大紅甜橙和冰糖橙果實發育過程中有機酸和氨基酸含量變化研究
孫系巍 龍桂友 李菲菲 盧曉鵬


摘 要:以冰糖橙和大紅甜橙為材料,研究兩個品種果實發育過程中有機酸和氨基酸含量的變化。結果表明,果實發育過程中大紅甜橙果實檸檬酸含量、總氨基酸含量均顯著高于冰糖橙;大紅甜橙和冰糖橙成熟果實中氨基酸總量分別為5.06 g/100g DW和3.46 g/100g DW,以天冬氨酸、谷氨酸和半胱氨酸含量較高。果實發育過程中,谷氨酸族氨基酸在大紅甜橙果實中無明顯變化,而在冰糖橙果實中逐漸降低;果實發育前期天冬氨酸族氨基酸含量在大紅甜橙果實中高于冰糖橙,而果實成熟期兩品種無明顯差異;鮮味和甜味氨基酸在大紅甜橙果實中含量均高于冰糖橙,且均伴隨果實成熟而降低。
關鍵詞:冰糖橙;大紅甜橙;有機酸;氨基酸
中圖分類號:S666.4 文獻標識碼:A 文章編號:1006-060X(2017)01-0026-04
Abstract:The aim of this work was to study the changes of organic acid and amino acid content in “Bingtangcheng” and “Dahongtiancheng” sweet oranges (Citrus sinensis). The results showed that both citrate and amino acid in “Dahongtiancheng” was significantly higher than that in “Bingtangcheng” throughout fruit development. In ripening fruits, the total amino acid was 5.06 g/100g DW and 3.46 g/100g DW in “Dahongtiancheng” and “Bingtangcheng” respectively, in which Asp, Glu and Cys contributed to that difference significantly. During fruit development, glutamate families showed no significant change in “Dahongtiancheng” but decreased constantly in “Bingtangcheng”; aspartate families were higher in “Dahongtiancheng” than that in “Bingtangcheng”, but exhibited no difference at mature fruits; the flavor amino acids and sweet amino acids were higher in “Dahongtiancheng” than that in “Bingtangcheng”, and both of them decreased following fruits development.
Key words:Bingtangcheng; Dahongtiancheng; organic acid; amino acid
