海洋動物體內氧化三甲胺和甘氨酸甜菜堿的濃度特征及影響因素
陸長坤 宋若晗 曲克明 崔正國 趙婉玉 胡清靜 畢相東


摘要 氧化三甲胺(TMAO)和甜菜堿(GBT)廣泛存在于海洋生物體內,它們被降解后產(chǎn)生的有機胺可通過海氣交換進入大氣中,進而可以促進新粒子生成及增長,具有潛在重要的氣候效應。多數(shù)研究認為浮游植物體內含有大量的TMAO和GBT,它們是海洋大氣中有機胺的主要貢獻者。也有研究發(fā)現(xiàn)海洋動物體內也含有TMAO和GBT,但它們對大氣中有機胺的貢獻報道較少。概述了不同類型海洋動物體內TMAO和GBT合成方式及它們降解為有機胺的途徑,歸納了不同海洋動物體內TMAO和GBT的濃度分布特征,探討了影響動物體內TMAO和GBT濃度的因素,剖析了該領域待解決的科學問題,并對今后的研究工作進行了展望,以期為認識海洋環(huán)境中有機胺來源及其氣候效應提供科學參考。
關鍵詞 海洋動物;氧化三甲胺;甘氨酸甜菜堿;濃度;影響因素
中圖分類號 S917.4? 文獻標識碼 A? 文章編號 0517-6611(2021)22-0018-11
doi:10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2021.22.005
開放科學(資源服務)標識碼(OSID):
Concentration Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Trimethylamine Oxide and Glycine Betaine in Marine Animals
LU Chang-kun ??SONG Ruo-han ??QU Ke-ming 3 et al
(1. College of Fishery, Tianjin Agricultural University, Tianjin 300392;2.Yellow Sea Fisheries Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Fishery Sciences, Key Laboratory of Sustainable Development of Marine Fisheries, Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs, Qingdao,Shandong 266071;3. Laboratory for Marine Fisheries Science and Food Production Processes, Pilot National Laboratory for Marine Science and Technology (Qingdao), Qingdao,Shandong 266071)
Abstract Trimethylamine oxide (TMAO) and Glycine betaine (GBT) are widely present in marine organisms. The organic amines produced after they are degraded can enter the atmosphere through air-sea exchange, which can promote the generation and growth of new particles, which has a potentially important climate effect. Most studies believe that phytoplankton contains a large amount of TMAO and GBT, which are the main contributors to organic amines in the ocean atmosphere. Some studies have found that marine animals also contain TMAO and GBT, but their contribution to organic amines in the atmosphere is rarely reported. This article summarized the synthesis methods of TMAO and GBT in different types of marine animals and their degradation to organic amines, concluded the distribution characteristics of TMAO and GBT in different marine animals, and discussed the factors that affect the concentrations of TMAO and GBT in animals, analyzed scientific problems to be solved in this field, and forecasted future research work, in order to provide a scientific reference for understanding the sources of organic amines in the marine environment and their climate effects.
