土壤動物種群空間分布及影響因素研究進展
丁翔 張月 朱永恒 魯艷紅 廖育林
摘 要:土壤動物作為陸地生態系統的重要組成部分,對土壤生態系統物質循環和能量流動及土壤修復具有重要作用,并逐漸成為科學界研究的熱點。基于近年來國內外對土壤動物的文獻研究,介紹了土壤動物的群落結構多樣性和地理分布特征以及土壤動物對土壤環境變化指示功能,總結分析了影響土壤動物的環境因子,如土地利用方式的變遷、全球氣候的變化及土壤污染等,探討了目前研究中存在的不足,并對今后的研究方向提出了展望。
關鍵詞:土壤動物;群落結構;空間分布;影響因子;綜述
中圖分類號:S512.1 文獻標識碼:A 文章編號:1006-060X(2017)01-0119-04
Abstract:As an important component of terrestrial ecosystem, soil animals played an important role in the material cycle, energy flow and soil remediation of soil ecosystem, which had become one of the hotspots in the research community. Based on the domestic and abroad research on soil animal in recent years, this paper introduced the diversity of soil animals community structure and geographic distribution characteristics, and indicative function of soil animals for soil environment change. In this paper, environmental factors affecting soil animals also were summarized including land use change, global climate change and soil pollution. Problems existed in the current research were discussed and the future research direction was also proposed.
Key words:soil animal; community structure; spatial distribution; impact factor; review
隨著全球對生物多樣性及其保護和全球環境變化的關注,生態系統中的生物多樣性越來越受到人們的重視。土壤動物是土壤生態系統中不可分割的重要構成部分,在土壤有機質分解、改善土壤結構、促進土壤物質遷移與能量轉換及影響土壤質量等方面具有重要作用,能夠反映土壤生境優越程度及人類活動的印記[1-2]。土壤動物對環境變化極其敏感,是陸地生態系統健康評價、土壤環境管理與修復及生物多樣性保護等方面的重點研究對象,已成為全球土壤學和生物學界關注的熱點[3]。
從19世紀40年代對蚯蚓生物學研究開始,國外學者就對土壤動物群落結構及多樣性展開了研究[4],
而我國對這方面研究起步較晚,直到20世紀80年代,我國才開始對土壤動物學進行系統研究。近年來,尹文英等先后出版了《中國亞熱帶土壤動物》、《中國土壤動物檢索圖譜》和《中國土壤動物》等一系列有關土壤動物研究方面的專著,開啟了我國土壤動物學研究的新篇章[5-7]。
近年來,由于農業生產活動大量施用化肥、農藥、工業化生產排放的廢棄物和城市化進程的加快,土壤生態系統受到嚴重的干擾與破壞,土壤動物群落結構和多樣性銳減甚至消失[8-9]。CO2濃度的升高引起土壤C供應、養分等發生變化,顯著影響土壤生物的數量與分布。土地覆被變化及土壤污染導致土壤養分、土壤生產力、土壤理化性質及地表植物群落結構發生改變,進而對土壤生物生理過程和生態功能產生深刻影響。因此,基于以上幾點,筆者從全球氣候變化、土地利用變化及土壤污染等方面逐一闡述了土壤動物與環境要素間的相關性,并提出了土壤動物學今后的研究方向與建議。
