綜合性認(rèn)知康復(fù)訓(xùn)練在阿爾茨海默病患者中應(yīng)用的效果評(píng)價(jià)
胡國(guó)娣 向梅 張學(xué)平

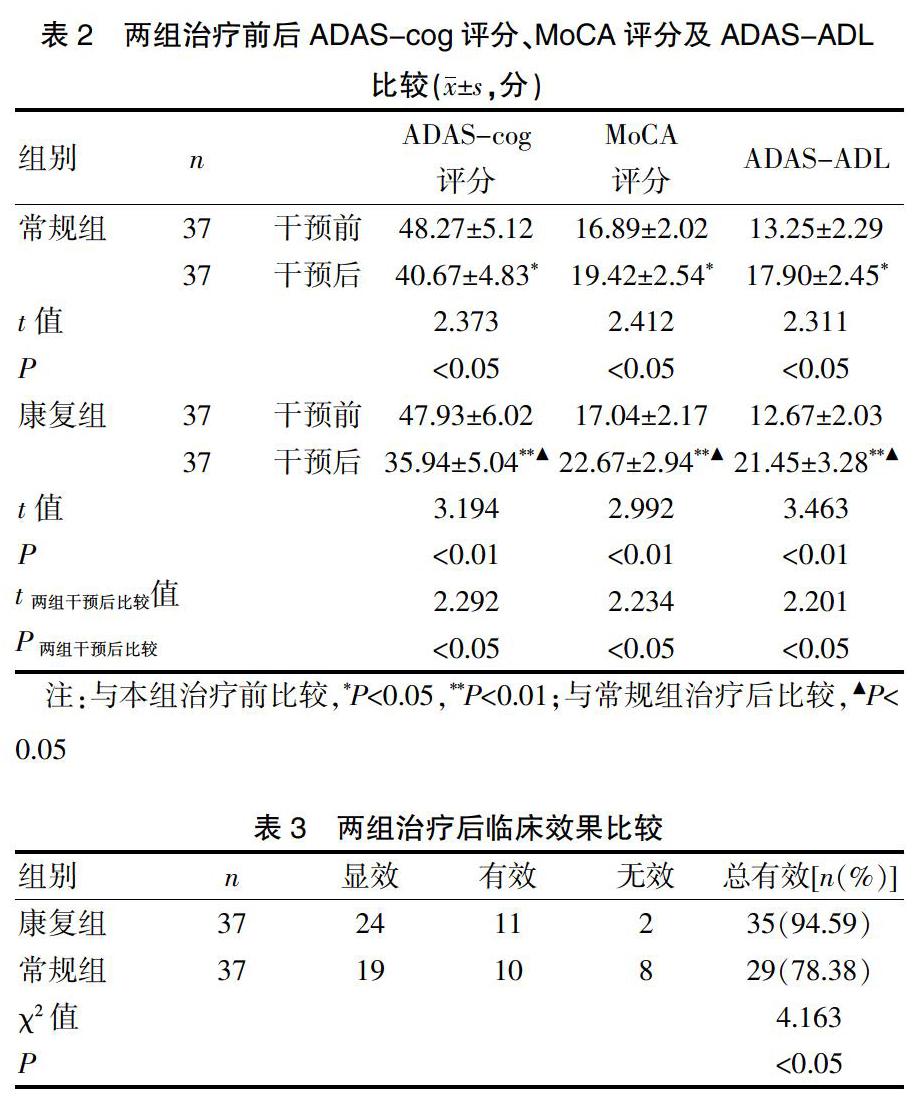
[摘要] 目的 探討綜合性認(rèn)知康復(fù)訓(xùn)練在阿爾茨海默病(AD)患者中應(yīng)用的效果評(píng)價(jià)。 方法 選取2015年1月~2017年12月老年科住院治療的AD患者74例,隨機(jī)分為康復(fù)組和常規(guī)組。兩組均予以尼麥角林片10 mg/次,2次/d+吡垃西坦片2片/次,3次/d聯(lián)合治療。常規(guī)組給予宣傳教育、心理安慰、用藥干預(yù)、飲食和睡眠指導(dǎo)等常規(guī)干預(yù)措施。康復(fù)組在常規(guī)組基礎(chǔ)上給予綜合性認(rèn)知康復(fù)訓(xùn)練。兩組均干預(yù)12周。比較兩組患者治療前后認(rèn)知功能及日常生活能力的變化,并比較其臨床效果。 結(jié)果 干預(yù)12周后,兩組ADAS-cog評(píng)分較干預(yù)前顯著下降,MoCA評(píng)分及ADAS-ADL較干預(yù)前顯著上升(P<0.05或P<0.01),且康復(fù)組下降或上升值較常規(guī)組更顯著(P<0.05);同時(shí)康復(fù)組臨床總有效率(94.59%)較常規(guī)組(78.38%)更佳(χ2=4.163,P<0.05)。 結(jié)論 綜合性認(rèn)知康復(fù)訓(xùn)練用于AD患者的臨床效果確切,不僅能更明顯改善患者的認(rèn)知功能,延緩認(rèn)知功能障礙的進(jìn)展,而且能提高患者的日常生活能力,增強(qiáng)其獨(dú)立生活能力。
[關(guān)鍵詞] 阿爾茨海默病;綜合性認(rèn)知康復(fù)訓(xùn)練;認(rèn)知功能;日常生活能力
[中圖分類號(hào)] R743.1 ? ? ? ? ?[文獻(xiàn)標(biāo)識(shí)碼] B ? ? ? ? ?[文章編號(hào)] 1673-9701(2020)12-0098-04
[Abstract] Objective To explore the effect of comprehensive cognitive rehabilitation training in patients with Alzheimer's disease (AD). Methods 74 patients with AD who were hospitalized in the Deprtmetn of Geriatrics from January 2015 to December 2017 were randomly divided into rehabilitation group and routine group. The both groups were given Nigra horn tablets 10 mg/time, twice a day +piracetam 2 tablets/time, 3 times/d. The routine group gave routine interventions such as education, psychological comfort, medication intervention, diet and sleep guidance. The rehabilitation group was given comprehensive cognitive