Key words Marine animals;Trimethylamine oxide;Glycine betaine;Concentration;Influencing factors
近年研究表明,大氣中的甲胺(MMA)、二甲胺(DMA)和三甲胺(TMA)可以促進新粒子的生成及顆粒物增長,進而增加云凝結核數(shù)濃度,通過改變輻射強迫對氣候變化產(chǎn)生重要影響[1-4]。因此,有機胺是當今國際的研究熱點之一。海洋是有機胺的重要來源,海洋生物體內的氧化三甲胺(TMAO)、甘氨酸甜菜堿(GBT)、膽堿(CHO)等有機胺前體物被細菌降解后會產(chǎn)生有機胺[5-10],然后通過海氣交換進入大氣中,其對全球大氣中有機胺的貢獻約占28%[11]。多數(shù)研究發(fā)現(xiàn),海洋水體或大氣中有機胺的濃度隨浮游植物生物量的增加而增加,且在浮游植物體內檢測出大量的TMAO和GBT[12-16],因此,推測浮游植物是海洋環(huán)境中有機胺的主要貢獻者。但是,除了浮游植物外,海洋動物體內也含有大量的TMAO和GBT等有機胺前體物[17-19]。1938年Beatty[20]在腐爛的魚體中第一次發(fā)現(xiàn)了TMAO的代謝產(chǎn)物TMA。Namies′nik等[21]在Gdańsk城市的魚攤附近測得大氣中MMA、DMA和TMA的濃度分別高達112.4、140.1和24.3 mg/m3。Hu等[15]研究發(fā)現(xiàn)我國近海大氣顆粒物中DMA+、TMA+的濃度比世界其他海域高1~3個數(shù)量級,推測其可能與我國近海大規(guī)模的海水養(yǎng)殖有關。這說明海洋魚類等動物體內的TMAO可能對大氣中有機胺具有重要的貢獻。盡管現(xiàn)階段對于不同種類海洋浮游植物體內有機胺前體物的濃度特征及影響因素的研究開展了大量的工作[7,9,22-25],但關于海洋動物體內TMAO和GBT的濃度特征及影響因素的研究較少。此外,TMAO和GBT還具有為海洋動物提供浮力[26]、調節(jié)滲透壓[27-29]、維持其蛋白質結構和功能穩(wěn)定等重要作用[30-37]。筆者對不同種類海洋動物體內TMAO和GBT的代謝途徑、濃度特征和影響因素等進行了詳細的綜述,從而為進一步認識海洋動物對大氣中有機胺的貢獻、評估其潛在氣候效應提供理論依據(jù)。
1 海洋動物體內TMAO和GBT的合成與降解
1.1 海洋動物體內TMAO和GBT的合成
海洋動物體內的TMAO和GBT主要有2個來源(圖1):①動物自身合成,一些浮游植物體內的CHO、磷脂酰膽堿和肉堿等在單加氧酶的催化下氧化為甜菜堿醛,然后在甜菜堿醛脫氫酶的作用下氧化為GBT,GBT經(jīng)甜菜堿脫甲基作用后產(chǎn)生TMA,最后由三甲胺氧化酶將TMA氧化為TMAO[17,38-42];②從攝取的食物中直接積累[43],部分海洋動物不能合成TMAO或GBT[44],必須通過攝食藻類或小型動物等獲得[ 45-49]。
1.2 海洋動物體內TMAO和GBT的降解
海洋動物體內TMAO的降解主要有2種途徑(圖1):①外源途徑,主要通過海洋細菌產(chǎn)生的TMAO還原酶等降解為TMA[1 18,2 50-52];②海洋動物的內源性酶解,即在動物體內TMAO去甲基化酶的作用下直接降解為DMA和甲醛[53-55]。GBT是通過甜菜堿脫甲基作用降解為TMA[56],之后TMA經(jīng)過三甲胺脫氫酶的作用生成DMA,或是先由三甲胺氧化酶催化生成TMAO,再經(jīng)氧化三甲胺脫甲基酶生成DMA;最后DMA在二甲胺脫氫酶的催化作用下生成MMA,MMA再進一步被降解為氨氣(圖1)。
2 海洋動物體內TMAO和GBT的含量特征
2.1 海洋動物體內TMAO和GBT的含量
