產超廣譜β—內酰胺酶肺炎克雷伯菌的檢測及耐藥性分析
李麗+劉丹+王佳賀
[摘要] 目的 調查中國醫(yī)科大學附屬盛京醫(yī)院(以下簡稱“我院”)住院患者產超廣譜β-內酰胺酶(ESBLs)肺炎克雷伯菌的臨床分布及耐藥性,為臨床醫(yī)師抗感染治療提供依據(jù)。 方法 收集2015年1~12月我院住院患者送檢的各類標本,采用VITEK 2 Compact進行細菌鑒定和藥敏試驗,按照CLSI推薦的方法進行ESBLs初步篩選和表型確證試驗,并對陽性患者耐藥性進行分析。 結果 共檢出產ESBLs肺炎克雷伯菌302株,其中痰液標本中檢出最多,占38.74%,其次是全血和尿液,分別占28.81%和13.91%;科室分布以兒科和普通外科為主,分別占53.97%和7.95%。產ESBLs肺炎克雷伯菌對氨芐西林、頭孢唑啉、哌拉西林、頭孢曲松、頭孢噻肟的耐藥率均在95%以上,而對碳青霉烯類藥物的耐藥率較低,低于3%。 結論 住院患者產ESBLs肺炎克雷伯菌的耐藥率高,治療難度大,醫(yī)師應根據(jù)藥敏試驗結果加強對抗生素的合理使用。
[關鍵詞] 肺炎克雷伯菌;超廣譜β-內酰胺酶;耐藥性;病原菌
[中圖分類號] R969.3 [文獻標識碼] A [文章編號] 1673-7210(2017)05(b)-0103-04
[Abstract] Objective To analyze the clinical distribution and drug resistance of extended-spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBLs)-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae in hospitalized patients in Shengjing Hospital Affiliated to China Medical University ("our hospital" for short), in order to provide references for therapy of infections. Methods ESBLs-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae isolated in our hospital from January to December 2015 were collected. The bacteria identification and drug sensitivity test were performed by the VITEK 2 Compact. The ESBLs preliminary screening and the phenotypic confirmatory test were taken according to the guideline of CLSI, and at the same time, the results of the drug sensitivity test were analyzed. Results 302 strains of ESBLs-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae were isolated, which were mostly isolated from sputum samples (38.74%), followed by blood (28.81%) and urine (13.91%). The bacteria were mainly distributed in