1 土壤動物的定義與地理分布
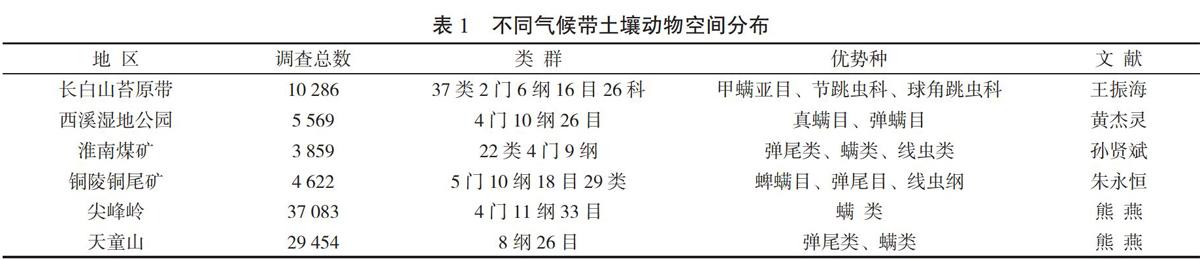
土壤動物是指經常或暫時棲息在包括大型植物殘體在內的土壤環境中,并在其中進行某些活動,對土壤有一定影響的動物群 [7]。土壤動物種類繁多,主要包括原生動物門、扁形動物門、線形動物門、軟體動物門、環節動物門、節肢動物門和脊椎動物門等[10]。目前已在土壤中發現原生動物物種約1 500種、線蟲約30 000種、螨類約50 000種、跳蟲約7 600種、蚯蚓約4 000種、蜘蛛約43 768種和地表甲蟲約40 000種[11]。不同溫度帶土壤動物群落種群、種類及數量都存在明顯差異。邵元虎等[11]調查顯示,不同溫度帶土壤動物類群數由多到少排列依次為浙江天目山(733種)>云南西雙版納(607種)>海南尖峰嶺(486種)>長白山>高寒草原(204種)。表1列出了中國不同地帶土地覆被下動物物種數、類群數及優勢種的基本情況。其中,土壤受到嚴重污染的礦區,主要以彈尾類、螨類及線蟲為主[12];土壤濕度較大的西溪公園螨類占據絕大部分比例[13],而北方農牧交錯區的科爾沁沙地,擬步甲科、鰓金龜科幼蟲、蟻科為優勢種群,占據41.79%[14];溫度較低的長白山苔原帶主要以甲螨亞目、跳蟲為主[15],而熱帶雨林、亞熱帶常綠闊葉林帶土壤動物類群顯著高于長白山苔原帶,主要以螨類和彈尾類為主,在天童山常綠闊葉林帶彈尾類和螨類高達92.17%,大型土壤動物雙翅目占到45.30%[16]。
2 土壤動物的指示功能
土壤動物是反應土壤環境變化的重要指標,在一定程度上土壤動物能夠敏感地反應土壤的污染程度、人類活動的印記及全球氣候的變化等[17]。研究指出,污染土壤中蚯蚓的總豐度、種類豐度及多樣性等指標可用來評價土壤環境的污染程度[18]。研究表明,通過毒性和繁殖試驗可進一步揭示蚯蚓對環境污染變化的響應[19]。農藥廠附近的農田區域,蚯蚓的種類和數量隨著有機氯和有機磷農藥污染程度的上升而呈現減少趨勢,優勢種為微小的雙胸蚓和壯偉的環毛蚓[20]。Goralczyk等[21]研究指出,線蟲群落對沿海地區的沙丘土壤生態演替過程具有顯著的生物指示作用[22]。付秀芹等[23]研究表明,原尾目、彈尾目、線蟲類、線蚓類和蜱螨目等土壤動物對土地利用變化具有響應作用,是監測土壤質量的重要指示性生物。同時,也有文獻指出:Shannon-Wiener多樣性指數和豐富度指數是評價黑土區線蟲群落對化肥投入最敏感的指數[24];土壤動物是檢測長期定位施肥條件下土壤養分變化的重要指示性生物[25]。
3 環境因子對土壤動物的影響
3.1 土壤污染對土壤動物的影響
農業生產活動中農藥化肥的施用和工業三廢的排放都會引起土壤污染。而土壤污染是土壤動物多樣性和群落結構的重要影響因子,直接威脅土壤動物的生存繁衍,嚴重干擾土壤動物群落結構與多樣性特征。在農田和林地中,當除草劑和N肥過量施用時,土壤跳蟲種群數量明顯下降[26]。
孫賢斌等[27-28]對淮南煤礦和發電廠灰場的研究表明,土壤動物群落多樣性指數、均勻性指數以及密度指數均隨著土壤重金屬污染的負荷加重而降低,且土壤表層動物的個體數和類群數小于土壤深層。在受錳礦廢水影響的水稻田中,王振中等[29]發現土壤重金屬污染直接導致土壤動物數量和種群結構失衡。而相關模擬試驗也進一步證實,土壤動物種群數、多樣性指數及個體數數量隨著土壤污染程度上升而逐漸減少[30]。李濤等[31]發現土壤動物類群數(r =-0.962,P<0.01)、個體數(r =-0.915,P<0.05)及多樣性指數(r =-0.821,P<0.05)均與土壤重金屬污染程度呈負相關關系。
3.2 土地利用方式的變遷對土壤動物的影響