TMAO廣泛存在于海洋動物中[57-58],其含量高達魚類、甲殼類等動物組織干重的7%[4 59]。通過對230種海洋動物統(tǒng)計分析發(fā)現(xiàn),海洋動物體內TMAO含量是0.01~25.01 g/kg,但不同種類動物體內TMAO的含量存在差異(表1),整體呈現(xiàn)軟骨魚類>頭足類>甲殼類>硬骨魚類>貝類的趨勢(圖2)。軟骨魚類體內TMAO平均含量為9.58 g/kg,70%軟骨魚類TMAO含量在5.00 g/kg以上,其中,鯊魚、鰩魚含量分別為10.09、12.41 g/kg,深海鰩更是高達21.71 g/kg[5]。軟骨魚TMAO含量約為甲殼類動物的2倍,是貝類含量的10倍之多。頭足類動物TMAO含量次之,平均在8.02 g/kg,是硬骨魚類的2倍多。甲殼類動物TMAO平均含量為5.36 g/kg,其中50%甲殼類動物TMAO含量分布在1.00~5.00 g/kg,含量最高的是真蝦(Caridean shrimp),達到22.46 g/kg[60],最低的刀額新對蝦(Metapenaeus ensis)僅含0.05 g/kg[61]。70%的硬骨魚含量低于3.50 g/kg,但有個別極地硬骨魚肌肉中TMAO含量高達21.78 g/kg[62],其中,含量最低的是長尾蛇魚(Macrurous berglax)和鯰魚(Silurus asotus),均為0.02 g/kg[63-64]。在所有種類海洋動物中,貝類中TMAO平均含量最低,僅為0.98 g/kg,這可能是因為其常棲息于河口附近或有少量淡水注入的淺海內灣中,環(huán)境鹽度較低,從而導致TMAO含量較低。因此,各種動物生活習性以及所處環(huán)境的不同會導致體內TMAO含量存在差異。
GBT也是甲殼類、貝類等海洋動物體內主要的滲透調節(jié)物質之一,但目前國際上對于海洋動物體內GBT的報道較少。通過對42種不同種類海洋動物統(tǒng)計分析發(fā)現(xiàn),GBT在海洋動物體內的含量為0.01~16.82 g/kg(表2),其在不同種類動物體內的含量與TMAO相反,整體呈現(xiàn)貝類>硬骨魚類≈甲殼類≈頭足類>軟骨魚類(圖2)。含量最高的是貝類,平均在4.95 g/kg,約為軟骨魚類(2.60 g/kg)的2倍,其中貽貝含量可高達10.00 g/kg[66]。貝類體內GBT較高,可能與它們攝食含GBT較高的浮游植物有關。頭足類、硬骨魚類和甲殼類含量相差不明顯,分別為4.10、4.13和 4.26 g/kg。
2.2 海洋動物組織器官中TMAO和GBT的分布特征
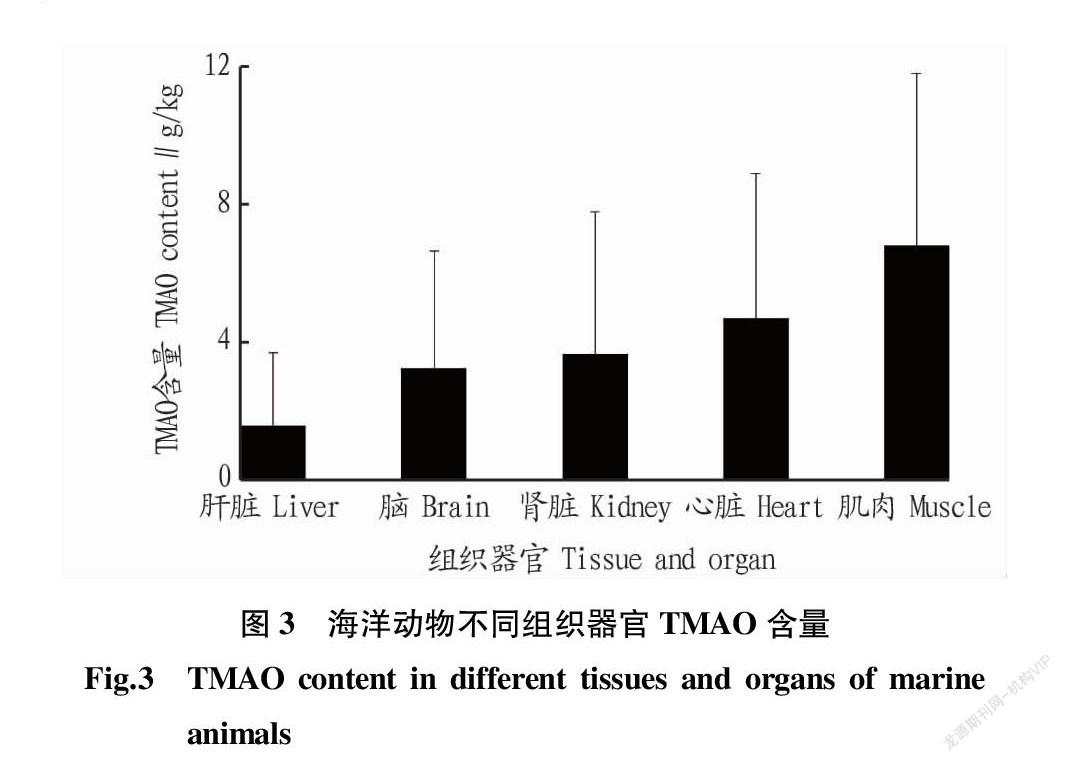
TMAO和GBT在海洋動物體內的分布并不均勻(表3),整體呈現(xiàn)肌肉>心臟>腎臟≈腦>肝臟的趨勢(圖3)。海洋動物肌肉中TMAO平均含量為6.80 g/kg,其中黑霞鯊(Centroscyllium fabricii)肌肉中TMAO含量達18.63 g/kg[63]。海洋動物心臟中含量次之(4.70 g/kg),黑霞鯊心臟中TMAO含量可達13.52 g/kg[63]。而在腎臟和腦組織中TMAO含量差別不大,其平均含量分別為3.66和3.25 g/kg。肝臟含量最低,TMAO含量為1.55 g/kg。
關于海洋動物不同組織內GBT含量的報道較少,Treberg等[49]報道冬鰩魚(Leucoraja ocellata)心臟中GBT含量高達3.16 g/kg,顯著高于其他組織器官,角鯊組織器官中GBT也主要聚積在心臟。
3 海洋動物體內TMAO和GBT含量的主要影響因素
3.1 深度