有機酸和氨基酸是柑橘果實的重要組成成分,其含量反映果實內在品質,直接影響柑橘果實的口感和被消費者的認可度。柑橘果實有機酸以檸檬酸為主,其來源是三羧酸循環的中間產物,其含量主要由檸檬酸的合成、降解和貯藏共同決定[1-4]。氨基酸是果實中主要的含氮化合物,但由于其在果實中含量較少,故在氨基酸參與果實品質形成方面研究較少。研究表明,果實檸檬酸與氨基酸之間有密切的關系,如檸檬酸可轉化為谷氨酸,檸檬酸代謝的中間產物2-酮戊二酸參與多種氨基酸的形成等[5-7]。大紅甜橙和冰糖橙是兩個湖南省自主選育、推廣主栽的優勢甜橙品種,均源于洪江普通甜橙的變異。大紅甜橙風味濃郁、含酸量高,冰糖橙果實含糖量高、含酸量低,通過對品質差異明顯的兩個甜橙品種果實發育過程中的有機酸和氨基酸含量變化進行研究,以期為揭示甜橙果實品質形成機理及調控品質形成提供理論依據。
1 材料與方法
1.1 試驗材料與處理
以湖南省洪江市同一果園的冰糖橙和大紅甜橙為材料。兩品種分別于盛花后70、90、110、130、160、190、220 d取果實樣品,每品種3株重復,采樣時每株樹冠四周均勻采集果實10個,采集后立即帶回實驗室,分離果肉樣品并置于-20℃保存。
1.2 果汁中有機酸含量測定
有機酸測定時每品種每株樹取5個果實的果肉樣品作為一個重復,每品種重復3次。果肉樣品用榨汁機充分榨取汁液,后用8層紗布過濾,將過濾后的汁液在12℃的條件下離心(5 000 r/min)15 min,取其上清液。將上清液用超純水稀釋到10倍,稀釋后的樣品超聲波脫氣后檢測。有機酸采用HPLC方法檢測,色譜條件為:色譜柱:ODS-SP(C18)分析柱(4.6 mm×150 mm,5 μm);柱溫:40℃;檢測器:紫外檢測器;檢測池溫度:40℃;流動相為3%甲醇和0.01 mol/L K2HPO4,用磷酸調pH值至2.7,真空泵脫氣,經過0.45 μm濾膜過濾;流速:0.6 mL/min;進樣體積:20 μL。
1.3 果肉主要氨基酸含量測定
5個果實剝出果肉,105℃殺青15 min,75℃烘干至恒重,粉碎后過100目篩。果肉樣品氨基酸含量測定參照GB/T5009.124—2003進行。
1.4 味覺氨基酸含量
鮮味氨基酸含量為天冬氨酸、谷氨酸含量之和,甜味氨基酸含量為丙氨酸、甘氨酸、脯氨酸、絲氨酸含量之和,芳香族氨基酸含量為苯丙氨酸、酪氨酸含量之和[11]。
1.5 數據統計與分析
采用Excel 2013和SigmaPlot 10.0對數據進行分析和作圖。
2 結果與分析
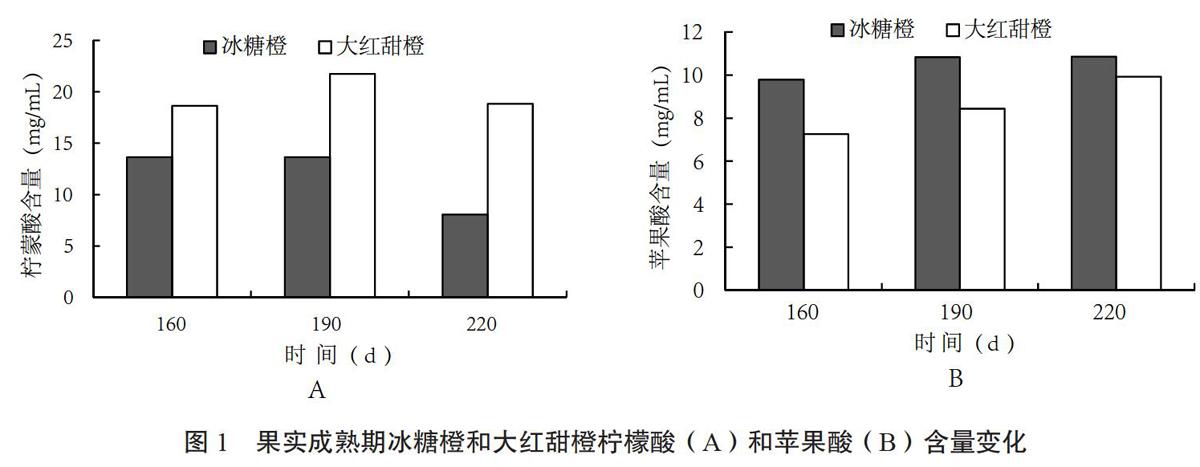
2.1 冰糖橙和大紅甜橙果實成熟過程中有機酸含量變化
由圖1可知,兩個甜橙品種果實果汁中檸檬酸含量顯著高于蘋果酸,大紅甜橙果實檸檬酸含量明顯高于冰糖橙。大紅甜橙果實在花后160~220 d檸檬酸含量均高于冰糖橙,且檸檬酸含量在果實成熟過程中變化不大,而冰糖橙果實中檸檬酸含量隨果實成熟降低。冰糖橙果實蘋果酸含量略高于大紅甜橙,隨果實成熟蘋果酸在冰糖橙中無明顯變化,而在大紅甜橙果實中呈現逐漸升高的趨勢。
2.2 果實氨基酸組成及發育過程中氨基酸總量的變化
由表1可知,大紅甜橙成熟果實氨基酸總量為5.06 g/100g DW(干重,下同),明顯高于冰糖橙的3.46 g/100g DW。冰糖橙和大紅甜橙果實中均含有天冬氨酸(Asp)、谷氨酸(Glu)、蛋氨酸(Met)、半胱氨酸(Cys)、脯氨酸(Pro)、亮氨酸(Leu)、丙氨酸(Ala)、纈氨酸(Val)、賴氨酸(Lys)、異亮氨酸(Ile)、精氨酸(Arg)、絲氨酸(Ser)、甘氨酸(Gly)、蘇氨酸(Thr)、組氨酸(His)、苯丙氨酸(Phe)和酪氨酸(Tyr)17種氨基酸組分。大紅甜橙果實天冬氨酸、谷氨酸和脯氨酸含量較高,含量均在0.5 g/100g DW以上,三者占果實氨基酸總量的37%以上。冰糖橙和大紅甜橙果實中含人體必需氨基酸,其中以蛋氨酸/半胱氨酸較多,果實中人體必需氨基酸組分含量從高到低的大致排列順序為:蛋氨酸/半胱氨酸、苯丙氨酸/酪氨酸、亮氨酸、纈氨酸、賴氨酸、異亮氨酸、組氨酸[8]。