Paediatrics Department (53.97%) and General Surgery Department (7.95%). The drug resistances of ESBLs-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae to Ampicillin, Cefazolin, Piperacillin, Ceftriaxone, Cefotaxime in hospitalized patients were more than 95%, and the resistance rate to carbapenemes was lower, less than 3%. Conclusion The isolated ESBLs-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae in hospitalized patients are highly resistant to the commonly used antibiotics, and the treatment is difficult. Therefore, the drug sensitive test should be strengthened to direct clinical rational use of antibiotics.
[Key words] Klebsiella pneumoniae; Extended spectrum beta-lactamases; Drug resistance; Pathogens
肺炎克雷伯菌廣泛分布于自然界,是引起呼吸道感染重要的條件致病菌,其臨床分離率在革蘭陰性桿菌中居第3位[1-2]。產生超廣譜β-內酰胺酶(extended-spectrum beta-lactamase,ESBLs)是肺炎克雷伯菌的主要耐藥機制之一[3],由其引起的感染在兒童及老年患者、免疫力低下的患者以及接受各種侵入性診療操作的重癥患者中發(fā)病率高[4]。隨著抗菌藥物的廣泛使用,尤其是第三代頭孢菌素類藥物在臨床上的大量使用,使得產ESBLs肺炎克雷伯菌的耐藥性不斷上升[5]。因此,本研究收集2015年1~12月中國醫(yī)科大學附屬盛京醫(yī)院(以下簡稱“我院”)住院患者送檢的標本的培養(yǎng)結果,對其產ESBLs肺炎克雷伯菌的感染情況及其耐藥特點進行回顧性分析,為臨床合理選擇抗產ESBLs肺炎克雷伯菌的藥物提供參考依據(jù),現(xiàn)報道如下:
1 資料與方法
1.1 一般資料
收集我院住院患者的痰液、全血、尿液及分泌物等各類臨床感染標本,同一患者相同類型標本中多次分離的同一菌株陽性標本按一例計算。質控菌株為肺炎克雷伯菌ATCC700603,購自原衛(wèi)生部臨床檢驗中心。
1.2 方法
1.2.1 細菌學鑒定及藥敏實驗 送檢樣本均按照《全國臨床檢驗操作規(guī)程》[6]的操作要求對各種臨床標本進行培養(yǎng)分離,采用法國生物梅里埃公司的全自動細菌鑒定和Vitek2 Compact藥敏分析系統(tǒng)進行分析鑒定和藥敏試驗。操作方法和結果評價嚴格按照美國臨床實驗室標準化委員會(CLSI)標準和指南[7]進行。
1.2.2 ESBLs檢測 根據(jù)CLSI推薦的ESBLs初步篩選和表型確證試驗檢測[8]。
2 結果
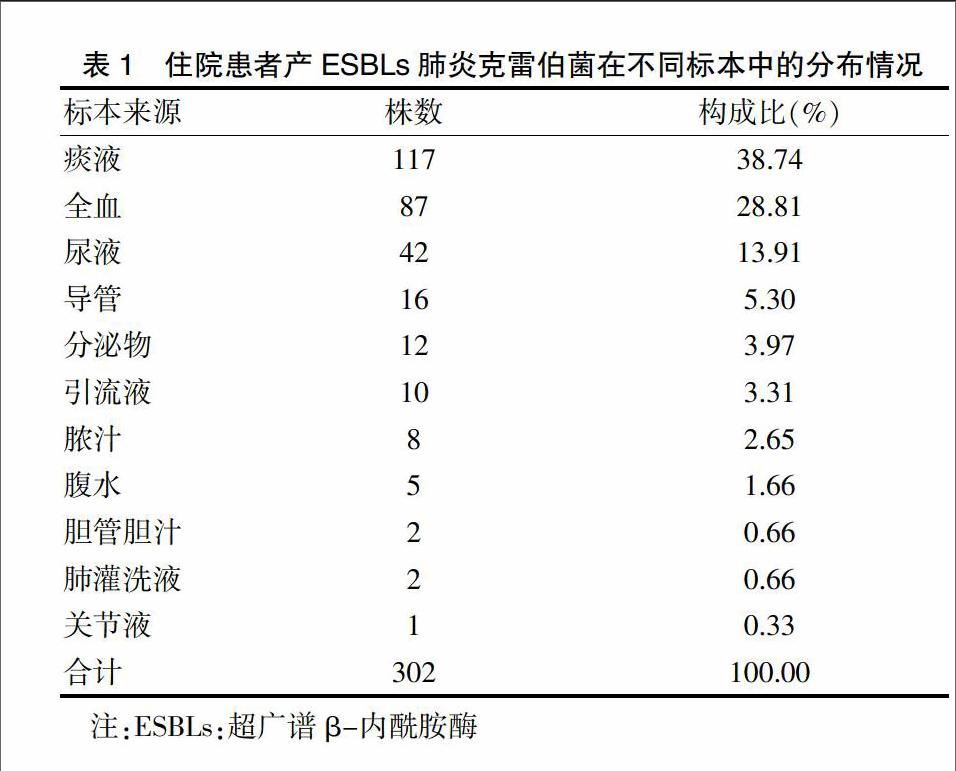
2.1 我院住院患者產ESBLs肺炎克雷伯菌的標本來源分布
經培養(yǎng)共檢出產ESBLs肺炎克雷伯菌302株,主要來源于痰液、全血、尿液,分別占38.74%、28.81%、13.91%。見表1。