海洋動物體內TMAO含量受環(huán)境深度的影響較大,主要因為TMAO具有增加海洋動物浮力的作用。海洋動物所處環(huán)境越深,外部的壓力越大,從而促使動物體內積累更高濃度的TMAO以應對環(huán)境壓力[ 3 67]。Yancey等[68]在對太平洋幾種硬骨魚類的研究發(fā)現(xiàn),隨著水深從0到1 400 m逐漸增加時,其肌肉中TMAO含量從3.00 g/kg增加至11.25 g/kg。Keller等[69]通過對不同深度下同一物種中TMAO含量進行檢測發(fā)現(xiàn),深海(4 850 m)硬骨魚肌肉中TMAO的含量是近岸淺水區(qū)個體的5倍。在大西洋4 800 m深處的長尾鱈魚肌肉中TMAO含量高達19.58 g/kg[70]。在水深7 000 m的克馬德里海溝,黑線鱈體內TMAO含量高達28.95 g/kg,幾乎是透光區(qū)魚類平均含量的8倍[71]。
通過對28種軟骨魚及58種硬骨魚體內TMAO含量及其所棲息的深度分析發(fā)現(xiàn)(圖4),這2類魚類體內TMAO含量隨深度的增加而顯著增高[3 49,67,69-70]。通過對<500 m、500~2 000 m和>2 000 m 3種水深中的5大類(軟骨魚類、頭足類、甲殼類、硬骨魚類和貝類)動物統(tǒng)計分析發(fā)現(xiàn)(圖5),當水深<500 m時,軟骨魚類體內TMAO含量最高(為5.63 g/kg),是其他4類(頭足類、甲殼類、硬骨魚類和貝類)的3.1~5.8倍;當水深在500~2 000 m時,依然是軟骨魚類體內TMAO含量最高,而甲殼類和頭足類含量相近,約占軟骨魚類的75%,硬骨魚類含量最低,約為軟骨魚類的47%;當水深>2 000 m時,甲殼類TMAO平均含量為16.49 g/kg,與軟骨魚類和頭足類含量相差不大,是硬骨魚類的1.9倍。對于同種類型的動物來說,水深>2 000 m的軟骨魚類體內TMAO含量分別是500~2 000 m和<500 m的1.4和2.7倍,硬骨魚類分別為1.6和5.6倍,甲殼類動物分別為2.0和9.0倍,頭足類動物為2.3和12.4倍。說明頭足類動物體內TMAO隨深度變化最顯著,硬骨魚類、甲殼類次之,軟骨魚類變化最小。
并非所有報道都表明TMAO含量隨深度增加而增加,Laxson等[ 17]研究表明TMAO含量不會隨著深度的變化而發(fā)生變化。這也說明不同海洋動物對深度的敏感性存在差異。
3.2 鹽度
TMAO是海洋動物重要的滲透調節(jié)物質,鹽度也會影響海洋動物體內TMAO含量。廣鹽性白真鯊從淡水中放入海水中,體內TMAO含量增加到之前的1.5倍[72]。當鹽度減小為80%時,廣鹽性鰩魚體內TMAO含量降低了5%;當鹽度減小為50%時,TMAO的含量降低了36%[73]。Summers等[18]研究發(fā)現(xiàn),當海洋魚類進入到低鹽度河口水域時,其體內TMAO含量往往很低。將鳉魚(Killifish)從100%的海水轉移到淡水時,也觀察到其肌肉中TMAO含量下降了46%[74]。在對白斑角鯊(Squalus acanthias)的研究中發(fā)現(xiàn),隨著環(huán)境鹽度降低至70%時,白斑角鯊的腮中TMAO含量會下降至原來的85%[65]。Chung等[75]通過對香港89種(共266條)淡水魚、海水和淡水兩棲的魚、海水魚體內的TMAO分析發(fā)現(xiàn),75%的海水和淡水兩棲的魚中可檢測出TMAO,而僅有33%的淡水魚中可檢測出TMAO。因此,海洋動物為應對較高鹽度壓力,其體內會積累更多的TMAO。
鹽度對海洋動物體內GBT含量也具有顯著的影響。海洋動物在高鹽度環(huán)境中積累大量GBT,并在鹽度降低時釋放。一般情況下,海洋動物體內GBT含量是淡水動物的10~100倍[76]。Brictkux-Grégoire等[77]研究發(fā)現(xiàn),鹽度下降50%時,貽貝的肌肉中GBT含量會降低35%。Delgado-Gaytán等[78]研究也表明,與對照組鹽度(35‰)相比,在40‰、50‰和60‰的鹽度下,蝦鰓中GBT含量高出7.3~8.3倍,而在肌肉中GBT含量則高出9倍。因此,為適應鹽度的壓力,海洋動物體內TMAO或GBT含量遠高于淡水動物[57,65]。
