度與患者的預后密切相關[3]。近年來,研究調查顯示腸內營養具有不刺激胰腺分泌、調節免疫功能紊亂及保護腸道黏膜屏障等功能[4-5],被廣泛應用于SAP臨床治療,但是關于腸內營養干預的時間點尚有很大的爭議。本研究旨在探討早期腸內營養與延遲腸內營養對SAP患者腹內高壓水平及免疫功能的影響,以期為SAP患者腸內營養時機的選擇提供一定的參考依據。
1對象與方法
1.1臨床資料選取2013年1月—2014年12月在皖南醫學院附屬弋磯山醫院急診內科就診的SAP患者40例。患者均符合納入標準:(1)符合SAP診斷標準[6];(2)發病72 h內入院;(3)年齡≤75歲;(4)簽署知情同意書。排除標準:(1)存在嚴重心、肝、腎或其他全身系統性疾病;(2)妊娠或哺乳期婦女;(3)正在參加其他藥物試驗;(4)在干預時間內死亡。將患者按照隨機數字表法分為觀察組和對照組,各20例。其中觀察組男13例,女7例;年齡23~69歲,平均年齡(43.8±14.6)歲;病因:膽源性10例,酒精性5例,暴飲暴食4例,不明原因1例;病程:3~58 h,平均病程(30.6±10.0)h;體質指數(BMI):20.7~32.6 kg/m2,平均BMI(25.3±1.2)kg/m2。對照組男12例,女8例;年齡26~72歲,平均年齡(45.9±13.3)歲;病因:膽源性11例,酒精性4例,暴飲暴食3例,不明原因2例;病程:5~63 h,平均病程(32.4±11.6)h;BMI:21.2~31.7 kg/m2,平均BMI(25.6±1.4)kg/m2。兩組患者性別、年齡、病因、病程、BMI比較,差異均無統計學意義(χ2=0.11、t=0.48、χ2=0.63、t=0.53、t=0.73,P>0.05)。
1.2治療方法患者入院后均予禁食、胃腸減壓、抗感染及抑制胰酶分泌、糾正電解質和酸堿平衡紊亂等治療。兩組患者在X線引導下放置鼻-空腸管至Treitz韌帶下30~40 cm處。觀察組患者入院48 h后行腸內營養支持治療。營養物質的供應遵循由少到多、由淡到濃、由慢到快的原則;第1天予糖鹽水500 ml,按照40~60 ml/h的速度滴入,之后改為500 ml百普力(荷蘭紐迪希亞制藥,批號:國藥準字H20010285),2次/d。對照組患者在入院后5 d予腸內營養支持,具體方法同觀察組。兩組腸內營養支持干預療程均為2周。


2結果
2.1兩組IAP及腹內高壓發生率比較兩組患者治療前IAP比較,差異無統計學意義(P>0.05);治療后,觀察組IAP低于對照組,差異有統計學意義(P<0.05);且兩組患者IAP均低于同組治療前,差異有統計學意義(P<0.05,見表1)。兩組患者第1天和第14天腹內高壓發生率比較,差異均無統計學意義(P>0.05);觀察組第7天和第10天腹內高壓發生率低于對照組,差異均有統計學意義(P<0.05,見表2)。

Table1ComparisonofIAPbetweenthetwogroupsbeforeandaftertreatment

組別例數治療前治療后對照組2018.6±4.315.9±1.2a觀察組2019.1±3.613.2±2.9at值0.403.85P值0.69<0.05
注:與同組治療前比較,aP<0.05
表2兩組治療前后腹內高壓發生率比較〔n(%)〕
Table 2Comparison of the incidence rate of intra-abdominal pressure between the two groups before and after treatment

組別例數第1天第7天第10天第14天對照組2014(70)13(65)10(50)5(25)觀察組2012(60) 6(30) 4(20) 2(10)χ2值0.444.913.961.56P值0.510.030.040.21