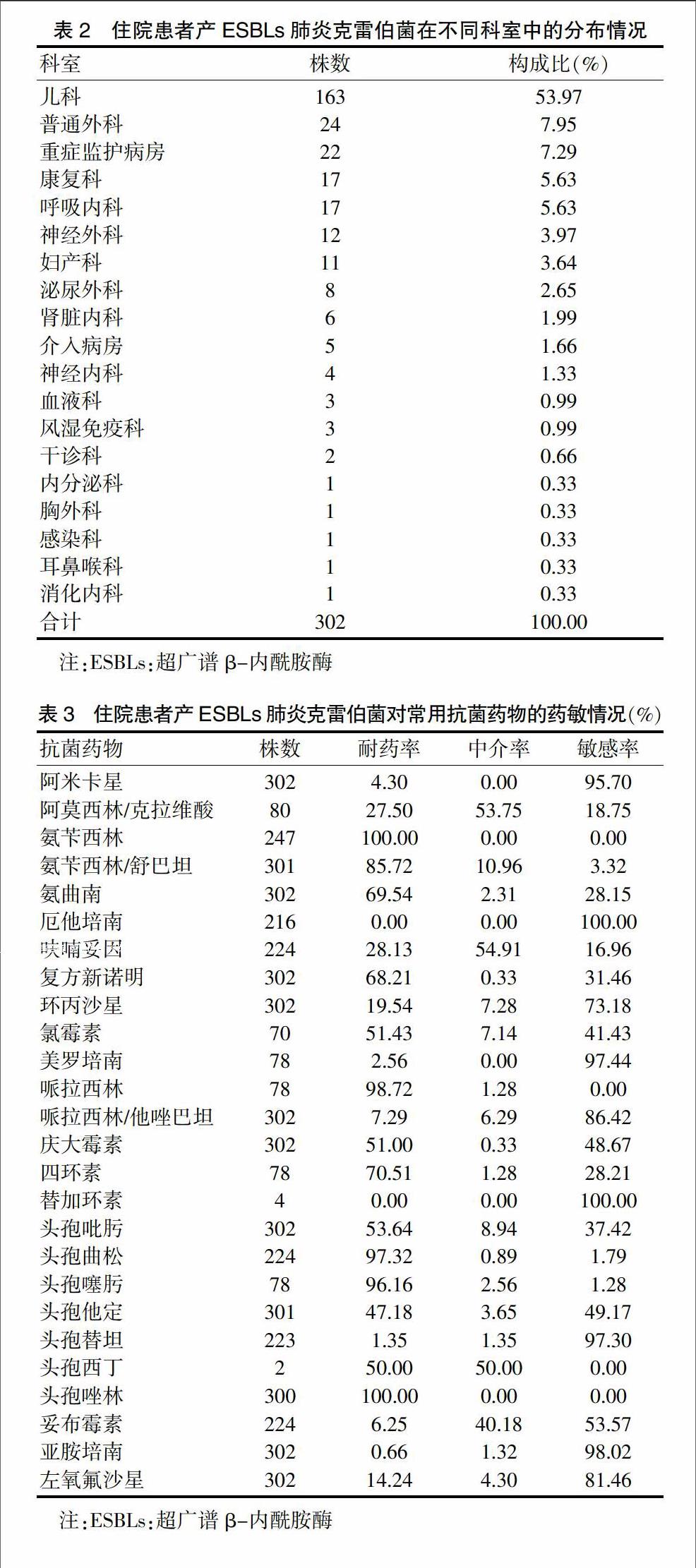
2.2 我院住院患者產ESBLs肺炎克雷伯菌的科室分布
我院住院患者產ESBLs肺炎克雷伯菌主要分布在兒科、普通外科及重癥監(jiān)護病房,分別占53.97%、7.95%、7.29%。見表2。
2.3 我院住院患者產ESBLs肺炎克雷伯菌對常用抗菌藥物的耐藥性
我院住院患者產ESBLs肺炎克雷伯菌對氨芐西林、頭孢唑啉、哌拉西林、頭孢曲松、頭孢噻肟的耐藥率較高,分別為100.00%、100.00%、98.72%、97.32%、96.16%,對厄他培南、亞胺培南、美羅培南、頭孢替坦、阿米卡星的敏感率較高,分別為100.00%、98.02%、97.44%、97.30%、95.70%。見表3。
3 討論
ESBLs由質粒介導,能水解青霉素類、單酰胺類及頭孢菌素類等抗菌藥物[9],其特點是能使細菌對多種類型的β-內酰胺類抗菌藥物產生耐藥性[10],具有作用底物廣、易播散、數(shù)量種類多、個體差異大的特點[11-12]。近年來,隨著臨床上廣泛使用β-內酰胺類抗生素治療各類感染,使得革蘭陰性菌中的許多菌株對抗生素類藥物的耐藥性越發(fā)突出,以產ESBLs菌耐藥性最為顯著,尤其是產ESBLs肺炎克雷伯菌具有較高的多重耐藥性和交叉耐藥性,容易引起暴發(fā)和流行[13-15],給臨床治療帶來極大困擾。
分析本研究我院住院患者中檢出的產ESBLs肺炎克雷伯菌標本分布可見,302株肺炎克雷伯菌分離自臨床的各類標本,其中以痰液中最多,占38.74%,表明產ESBLs肺炎克雷伯菌主要引起呼吸系統(tǒng)感染;其次為全血和尿液,分別占28.81%和13.91%,說明產ESBLs肺炎克雷伯菌亦容易引起血流感染和尿路感染。科室分布方面,我院住院患者產ESBLs肺炎克雷伯菌主要分布在兒科,占53.97%,說明產ESBLs肺炎克雷伯菌容易引起兒童院內感染,與何麗蕓等[16]報道一致;其次為普通外科、重癥監(jiān)護病房、康復科和呼吸內科等科室,分別占7.95%、7.29%、5.63%和5.63%,這些科室患者抵抗力較低,住院時間長,經驗性應用三代頭孢菌素較多,說明產ESBLs肺炎克雷伯菌是引起院內感染的重要病原菌,應引起醫(yī)護人員的重視。這與孫紅等[17]報道的多見于重癥監(jiān)護病房和感染科病房略有差異,可能與各臨床科室感染特點不同、地區(qū)差異以及標本的送檢等因素有關。
從產ESBLs肺炎克雷伯菌對臨床常用的抗菌藥物耐藥率的統(tǒng)計結果中發(fā)現(xiàn):產ESBLs肺炎克雷伯菌對氨芐西林、哌拉西林等β-內酰胺類藥物耐藥,而對亞胺培南、美羅培南、厄他培南等碳青霉烯類藥物敏感。與2013年孫立群等[18]報道的產ESBLs肺炎克雷伯菌對亞胺培南和美羅培南的耐藥率均為0相比,我院產ESBLs肺炎克雷伯菌對亞胺培南和美羅培南的耐藥率較高,分別為0.66%和2.56%,應引起臨床醫(yī)生的關注。產ESBLs肺炎克雷伯菌對碳青霉烯類抗菌藥物敏感與碳青霉烯類藥物特殊的分子結構有關,碳青霉烯類的β-內酰胺環(huán)較小,容易進入細菌的微孔蛋白通道,同時,碳青霉烯類藥物有特異的反式結構,兩者相互作用使其對β-內酰胺酶高度穩(wěn)定[19-21]。此外,分析結果顯示我院產ESBLs肺炎克雷伯菌對β-內酰胺酶抑制劑藥物阿莫西林/克拉維酸、氨芐西林/舒巴坦、哌拉西林/他唑巴坦的耐藥率分別為27.50%、85.72%、7.29%,說明ESBLs可以被舒巴坦、他唑巴坦等β-內酰胺酶抑制劑所抑制[22]。我院產ESBLs肺炎克雷伯菌對慶大霉素的耐藥率為51%,對左氧氟沙星的耐藥率為14.24%,說明產ESBLs肺炎克雷伯菌對喹諾酮類和氨基糖苷類抗菌藥物亦有一定的耐藥性,與其質粒攜帶的耐藥基因的多重耐藥性有關[23]。因此,在臨床上對產ESBLs肺炎克雷伯菌引起感染的治療應首選敏感的碳青霉烯類抗菌藥物,根據(jù)藥敏結果慎重選用β-內酰胺酶抑制劑、氨基糖苷類和喹諾酮類,而大多數(shù)β-內酰胺類和第一、二代頭孢菌素類對其無效。