由圖2可知,果實發育過程中,大紅甜橙和冰糖橙果實中氨基酸總量均呈現下降趨勢,但前者果實氨基酸總量始終高于后者。大紅甜橙果實氨基酸總量在盛花后70 d含量最高,后逐漸下降至花后110 d,花后110~160 d維持在一定水平,160 d后持續下降至果實成熟。冰糖橙果實氨基酸總量在花后70~160 d無明顯變化,維持在約5 g/100g DW的水平,160 d后持續下降至果實成熟。
2.3 谷氨酸族氨基酸含量變化
如圖3所示,大紅甜橙中的谷氨酸族氨基酸含量顯著高于冰糖橙。隨果實的發育,大紅甜橙谷氨酸族氨基酸含量在盛花后70 d和160 d呈現兩個峰值,在盛花后90~130 d和190 d兩個階段維持在較低水平;冰糖橙果實中,谷氨酸族氨基酸含量呈現果實發育中期(盛花后70~160 d)基本穩定,果實成熟期(盛花后160~220 d)降低的趨勢。果實發育過程中,大紅甜橙果實中谷氨酸族氨基酸占氨基酸總量的比例在花后70~130 d基本不變,后緩慢升高至果實成熟,而冰糖橙果實中谷氨酸族氨基酸占氨基酸總量的比例始終約20%。
2.4 天冬氨酸族氨基酸含量變化
由圖4可知,大紅甜橙中的天冬氨酸族氨基酸含量在果實發育期高于冰糖橙,果實成熟期兩者差異不明顯。冰糖橙中天冬氨酸族氨基酸含量在花后160 d前變化不明顯,后迅速下降。大紅甜橙果實發育過程中天冬氨酸族氨基酸含量依次呈現高量(花后70~90 d)、中量(花后110~160 d)、低量(花后190~220 d)3個階段的變化。果實發育過程中,冰糖橙果實天冬氨酸族氨基酸含量占氨基酸總量的比例始終保持約40%,在大紅甜橙果實發育前中期(花后70~160 d)相對穩定,而在果實成熟期(花后160~220 d)略有下降。
2.5 味覺類氨基酸含量變化
由圖5可知,冰糖橙和大紅甜橙果實中味覺氨基酸含量以鮮味氨基酸含量最高,甜味氨基酸次之,芳香類氨基酸最低。大紅甜橙和冰糖橙果實中鮮味氨基酸量在花后70~160 d保持穩定,后逐漸降低;果實發育過程中大紅甜橙鮮味和甜味氨基酸含量多數時期高于冰糖橙(圖5A和B)。芳香類氨基酸在大紅甜橙和冰糖橙果實中含量較低,在果實發育過程中無明顯變化(圖5C)。
3 結論與討論
氨基酸作為柑橘果實重要的內含物之一,與其他風味物質一起參與果實品質形成。研究表明,柑橘果實檸檬酸循環的中間產物可以轉化為多種其他氨基酸,其中檸檬酸可通過GABA途徑直接轉化為谷氨酸[5,9]。冰糖橙和大紅甜橙均源于黔陽甜橙的變異,而兩者在果實有機酸含量方面差異巨大。因此,以該兩個品種研究進行甜橙果實有機酸和氨基酸形成研究有較大的優勢。研究結果顯示,檸檬酸是大紅甜橙和冰糖橙果實主要的有機酸類型,且大紅甜橙果實檸檬酸含量顯著高于冰糖橙,與前人報道一致[10]。采用榨汁的方法進行果實有機酸含量測定,在果實發育后期檢測有機酸含量有較大優勢,而在果實發育前期有機酸檢測中存在不足,因此在果實有機酸測定方法上尚需進一步優化。
研究結果顯示,冰糖橙和大紅甜橙均含有17種可檢測氨基酸,其中以天冬氨酸、谷氨酸、半胱氨酸含量豐富,包括人體必需氨基酸,表明兩個甜橙品種氨基酸含量豐富,可提供人體需要的氨基酸。大紅甜橙果實氨基酸含量高于冰糖橙,與大紅甜橙檸檬酸含量高、氨基酸合成上調有密切關系。果實中總氨基酸含量呈現隨果實發育成熟而下降的趨勢,與柑橘有機酸在果實發育前期迅速積累,后期下降有關[1]。谷氨酸在人體內具有促進紅細胞生成、改善腦細胞營養及活躍思維等作用,是治療神經衰弱和記憶力減退的有效成分[11]。研究還表明,谷氨酸族氨基酸是柑橘果實中含量較多的氨基酸;其含量在大紅甜橙果實成熟期升高,而在冰糖橙成熟期下降,這與檸檬酸在大紅甜橙果實成熟期含量穩定而在冰糖橙果實中含量降低、谷氨酸來源差異較大有關。大紅甜橙和冰糖橙果實中均以鮮味氨基酸含量最高,甜味氨基酸次之,芳香類氨基酸最少,與前人在核桃、番茄果實中的結果一