2.3兩組血淀粉酶、腹痛及BMI比較治療前,兩組血淀粉酶、BMI及VAS比較,差異均無統計學意義(P>0.05);治療后,觀察組血淀粉酶、BMI及VAS均低于對照組,差異有統計學意義(P<0.05);兩組治療后血淀粉酶、BMI及VAS均較治療前降低,差異有統計學意義(P<0.05,見表4)。
2.4安全性評價在治療過程中對照組患者有5例發生不良反應,觀察組有3例發生不良反應,兩組不良反應發生率比較,差異無統計學意義(χ2=0.625,P>0.05)。兩組患者不良反應均主要表現為頭暈、嗜睡、呼吸道及泌尿道感染等,不良反應均未特殊處理,10 d后自行緩解。
3討論
營養支持是治療SAP的重要方法,主要包括腸外營養和腸內營養。研究已經證實腸外營養雖然可以明顯改善SAP患者的預后、緩解胃腸道反應,但是長期腸外營養會導致腸道菌群改變、胰腺及胰周組織壞死,出現腸源性感染,甚至死亡[7]。近些年,研究發現腸內營養不僅可以提供足夠的營養支持,還可以降低腸道感染發生率、調節腸道菌群平衡,且并不會增加胃腸道負擔[8]。但是關于腸內營養的時機選擇,目前尚無定論。有研究認為,早期腸內營養支持會增加腸道及胰腺負擔,加重病情發展[9]。但也有一些研究的結果卻恰恰相反,如季占峰等[10]研究發現入院后72 h內行早期腸內營養支持可以提高臨床療效,減少并發癥發生率。因此,探求適宜時機的腸內營養對SAP的治療有著重要的臨床價值。
SAP引發的腹內高壓與胰腺炎癥及醫源性大量液體復蘇之間密切相關[11]。流行病學調查顯示腹內高壓在SAP中的發生率約為40%,在臨床治療中腹內高壓已經成為SAP預后的重要指標[12]。英國的一項調查研究顯示,全英國ICU中約93%的SAP患者會進行常規腹腔壓力監測,而根據腹腔壓力的變化情況可以隨時制定治療方案,評估患者的預后[13]。動物研究發現,當SAP模型大鼠IAP超過20 mm Hg時,會導致腸黏膜對內毒素的通透性增加、腸道免疫力下降、炎性遞質增多[11,14]。目前臨床上主要通過手術或補充液體達到減輕腹內高壓的目的,如中藥灌腸,但是具體療效如何尚不得知。本研究從腸內營養支持入手,動態監測SAP患者IAP,結果證實腸內營養支持對降低IAP有一定療效,而早期腸內營養的療效明顯優于晚期腸內營養,但本研究缺乏干預后隨訪,因此早期腸內營養是否可以提高SAP患者預后尚需要進一步跟蹤隨訪。
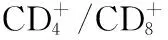