3.3 溫度
TMAO和GBT作為海洋動物重要的冷凍保護劑,其含量也會受溫度的影響。Treberg等[33]的室內試驗顯示,低溫可以誘導胡瓜魚(Osmerus mordaxa)體內TMAO的積聚。在格陵蘭鱈魚(Gadus ogac)等一些冷水動物的血清和肝臟中,TMAO水平異常高(0.60~2.10 g/kg)[79-81]。在夏季溫度較高時,長鰭線指鰕翁(Nemadactylus macropterus)和綠鰭魚(Chelidonichthys kumu)TMAO含量會降低[18]。在冬季溫度較低時,三文魚(Oncorhynchus)的血清、彩虹魚(Poecilia)的血漿和鯡魚(Herring)的肌肉中TMAO含量都有所增加[6 79,82]。林海生等[66]研究發(fā)現(xiàn)我國南北方海域牡蠣中GBT含量呈現(xiàn)“南低北高”的特征,這可能是由于北方溫度較南方低造成的。因此,溫度較低時,海洋動物體內會產(chǎn)生較多的TMAO或GBT以適應溫度較低的環(huán)境[3 67]。
4 展望
綜上所述,雖然目前國內外對海洋動物體內TMAO和GBT的合成與降解途徑、濃度特征及影響因素進行了較多研究,但還有許多問題需要解決,具體體現(xiàn)在以下3點:
①現(xiàn)階段國內外對海洋動物體內TMAO開展了一定研究,但對GBT報道較少,未來需加強在海洋動物體內GBT的代謝機制、不同組織的濃度特征及影響因素等方面的研究;
②揭示海洋動物體內TMAO和GBT的轉化機制,闡明不同種類海洋動物體內兩者濃度存在差異的原因;
③我國是世界海水養(yǎng)殖第一大國,進一步探索我國大規(guī)模海水養(yǎng)殖生物體內TMAO和GBT對水體及大氣中有機胺的貢獻及其潛在的氣候效應。
參考文獻
[1] SELLEGRI K,PEY J,ROSE C,et al.Evidence of atmospheric nanoparticle formation from emissions of marine microorganisms[J].Geophysical research letters,201 43(12):6596-6603.
[2] ALMEIDA J,SCHOBESBERGER S,KRTEN A,et al.Molecular understanding of sulphuric acid-amine particle nucleation in the atmosphere[J].Nature,201 502(7471):359-363.
[3] CHEN H H,VARNER M E,GERBER R B,et al.Reactions of methanesulfonic acid with amines and ammonia as a source of new particles in air[J].The journal of physical chemistry B,201 120(8):1526-1536.
[4] YAO L,GARMASH O,BIANCHI F,et al.Atmospheric new particle formation from sulfuric acid and amines in a Chinese megacity[J].Science,2018,361(6399):278-281.