綜上所述,住院患者產ESBLs肺炎克雷伯菌菌株檢出率比較高,引起的院內感染不斷增加,并且抗菌藥物耐藥類型眾多。在臨床研究中,應對產ESBLs肺炎克雷伯菌株進行嚴密監(jiān)測,根據(jù)細菌培養(yǎng)及藥敏試驗結果耐藥情況,選擇合理的抗菌藥物,可有效預防醫(yī)院感染。
[參考文獻]
[1] Kazmierczak KM,Lob SH,Hoban DJ,et al. Characterization of extended-spectrum beta-lactamases and antimicrobial resistance of Klebsiella pneumoniae in intra-abdominal infection isolates in Latin America,2008-2012. Results of the Study for Monitoring Antimicrobial Resistance Trends [J]. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis,2015,82(3):209-214.
[2] Peralta G,Lamelo M,Alvarez-García P,et al. Impact of empirical treatment in extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli and Klebsiella spp. bacteremia. A multicentric cohort study [J]. BMC Infect Dis,2012,12(1):245.
[3] Gholipour A,Soleimani N,Shokri D,et al. Phenotypic and Molecular Characterization of Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase Produced by Escherichia coli,and Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolates in an Educational Hospital [J]. Jundishapur J Microbiol,2014,7(10):e11758.
[4] Mansury D,Motamedifar M,Sarvari J,et al. Antibiotic susceptibility pattern and identification of extended spectrum β-lactamases (ESBLs) in clinical isolates of Klebsiella pneumoniae from Shiraz,Iran [J]. Iran J Microbiol,2016,8(1):55-61.
[5] Somily AM,Habib HA,Absar MM,et al. ESBL-producing Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae at a tertiary care hospital in Saudi Arabia.[J]. J Infect Dev Ctries,2014,8(9):1129-1136.