表3 兩組治療前后免疫指標水平比較±s)
注:與同組治療前比較,aP<0.05

表4 兩組血淀粉酶、BMI及VAS比較
注:與同組治療前比較,aP<0.05;BMI=體質指數,VAS=視覺模擬評分
綜上所述,早期腸內營養支持可以提高SAP的臨床療效,改善患者的營養狀況,增強機體免疫力,有效降低腹內高壓,從而改善患者的預后情況,值得臨床推廣。
本文要點:
對于重癥急性胰腺炎患者的腸內營養干預時間,可以提前到入院后48 h,研究證實及早行腸內營養可以明顯降低腹內高壓的發生率,調節并改善機體的免疫功能,從而改善患者的預后情況。
本文無利益沖突。
參考文獻
[1]Shao JW,Cai X,Ma DD,et al.Relationship between intra-abdominal pressure and severity of acute pancreatitis[J].Chinese Journal of Experimental Surgery,2014,31(7):1582-1584.(in Chinese)
邵俊偉,蔡遜,馬丹丹,等.急性胰腺炎疾病嚴重程度與腹內髙壓的關系[J].中華實驗外科雜志,2014,31(7):1582-1584.
[2]Mounzer R,Langmead CJ,Wu BU,et al.Comparison of existing clinical scoring systems to predict persistent organ failure in patients with acute pancreatitis[J].Gastroenterology,2012,142(7):1476-1482,quiz e15-16.
[3]Sun B,Zhang TP.Immune therapy in patients with severe acute pancreatitis[J].Chinese Journal of Practical Surgery,2011,11(8):737-738.(in Chinese)
孫備,張太平.重癥急性胰腺炎病人的免疫治療[J].中國實用外科雜志,2011,11(8):737-738.
[4]Sun JK,Li WQ,Ke L,et al.Early enteral nutrition prevents intra-abdominal hypertension and reduces the severity of severe acute pancreatitis compared with delayed enteral nutrition:a prospective pilot study[J].World J Surg,2013,37(9):2053-2060.
[5]Hegazi R,Raina A,Graham T,et al.Early jejunal feeding initiation and clinical outcomes in patients with severe acute pancreatitis[J].JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr,2011,35(1):91-96.
[6]Sun JK,Mu XW,Li WQ,et al.Effects of early enteral nutrition on immune function of severe acute pancreatitis patients[J].World J Gastroenterol,2013,19(6):917-922.
[7]胡毅,博濤,高文彪.早期腸內營養支持對重癥急性胰腺炎患者炎癥反應和免疫功能的影響[J].中國老年學雜志,2014,35(8):2083-2085.
[8]Xu CF,Huang XX,Shen YZ,et al.The effects of enteral nutrition versus total parenteral nutrition on gut barrier function in severe acute pancreatitis[J].Chinese Journal of Internal Medicine,2011,50(5):370-373.(in Chinese)
許春芳,黃曉曦,沈云志,等.腸內營養與腸外營養對重癥急性胰腺炎患者腸屏障功能影響的比較[J].中華內科雜志,2011,50(5):370-373.
[9]Yao HB,Zeng RC,Wen MB,et al.Comparation of therapeutic effects of early enteral nutrition and delayed enteral nutrition on severe acute pancreatitis[J].The Journal of Practical Medicine,2014,30(14):2231-2233.(in Chinese)
姚紅兵,曾榮城,文明波,等.早期腸內營養與延遲腸內營養治療重癥急性胰腺炎的臨床療效比較[J].實用醫學雜志,2014,30(14):2231-2233.
[10]Ji ZF,Li YH,Zhang HX,et al.Comparison of early enteral elemental nutrition,and parenteral,enteral stage nutrition in treatment of severe acute pancreatitis[J].The Journal of Practical Medicine,2010,26(4):581-583.(in Chinese)
季占峰,李月華,張紅霞,等.早期要素腸內營養與腸外、腸內階段性營養治療急性重癥胰腺炎的對比研究[J].實用醫學雜志,2010,26(4):581-583.
[11]Ma J,Gu PY,Yu Z.Effect of Ulinastation on intra-abdominal hypertension and intestinal mucosa barrier in older patients with severe acute pancreatitis[J].Chinese Journal of Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics,2011,16(1):93-97.(in Chinese)
馬靜,顧佩瑜,余追.烏司他丁對老年重癥胰腺炎患者腹內高壓及腸黏膜功能影響的臨床研究[J].中國臨床藥理學與治療學,2011,16(1):93-97.
[12]Rosas JM,Soto SN,Aracil JS,et al.Intra-abdominal pressure as a marker of severity in acute pancreatitis[J].Surgery,2007,141(2):173-178.
[13]Ravishankar N,Hunter J.Measurement of intra-abdominal pressure in intensive care units in the United Kingdom:a national postal questionnaire study[J].Br J Anaesth,2005,94(6):763-766.
[14]Cheng JT,Li XY,Feng Z,et al.Elevated intra-abdominal pressure induces marked oxidative stress and redox imbalance in intestinal mucosa in rabbits[J].World Chinese Journal of Digestology,2009,17(26):2673-2678.(in Chinese)
程君濤,李小毅,馮智,等.腹內高壓對腸黏膜氧化還原狀態的影響[J].世界華人消化雜志,2009,17(26):2673-2678.