致[8,12];大紅甜橙果實中鮮味氨基酸和甜味氨基酸含量始終高于冰糖橙,可能是大紅甜橙果實風味較冰糖橙濃郁的重要原因之一。
參考文獻:
[1]趙 淼. 柑橘果實有機酸代謝及調控研究[D]. 合肥:安徽農業大學.
[2]Sadka A.,Dahan E.,Cohen L,et al. Aconitase activity and expression during the development of lemon fruit[J]. Physiologia Plantarum,2000,108(3):255-262.
[3]Sadka A,Dahan E,Or E,et al. NADP(+)-isocitrate dehydrogenase gene expression and isozyme activity during citrus fruit development[J]. Plant Science,2000,158(12):173-181.
[4]趙 淼,吳延軍,蔣桂華,等. 柑橘果實有機酸代謝研究進展[J]. 果樹學報,2008,25(2):225-230.
[5]Cercos M,Soler G,Iglesias D J,et al. Global analysis of gene expression during development and ripening of citrus fruit flesh. A proposed mechanism for citric acid utilization[J]. Plant Molecular Biology,2006,62(4-5):513-527.
[6]Chen M.,Jiang Q,Yin X R,et al. Effect of hot air treatment on organic acid-and sugar-metabolism in Ponkan (Citrus reticulata) fruit[J]. Scientia Horticulturae,2012,(147):118-125.
[7]Chen M,Xie X,Lin Q,et al. Differential expression of organic acid degradation-related genes during fruit development of Navel oranges (Citrus sinensis) in two habitats[J]. Plant Molecular Biology Reporter,2013,(31):1131-1140.
[8]岳 冬,劉 娜,朱為民,等. 櫻桃番茄與普通番茄部分品質指標及氨基酸組成比較[J]. 食品科學,2015,36(4):92-96.
[9]Degu A,Hatew B,Nunes-Nesi A,et al. Inhibition of aconitase in citrus fruit callus results in a metabolic shift towards amino acid biosynthesis[J]. Planta,2011,234(3):501-513.
[10]劉靈智. 冰糖橙和大紅甜橙果實成熟過程中糖酸含量變化與風味品質的關系[D]. 長沙:湖南農業大學,2011.
[11]張憲政,陳風玉,王榮富. 植物生理學實驗技術[M]. 沈陽:遼寧科學技術出版社,1994. 144-151.
[12]馬艷萍,呂新剛,劉 丹,等. 鮮食核桃冷藏期間氨基酸組分及含量的變化[J]. 食品研究與開發,2013,34(21):112-115.
(責任編輯:夏亞男)