[5] LAXSON C J,CONDON N E,DRAZEN J C,et al.Decreasing urea:Trimethylamine N-oxide ratios with depth in chondrichthyes:A physiological depth limit?[J].Physiological & biochemical zoology,201 84(5):494-505.
[6] HATTON A D,GIBB S W.A technique for the determination of trimethylamine-N-oxide in natural waters and biological media[J].Analytical chemistry,1999,71(21):4886-4891.
[7] CARPENTER L J,ARCHER S D,BEALE R.Ocean-atmosphere trace gas exchange[J].Chemical society reviews,201 41(19):6473-6506.
[8] OREN A.Cyanobacteria in hypersaline environments:Biodiversity and physiological properties[J].Biodiversity and conservation,201 24(4):781-798.
[9] CHARLOTTE C.Distributions of glycine betaine and the methylamines in coastal waters:Analytical developments and a seasonal study[D].Devon,UK:University of Plymouth,2015.
[10] SUN Y,DING S S,HE M W,et al.Construction and analysis of the immune effect of Vibrio harveyi subunit vaccine and DNA vaccine encoding TssJ antigen[J].Fish and shellfish immunology,2020,98:45-51.
[11] GE X L,WEXLER A S,CLEGG S L.Atmospheric amines-Part I.A review[J].Atmospheric environment,201 45(3):524-546.
[12] GIBB S W,MANTOURA R F C,LISS P S.Ocean-atmosphere exchange and atmospheric speciation of ammonia and methylamines in the region of the NW Arabian Sea[J].Global biogeochemical cycles,1999,13(1):161-178.
[13] KING G M.Methanogenesis from methylated amines in a hypersaline algal mat[J].Applied and environmental microbiology,1988,54(1):130-136.
[14] VAN PINXTEREN M,F(xiàn)OMBA K W,VAN PINXTEREN D,et al.Aliphatic amines at the Cape Verde Atmospheric Observatory:Abundance,origins and sea-air fluxes[J].Atmospheric environment,2019,203(APR):183-195.