rehabilitation training on the basis of the treatment in the routine group. Both groups were treated for 12 weeks. The changes of cognitive function and daily living ability between two groups before and after treatment were observed and compared, and the clinical effects were compared. Results After 12 weeks of intervention, the ADAS-cog scores of the two groups were significantly lower than those before the intervention, and the MoCA score and ADAS-ADL were significantly higher than those before the intervention(P<0.05 or P<0.01). And the decrease or increase of the rehabilitation group was more significant than that of the conventional group(P<0.05). At the same time, the total clinical effective rate (94.59%) was better in the rehabilitation group than that (78.38%) in the conventional group (χ2=4.163, P<0.05). Conclusion The comprehensive cognitive rehabilitation training for patients with AD has a clear clinical effect, which not only can significantly improve the cognitive function of patients, delay the progress of cognitive dysfunction, but also can improve the daily living ability of patients and enhance their independent living ability.?
[Key words] Alzheimer's disease; Comprehensive cognitive rehabilitation training; Cognitive function; Daily living ability
阿爾茨海默病(Alzheimer disease,AD)是一種病因未明的進(jìn)行性退行性腦神經(jīng)變性疾病,好發(fā)于老年期或老年前期,主要表現(xiàn)為記憶力、判斷力及注意力等慢性進(jìn)行性衰退,嚴(yán)重時(shí)出現(xiàn)全面的認(rèn)知能力喪失,引起患者社會(huì)生活功能障礙,生活質(zhì)量明顯下降[1,2]。AD的發(fā)病機(jī)制目前國(guó)內(nèi)外暫不明確,藥物治療雖能在一定程度上延緩其認(rèn)知癥狀的進(jìn)展,但不能逆轉(zhuǎn)病情,尚存在一定的缺陷[3,4]。……