[6] 尚紅,王毓三,申子瑜.全國臨床檢驗操作規(guī)程[M].北京:人民衛(wèi)生出版社,2015.
[7] 李小鵬,王治國.美國臨床實驗室標準化委員會標準與指南[J].中華檢驗醫(yī)學雜志,2001,24(4):251-252.
[8] 張長虹,孟存仁,曉英.產ESBLs大腸埃希菌和肺炎克雷伯菌耐藥性分析及TEM、SHV基因檢測[J].國際檢驗醫(yī)學雜志,2015,36(5):583-585.
[9] Shaikh S,F(xiàn)atima J,Shakil S,et al. Antibiotic resistance and extended spectrum beta-lactamases:Types,epidemiology and treatment [J]. Saudi J Biol Sci,2015,22(1):90-101.
[10] Van Aken S,Lund N,Ahl J,et al. Risk factors,outcome and impact of empirical antimicrobial treatment in extended-spectrum β-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli bacteraemia [J]. Scand J Infect Dis,2014,46(11):753-762.
[11] Giske CG,Sundsfjord AS,Kahlmeter G,et al. Redefining extended-spectrum beta-lactamases:balancing science and clinical need [J]. J Antimicrob Chemother,2009,63(1):1-4.
[12] 朱瑞琪,張?zhí)N莉,張淑芹,等.2011-2013年某綜合性醫(yī)院產ESBLs 細菌的分布及耐藥動態(tài)監(jiān)測[J].現(xiàn)代預防醫(yī)學,2015,42(18): 3450-3453.
[13] Biedenbach DJ,Bouchillon SK,Hoban DJ,et al. Antimicrobial susceptibility and extended-spectrum beta-lactamase rates in aerobic gram-negative bacteria causing intra-abdominal infections in Vietnam:report from the Study for Monitoring Antimicrobial Resistance Trends(SMART 2009-2011)[J]. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis,2014,79(4):463-467.
[14] Leistner R,Gürntke S,Sakellariou C,et al. Bloodstream infection due to extended-spectrum beta-lactamase(ESBL)-positive K. pneumoniae and E. coli:an analysis of the disease burden in a large cohort [J]. Infection,2014, 42(6):991-997.
[15] Vibet MA,Roux J,Montassier E,et al. Systematic analysis of the relationship between antibiotic use and extended-spectrum beta-lactamase resistance in Enterobacteriaceae in a French hospital:a time series analysis [J]. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis,2015,34(10):1957-1963.
[16] 何麗蕓,王應建,李季美.嬰幼兒社區(qū)獲得性肺炎克雷伯菌肺炎的臨床特點及耐藥分析[J].中國當代兒科雜志,2012,14(11):827-829.
[17] 孫紅,喬艷,郭普,等.肺炎克雷伯菌產ESBLs的檢測及耐藥性分析[J].中華全科醫(yī)學,2011,9(5):797-798.
[18] 孫立群,梁金花,李榮輝.大腸埃希菌與肺炎克雷伯菌耐藥性及產ESBLs菌株的分析[J].中華醫(yī)院感染學雜志,2013,23(2):455-457.
[19] 李忠,曾金紅,李亞,等.基層醫(yī)院肺炎克雷伯菌的臨床感染分布和耐藥譜分析[J].中國醫(yī)藥科學,2015,5(3):66-69.
[20] Udomsantisuk N,Nunthapisud P,Tirawatanapong T,et al. Molecular characterization of extended spectrum beta-lactamase among clinical isolates Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae [J]. J Med Assoc Thai,2011,94(12):1504-1512.
[21] 唐景云,秦曉林.ESBLs在大腸埃希菌、肺炎克雷伯菌和陰溝腸桿菌中的檢出率及耐藥情況比較[J].中國醫(yī)藥科學,2016,6(3):175-178.
[22] Kaftandzieva A,Trajkovska-Dokic E,Panovski N. Prevalence and molecular characterization of Extended Spectrum Beta-Lactamases(ESBLs)producing Escherichia Coli and Klebsiella Pneumoniae.[J]. Prilozi,2011,32(2):129-141.
[23] Yadav KK,Adhikari N,Khadka R,et al. Multidrug resistant Enterobacteriaceae and extended spectrum β-lactamase producing Escherichia coli:a cross-sectional study in National Kidney Center,Nepal [J]. Antimicrob Resist Infect Control,2015,4(1):42.
(收稿日期:2017-01-10 本文編輯:程 銘)