土地利用方式的變遷伴隨著土壤理化性質的變化(如土壤有機質、土壤pH值和土壤含水量等),直接破壞了土壤動物原生棲息環境。同時,土地利用方式變遷引起地表植被群落結構,間接影響土壤動物多樣性。劉任濤等[32]對北方農牧交錯區草地、沙地及林地3種不同土地利用類型下土壤動物的研究發現,土壤動物物種數林地(5.67±1.20)>草地(5.07±0.75)>沙地(3.00±1.53)。尤其草地開墾為農田或過度放牧沙化后,土壤容重和土壤堿性相應增強,土壤養分降低,地表植物喪失,引起土壤環境惡化,導致鰓金龜科幼蟲和蟻科等大型土壤動物的數量顯著降低。吳玉紅[33]認為,在土壤動物個體數量上農田邊界(2 609只)>退耕林地(2 587只)>果園(2 503只)>農田(890只)。林蘭穩等[34]對廣州市東部郊區的水稻田、蔬菜地、果園旱地和林地等4種土地利用類型動物的取樣調查發現,土壤覆被的變化對土壤動物的多樣性影響顯著,其中水稻田和蔬菜地的類群數和個體數隨著土層的加深而急劇減少。趙哈林等[35]在科爾沁地區發現,天然草地土壤節肢動物群落有35個類群組成,流動沙地有8個類群組成,天然草地在類群豐富度、多樣性指數和個體密度上分別是流動沙地的4.4倍、1.4倍和9.4倍,人工林地、旱作農田及灌溉農田間類群差異變化不大。以上研究說明,不同的土地利用方式下土壤動物群落多樣性的特征差異很大,植被群落結構越好,人為干擾活動越少,其土壤動物類群的豐富度、多樣性和個體密度就會越高,相反土壤環境較差或者人為干擾強烈的地區,土壤動物的多樣性則較低。
3.3 氣候變化對土壤動物的影響
氣候變化對土壤動物起到直接或間接影響,如大氣CO2濃度升高,可以增強植物光合作用,促進地表植物生長,改變凋落物的質量和數量,同時可以增加土壤濕度,促進植物根系發育來間接影響土壤動物多樣性特征,而大氣溫度和降水變化會對土壤動物群落結構和多樣性產生直接影響[36]。陳靖等[37]通過野外開頂式氣室來模擬氣候變化,發現CO2濃度的升高,轉Bt水稻土壤中線蟲的總數就會高于親本水稻,植食性線蟲的比例也隨之上升。Yeates等[38]通過大氣CO2富集試驗也證實,大氣CO2濃度升高對放牧草地土壤表層線蟲數量具有正效應作用。而Eisenhauer等和Neher等認為CO2濃度升高會導致雜捕類線蟲數量和Aphelenchoides線蟲種群密度降低[39]。究其原因是CO2濃度升高會引起土壤中溶解有機碳含量發生變化,導致土壤動物群落結構及多樣性發生相應變化。
IPCC(2007)第四次評估報告指出,在過去的100 a(1906~2005年)中,大氣平均溫度上升了0.74℃[40],這對植物光合作用、凋落物分解、土壤呼吸及土壤動物活性具有顯著影響,是土壤動物群落結構多樣性的驅動因子。不同土壤環境中的土壤動物對溫度變化的敏感性不盡相同。研究表明,土壤動物數量與土壤溫度呈負相關,即溫度升高1℃后,土壤動物種群密度會顯著下降[41]。如Simmons等、Matute等、Bakong等及Jucevica等均認為土壤動物種群密度及數量隨著溫度上升而降低[42]。近年來,也有研究表明增溫會促進植物根系生長,增加根系分泌物,有利于土壤動物捕食和繁衍。陳靖等和Ruess等證實增溫會促進土壤線蟲數量的增長[43]。
4 展 望
(1)國內外對土壤動物學的研究主要集中在土壤動物的區系調查、探討土壤動物的分布特征及其與環境因子的關系、研究土壤動物在物質循環和能量轉換方面的作用,僅有少部分學者進行了土壤動物對環境指示作用的研究。
(2)土壤動物生態研究較為單一,多數僅從土壤動物學角度進行研究,綜合研究較少,缺乏與生態學、環境學等學科間的互動。
(3)目前對土壤動物的研究多集中在野外,僅從表面淺層發現土壤動物的一些生存特征,缺乏深層次的挖掘,今后應結合室內培養試驗,進一步研究土壤動物的活動機理。
參考文獻:
[1]Ayres E,Steltzer H,Berg S,et al.Soil biota accelerate decomposition in high-elevation forests by specializing in the breakdown of litter produced by the plant species above them[J]. Journal of Ecology,2009,97(5):901-912.