[15] HU Q J,YU P R,ZHU Y J,et al.Concentration,size distribution and formation of trimethylaminium and dimethylaminium ions in atmospheric particles over marginal seas of China[J].Journal of the atmospheric sciences,201 72(9):3487-3498.
[16] YU P R,HU Q J,LI K,et al.Characteristics of dimethylaminium and trimethylaminium in atmospheric particles ranging from supermicron to nanometer sizes over eutrophic marginal seas of China and oligotrophic open oceans[J].Science of the total environment,201 572:813-824.
[17] SEIBEL B A,WALSH P J.Trimethylamine oxide accumulation in marine animals:Relationship to acylglycerol storage[J].Journal of experimental biology,200 205(Pt 3):297-306.
[18] SUMMERS G,WIBISONO R D,HEDDERLEY D I,et al.Trimethylamine oxide content and spoilage potential of New Zealand commercial fish species[J].New Zealand journal of marine and freshwater research,2017,51(3):393-405.
[19] PIERCE S K,DRAGOLOVICH J,CROMBIE B N.Variations in intracellular choline levels may account for differences in glycine betaine synthesis between conspecific oyster populations responding to hyperosmotic stress[J].Journal of experimental zoology,1997,278(5):283-289.
[20] BEATTY S A.Studies of fish spoilage:II.The origin of trimethylamine produced during the spoilage of cod muscle press juice[J].Journal of the fisheries research board of Canada,1938,4(2):63-68.
[21] NAMIES'NIK J,JASTRZEBSKA A,ZYGMUNT B.Determination of volatile aliphatic amines in air by solid-phase microextraction coupled with gas chromatography with flame ionization detection[J].Journal of chromatography A,200 1016(1):1-9.
[22] IAN L.Microbial methylated amine metabolism in marine surface waters[D].Coventry,UK:University of Warwick,2015.
[23] GREEN T K,HATTON A D.The claw hypothesis:A new perspective on the role of biogenic sulphur in the regulation of global climate[M]//HUGHES R N,HUGHES D J,SMITH I P.Oceanography and marine biology:Volume 52.Boca Raton,F(xiàn)L:CRC Press,2014:315-336.
[24] WELSH D T.Ecological significance of compatible solute accumulation by micro-organisms:From single cells to global climate[J].FEMS Microbiology Reviews,2000,24(3):263-290.
[25] TORSTENSSON A,YOUNG J N,CARLSON L T,et al.Use of exogenous glycine betaine and its precursor choline as osmoprotectants in Antarctic sea-ice diatoms[J].Journal of phycology,2019,55(3):663-675.
[26] WITHERS P C,HEFTER G T,PANG T S.Role of urea and methylamines in buoyancy of elasmobranchs[J].Journal of experimental biology,199 188(1):175-189.
[27] YANCEY P H,CLARK M E,HAND S C,et al.Living with water stress:Evolution of osmolyte systems[J].Science,198 217(4566):1214-1222.
[28] CHOLETTE C,GAGNON A.Isosmotic adaptation in Myxine glutinosa L.-II.Variations of the free amino acids,trimethylamine oxide and potassium of the blood and muscle cells[J].Comparative biochemistry & physiology part A:Physiology,197 45(4):1009-1021.
[29] FORSTER R P,GOLDSTEIN L.Intracellular osmoregulatory role of amino acids and urea in marine elasmobranchs[J].The American journal of physiology,197 230(4):925-931.
[30] YANCEY P H,SIEBENALLER J F.Trimethylamine oxide stabilizes teleost and mammalian lactate dehydrogenases against inactivation by hydrostatic pressure and trypsinolysis[J].The journal of experimental biology,1999,202(Pt24):3597-3603.
[31] QU Y X,BOLEN D W.Hydrogen exchange kinetics of RNase A and the urea:TMAO paradigm[J].Biochemistry,200 42(19):5837-5849.
[32] BASKAKOV I,WANG A J,BOLEN D W.Trimethylamine-N-oxide counteracts urea effects on rabbit muscle lactate dehydrogenase function:A test of the counteraction hypothesis[J].Biophysical journal,1998,74(5):2666-2673.