[15]Shen Y,Cui NQ.Clinical observation of immunity in patients with secondary infection from severe acute pancreatitis[J].Inflamm Res,2012,61(7):743-748.
[16]Miao X,Zan JB,Song KJ,et al.Effect of early enteral nutrition for severe acute pancreatitis patients on serum C-reactive protein and T lymphocyte subsets[J].Journal of Hepatopancreatobiliary Surgery,2013,25(2):116-119.(in Chinese)
苗祥,昝建寶,宋康頡,等.早期腸內營養對重癥急性胰腺炎患者血清CRP及T淋巴細胞亞群的影響[J].肝膽胰外科雜志,2013,25(2):116-119.
(本文編輯:賈萌萌)
Influence of Early Enteral Nutrition and Delayed Enteral Nutrition on Intra-abdominal Hypertension and Immune Function of Patients With Severe Acute Pancreatitis
XUShou-ming.
YijishanHospitalofWannanMedicalCollege,Wuhu241001,China
【Abstract】ObjectiveTo investigate the influence of early enteral nutrition and delayed enteral nutrition on the intra-abdominal hypertension and immune function of patients with severe acute pancreatitis(SAP).MethodsFrom January 2013 to December 2014,40 SAP patients who received treatment in Yijishan Hospital of Wannan Medical College were enrolled and divided into observation group and control group with 20 patients in each group.On the basis of comprehensive treatment,the patients in observation group began to receive support treatment by enteral nutrition 48 hours after admission,and the patients in control group began to receive the same support treatment by enteral nutrition 5 days after admission. The treatment course lasted for 2 weeks for both groups.The incidence rates of intra-abdominal pressure and intra-abdominal hypertension of the two groups before and after treatment were recorded.The levels of serum immunoglobulin(IgG,IgM and IgA)and levels of peripheral blood T lymphocyte and )were detected.Blood amylase level,BMI and VAS of the two groups were recorded.ResultsThe two groups were not significantly different in IAP before treatment(P>0.05),while the observation group was lower than control group in IAP(P<0.05).The two groups had lower IAP after treatment than that before treatment(P<0.05).The two groups were not significantly different in the incidence rate of intra-abdominal hypertension on day 1 and day 14(P>0.05).The observation group was lower than control group in the incidence rate of intra-abdominal hypertension on day 7 and day 10(P<0.05).Before treatment,the two groups were not significantly different in the levels of IgG,IgM and IgA and the levels of and (P>0.05).After treatment,observation group was higher than control group in the levels of IgG,IgM and IgA and the levels of and (P<0.05),and the two groups had higher levels of IgG,IgM and IgA and higher levels of and after treatment than those before treatment(P<0.05).Before treatment,the two groups were not significantly different in blood amylase level,BMI and VAS(P>0.05).After treatment,observation group was lower than control group in blood amylase level,BMI and VAS(P<0.05),and the two groups had lower blood amylase level,BMI and VAS than those before treatment(P<0.05).In the treatment process,5 patients had adverse reactions in control group and 3 patients had adverse reactions in observation group,with no significant differences between the two groups in the incidence rate of adverse reaction(χ2=0.625,P>0.05).ConclusionEarly enteral nutrition can significantly decrease the incidence rate of intra-abdominal pressure and regulate and improve body immune function,thus improving prognosis.
【Key words】Enteral nutrition;Severe acute pancreatitis;Intra-abdominal hypertension;Immunocompetence
【中圖分類號】R 576
【文獻標識碼】A
doi:10.3969/j.issn.1007-9572.2016.14.021
(收稿日期:2015-10-24;修回日期:2016-02-06)
·膳食與營養·