[2]Carrillo T,Ball B A,Bradford M A,et al.Soil fauna alter the effects of litter composition on the nitrogen cycling in a mineral soil[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry,2011,43(7):1440-1449.
[3]閆修民.全球變暖對松嫩西部草原中小型土壤動物多樣性的影響[D].長春:中國科學院東北地理與農業生態研究所,2015.
[4]Pearse A S.Observations on the microfauna of the Duke forest[J].Ecological Monographs, 1946,16(2):127-150.
[5]尹文英,楊逢春,王振中,等.中國亞熱帶土壤動物[M].北京:科學出版社,1992.
[6]尹文英.中國土壤動物檢索圖鑒[M].北京:科學出版社,1998.
[7]尹文英.中國土壤動物[M].北京:科學出版社,2000.
[8]邢協加,王振中,張友梅,等.殺蟲雙農藥對土壤螨類和彈尾類影響的研究[J].湖南師范大學自然科學學報,1997,20(1):79-84.
[9]IPCC.Changes in atmospheric constituents and in radioactive forcing[A].Climate Change: The Physical Science Basis. Con tribution of Working Group I to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change[M].Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY,USA:Cambridge University Press,2007.
[10]尹文英.土壤動物學的回顧與展望[J].生物學通報,2001,36(8):1-3.
[11]邵元虎,張衛信,劉勝杰,等.土壤動物多樣性及其生態功能[J].生態學報,2015,35(20):6614-6625.
[12]孫賢斌,劉紅玉,李玉成,等.重金屬污染對土壤動物群落結構及空間分布的影響[J].應用生態學報,2007,18(9):2080-2084.
[13]黃杰靈,施時迪,王美花,等. 西溪國家濕地公園5種人工植物群落土壤動物群落的結構與多樣性[J]. 浙江大學學報,2012,39(4):434-442.
[14]劉任濤,朱 凡,趙哈林.北方農牧交錯區土地利用覆蓋變化對大型土壤動物群落結構的影響[J]. 草地學報,2013,21(4):643-649.
[15]王振海,殷秀琴,蔣云峰. 長白山苔原帶土壤動物群落結構及多樣性[J].生態學報,2014,34(3):755-765.
[16]熊 燕.熱帶、亞熱帶土壤動物群落多樣性及彈尾綱系統發生的研究[D]. 上海: 華東師范大學,2005.
[17]向昌國,楊世俊,聶 琴. 土壤動物對土壤環境的生物指示[J].農業資源與環境科學,2007,23(4):364-367.
[18]高 巖,駱永明.蚯蚓對土壤污染的指示作用及其強化修復的潛力[J]. 土壤學報,2005,42(1):140-148.
[19]陳 婕,張安龍.蚯蚓處理重金屬的毒理學研究啟示[J]. 環境科技,2008,21(6):27-29.
[20]蘧 丹.典型污染場地有機氯農藥污染特征研究[D]. 四川師范大學,2013.
