不同藥物治療糖尿病合并高血壓臨床效果分析
李延文
DOI:10.16658/j.cnki.1672-4062.2020.20.093
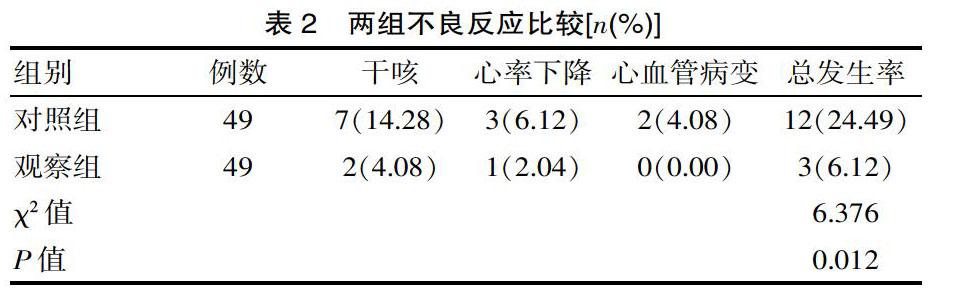
[摘要] 目的 分析不同藥物治療糖尿病合并高血壓臨床效果。方法 以該院2018年5月—2019年11月收治的糖尿病合并高血壓患者98例,依據藥物治療方式的不同隨機分為對照組(降糖藥、硝苯地平緩釋片治療)與觀察組(在對照組治療基礎上,厄貝沙坦片治療),每組49例。比較兩組不良反應、血糖水平及舒張壓與收縮壓水平。結果 觀察組不良反應明顯低于對照組,差異有統計學意義(P<0.05);相較于對照組治療而言,觀察組可有效控制患者血糖及血壓,治療效果顯著,差異有統計學意義(P<0.05)。結論 加用厄貝沙坦片,可顯著改善患者病情,促使機體血壓、血糖維持在正常水平,其價值值得廣泛推廣。
[關鍵詞] 不同藥物;糖尿病合并高血壓;治療效果
[中圖分類號] R587.2? ? ? ? ? [文獻標識碼] A? ? ? ? ? [文章編號] 1672-4062(2020)10(b)-0093-03
Analysis of the Clinical Effects of Different Drugs in the Treatment of Diabetes with Hypertension
LI Yan-wen
Department of Internal Medicine, Jinling Town Hospital, Zhaoyuan, Shandong Province, 265404 China
[Abstract] Objective To analyze the clinical effects of different drugs in the treatment of diabetes with hypertension. Methods 98 patients with diabetes and hypertension admitted to the hospital from May 2018 to November 2019 were randomly divided into a control group (treated with hypoglycemic drugs and nifedipine sustained-release tablets) and observation group (based on the treatment of the control group, irbesartan tablets treatment) according to different drug treatment methods, 49 cases in each group. The adverse reactions, blood glucose levels, and diastolic and systolic blood pressure levels were compared between the two groups. Results The adverse reactions of the observation group were significantly lower than those of the control group,and the difference wasstatistically significant(P<0.05); compared with the treatment of the control group, the observation group could effectively control the patient's blood glucose and blood pressure, the treatment effect was significant, and the difference was statistically significant(P<0.05). Conclusion The addition of irbesartan tablets can significantly improve the patient's condition and promote the maintenance of blood pressure and blood glucose at normal levels. Its value is worthy of widespread promotion.
[Key words] Different drugs; Diabetes mellitus with hypertension; Therapeutic effect
臨床大部分高血壓患者常伴有糖尿病,且糖尿病患者也大多伴有高血壓疾病,兩者并稱為同源性疾病,是臨床常見的合并癥。二者無論是病因、互相影響或危害性都存在共通性,且常常合并發作,是誘發心腦血管疾病的主要因素,二者并發使心腦血管疾病的發生率及病死率顯著提升[1]。而糖尿病患者對具有升壓作用的血管緊張素較為敏感,又容易造成患者腎損傷都可導致患者高血壓。且隨著我國生活習慣及水平的變化,其病發率顯著上升,對患者的身體健康危害性極大[2]。目前臨床以藥物治療為主要控制手段,該文選取2018年5月—2019年11月入院治療的98例糖尿病患者為例,探討糖尿病合并高血壓患者不同藥物治療的應用措施,并進行分析記錄,為臨床治療提供可靠依據,現報道如下。
1? 資料與方法
1.1? 一般資料
選取該院糖尿病合并高血壓患者98例,均符合臨床糖尿病相關診斷標準,亦符合《中國高血壓防止指南要點(2005版)》中的高血壓相關診斷病癥,并經臨床檢查確診為糖尿病合并高血壓患者,依據治療措施的不同隨機分為對照組與觀察組,每組49例。……

