體位性低血壓的護理干預在泌尿外科老年患者中的應用研究
陳瑞燕
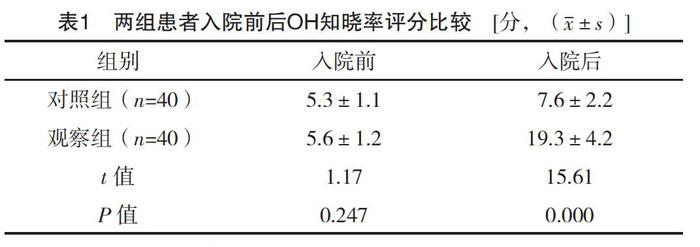
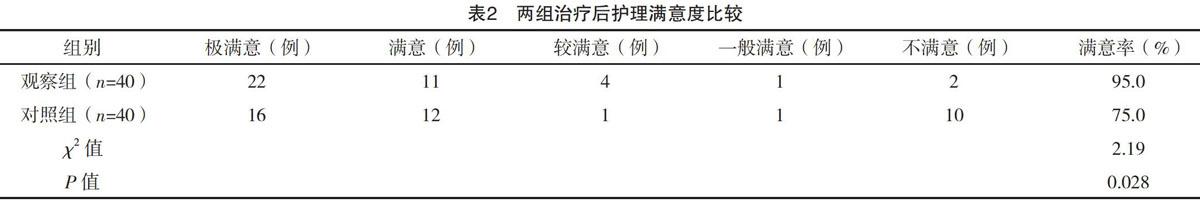
【摘要】 目的:分析體位性低血壓(OH)的護理干預在泌尿外科老年患者中的應用研究。方法:選取80例泌尿外科圍術期發生體位性低血壓的老年患者,隨機分為觀察組(n=40)和對照組(n=40)。對照組行常規護理,觀察組則采用針對性護理干預。比較兩組患者入院前后患者體位性低血壓知曉率評分、患者1周內跌倒發生率及護理滿意度。結果:兩組入院前各項指標差異無統計學意義(P>0.05);觀察組出院時,OH知曉率評分明顯高于對照組,而住院期間觀察組1周內跌倒發生率低于對照組(P<0.05);同時護理滿意度觀察組(95.0%)高于對照組(75.0%),差異有統計學意義(P<0.05)。結論:針對關鍵危險因素行針對性護理干預,可有效提升泌尿外科圍術期老年體位性低血壓患者對OH的認識,降低OH對患者的損害,進而提高護理滿意度。
【關鍵詞】 針對性護理 老年 泌尿外科 圍術期 體位性低血壓
doi:10.14033/j.cnki.cfmr.2020.15.052 文獻標識碼 B 文章編號 1674-6805(2020)15-0-03
Research on Nursing Intervention of Orthostatic Hypotension in Elderly Patients in Urology/CHEN Ruiyan. //Chinese and Foreign Medical Research, 2020, 18(15): -127
[Abstract] Objective: To analyze the application of orthostatic hypotension nursing intervention in elderly patients of urology. Method: A total of 80 elderly patients with orthostatic hypotension during perioperative period of urology were selected and randomly divided into observation group (n=40) and control group (n=40). The control group received routine nursing, and the observation group adopted targeted nursing intervention. Compared the two groups of patients with orthostatic hypotension awareness rate scores, incidence of falls within 1 week, and nursing satisfaction before and after admission. Result: There were no significant differences between the two groups before admission (P>0.05). When the observation group was discharged, the score of OH awareness rate was significantly higher than that of the control group, and the incidence of falls within 1 week of the observation group was lower than that of the control group (P<0.05). At the same time, the nursing satisfaction of observation group was 95.0% which higher than 75.0% of the control group, and the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05). Conclusion: Targeted nursing interventions for key risk factors can effectively improve the awareness of OH in elderly patients with orthostatic hypotension during perioperative period of urological surgery, reduce the damage caused by OH to patients, and then improve nursing satisfaction.
[Key words] Targeted nursing Elderly Urology Perioperative period Orthostatic hypotension
First-authors address: Wuchuan Peoples Hospital, Wuchuan 524500, China
體位性低血壓(orthostatic hypotension,OH)是指由人的體位變化引起的血壓下降[1-2],通過一定的研究發現體位性低血壓經常出現在夜間,由于泌尿外科老年患者多會出現夜尿增多的情況,如果此時出現體位性低血壓,很容易導致暈倒、暈厥或者心絞痛等心腦血管缺血癥狀[3-5],從而對老年人的身體造成一定危害。本院早期調查顯示,護士及患者對OH知曉率較低,為此自2018年12月起針對護理人員進行OH理論知識全科護理培訓,對OH患者進行針對性護理干預,并取得較好效果,現報道如下。
綜上所述,針對關鍵危險因素行針對性護理干預,有效提升泌尿外科圍術期老年體位性低血壓患者對OH的認識,降低OH對患者的損害,進而提高護理滿意度,值得推廣。
參考文獻
[1]程昌艷.老年體位性低血壓患者臨床護理效果分析[J].華南國防醫學雜志,2015,29(1):71-73.
[2]王曉蕾,張楠,張嵐.壓力梯度長襪預防老年重癥患者深靜脈血栓形成和體位性低血壓的效果觀察[J].天津護理,2016,24(4):293-295.
[3]秦莉.體位性低血壓節律評估用于老年高血壓患者護理中的作用分析[J].國際醫藥衛生導報,2019,25(6):966-968.
[4]譚英葵,農冬暉,高熙,等.老年體位性低血壓及其護理干預研究進展[J].內科,2018,13(4):633-635.
[5]耿慧,陳夏歡,杜佳麗,等.采用連續無創血壓監測系統監測老年住院患者體位改變時血壓的變化情況及其相關因素分析[J].中華心血管病雜志,2019,47(5):381-387.
[6]祖麗菲婭·木沙,胡爾西旦·那斯爾,艾斯卡爾·沙比提.老年高血壓患者變換體位造成血壓改變的特點及其并存神經認知障礙的臨床分析[J].實用老年醫學,2016,30(8):648-650.
[7]張潔.高齡老人體位性血壓變化與動脈粥樣硬化的相關性研究[J].中華老年心腦血管病雜志,2017,19(5):483-487.
[8]張海榮,王莉萍.腦血管病患者繼發體位性低血壓的安全護理[J].護士進修雜志,2013,28(10):903-904.
[9]陶思怡,黃金文.1例善思達引起體位性低血壓病人的護理[J].全科護理,2015,13(9):863-864.
[10]陳娜麗,崔智君,李秀川,等.5A模式護理干預方案在老年人體位性低血壓中的應用[J].蚌埠醫學院學報,2017,10(42):1399.
[11]韋玉敏.健康教育在老年高血壓病護理中的應用[J].大家健康:學術版,2016,10(6):21-22.
[12]高媛媛,李麗華.體位性低血壓節律評估在老年高血壓患者護理中的應用[J].中國病案,2017,18(6):110-112.
(收稿日期:2020-01-03) (本文編輯:張亮亮)