[21]Goralczyk K.Nematodes in a coastal dune succession:Indicators of soil properties ?[J]. Applied Soil Ecology,1998,9(1):465-469.
[22]向昌國,楊世俊,聶 琴. 土壤動物對土壤環境的生物指示作用[J]. 中國農學通報,2007,23(4):364-367.
[23]劉長海,王希群,王文強,等.濕地土壤動物及其與濕地恢復的關系[J]. 生態環境學報,2014,(4):705-709.
[24]梁文舉,張萬民,李維光,等. 施用化肥對黑土地區線蟲群落組成及多樣性影響.生物多樣性,2001,9(3):237-240.
[25]Riza K,Black H I J,Campbell C D,et al.Selecting biological indicators for monitoring soils: A framework for balancing scientific and technical opinion to assist policy development. Ecological Indicators,2009,(9):1212-1221.
[26]熊 燕.熱帶、亞熱帶土壤動物群落多樣性及彈尾綱系統發生的研究[D]. 上海:華東師范大學,2005.
[27]孫賢斌,李玉成.淮南煤礦廢棄地重金屬污染對土壤動物群落的影響[J]. 生態學雜志,2014,33(2):408-414.
[28]孫賢斌,劉紅玉,李玉成,等. 重金屬污染對土壤動物群落結構及空間分布的影響[J]. 應用生態學報,2007,18(9):2080-2084.
[29]王振中,張友梅,賀躍明,等.重金屬污染的稻田土壤中動物群落的研究[J]. 環境科學,1986,(6):34-39.
[30]張永志,徐建民.重金屬Cu污染對土壤動物群落結構的影響[J]. 農業環境科學學報,2006,25:127-130.
[31]李 濤,李燦陽,俞丹娜,等.交通要道重金屬污染對農田土壤動物群落結構及空間分布的影響[J]. 生態學報,2010,30(18):5001-5011.
[32]劉任濤,趙哈林,趙學勇.科爾沁沙地不同造林類型對土壤動物多樣性的影響[J]. 應用生態學報,2012,23(4):1104-1110.
[33]吳玉紅. 不同土地利用方式對土壤動物多樣性的影響研究[J].安徽農業科學,2012,40(17):9270-9273.
[34]林蘭穩,鐘繼洪,譚 軍,等.土地利用方式對土壤動物多樣性的影響[J]. 生態環境學報,2012,(10):1678-1682.
[35]趙哈林,劉任濤,周瑞蓮,等.沙漠化對科爾沁沙質草地大型土壤動物群落的影響及其成因分析[J]. 草業學報,2013,22(3):70-77.
[36]吳廷娟.全球變化對土壤動物多樣性的影響[J]. 應用生態學報,2013,24(2):581-588.
[37]陳 婧,陳法軍,劉滿強,等.溫度和CO2濃度升高下轉Bt水稻種植對土壤活性碳氮和線蟲群落的短期影響[J]. 生態學報,2014,34(6):1481-1489.
[38]Yeates G W,Newton P C D. Long-term changes in topsoil nematode populations in grazed pasture under elevated atmospheric carbon dioxide[J]. Biology and Fertility of Soils,2009,45(8):799-808.
[39]宋 敏,劉銀占,井水水.土壤線蟲對氣候變化的響應研究進展[J]. 生態學報,2015,35(20):6857-6867.
[40]IPCC.Climate Change 2007: the physical science basis[M]. New York:Cambridge University Press,2007.
[41]魏書精,羅碧珍,孫 龍,等.森林生態系統土壤呼吸時空異質性及影響因子研究進展[J]. 生態環境學報,2013,(4):689-704.
[42]閆修民. 全球變暖對松嫩西部草原中小型土壤動物多樣性的影響[D]. 長春:中國科學院研究生院(東北地理與農業生態研究所),2015.
[43]陳 靖,李天文,馮麗麗,等. GIS技術在洪水災害評估中的應用研究——以渭河中下游地區為例[J]. 西北大學學報:自然科學版,2008,38(4):663-667.
(責任編輯:肖 亮)