[33] TREBERG J R,BYSTRIANSKY J S,DRIEDZIC W R.Temperature effects on trimethylamine oxide accumulation and the relationship between plasma concentration and tissue levels in smelt(Osmerus mordax)[J].Journal of experimental zoology part A:Comparative experimental biology,200 303(4):283-293.
[34] VILLALOBOS A R A,RENFRO J L.Trimethylamine oxide suppresses stress-induced alteration of organic anion transport in choroid plexus[J].Journal of experimental biology,2007,210(Pt3):541-552.
[35] GILLETT M B,SUKO J R,SANTOSO F O,et al.Elevated levels of trimethylamine oxide in muscles of deep-sea gadiform teleosts:A high-pressure adaptation?[J].Journal of experimental zoology,1997,279(4):386-391.
[36] YANCEY P H,SOMERO G N.Methylamine osmoregulatory solutes of elasmobranch fishes counteract urea inhibition of enzymes[J].The journal of experimental zoology,1980,212(2):205-213.
[37] TRZECIAKOWSKI J P.Analysis of stimulus-response chains using nonlinear dynamics[J].Journal of pharmacological & toxicological methods,199 36(2):103-121.
[38] RAYMOND J A.Trimethylamine oxide and urea synthesis in rainbow smelt and some other northern fishes[J].Physiological zoology,1998,71(5):515-523.
[39] SCHLENK D.Occurrence of flavin-containing monooxygenases in non-mammalian eukaryotic organisms[J].Comparative biochemistry and physiology.Part C:Pharmacology,toxicology & endocrinology,1998,121(1/2/3):185-195.
[40] USSHER J R,LOPASCHUK G D,ARDUINI A.Gut microbiota metabolism of l-carnitine and cardiovascular risk[J].Atherosclerosis,201 231(2):456-461.
[41] UFNAL M,ZADLO A,OSTASZEWSKI R.TMAO:A small molecule of great expectations[J].Nutrition,201 31(11/12):1317-1323.
[42] BAKER J R,CHAYKIN S.The biosynthesis of trimethylamine-N-oxide[J].The journal of biological chemistry,196 237(3):1309-1313.
[43] DE VOOYS C G N,GEENEVASEN J A J.Biosynthesis and role in osmoregulation of glycine-betaine in the Mediterranean mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis LMK[J].Comparative biochemistry and physiology part B,200 132(2):409-414.
[44] VAN WAARDE A.Biochemistry of non-protein nitrogenous compounds in fish including the use of amino acids for anaerobic energy production[J].Comparative biochemistry and physiology part B:Comparative biochemistry,1988,91(2):207-228.
[45] TOKUNAGA T.Trimethylamine oxide and its decomposition in the bloody muscle of fish.I.TMAO,TMA,and DMA contents in ordinary and bloody muscles[J].Nippon suisan gakkaishi,1970,36(5):502-509.
[46] NIIZEKI N,DAIKOKU T,HIRATA T,et al.Mechanism of biosynthesis of trimethylamine oxide in tilapia reared under seawater conditions[J].Fisheries science,200 69(1):74-87.
[47] DELGADO-GAYTN M F,ROSAS-RODRGUEZ J A,YEPIZ-PLASCENCIA G,et al.Cloning and molecular characterization of the betaine aldehyde dehydrogenase involved in the biosynthesis of glycine betaine in white shrimp(Litopenaeus vannamei)[J].Chemico-biological interactions,2017,276:65-74.
[48] PIERCE S K,ROWLAND-FAUX L M,O′BRIEN S M.Different salinity tolerance mechanisms in Atlantic and Chesapeake Bay conspecific oysters:Glycine betaine and amino acid pool variations[J].Marine biology,199 113(1):107-115.
[49] TREBERG J R,DRIEDZIC W R.The accumulation and synthesis of betaine in winter skate(Leucoraja ocellata)[J].Comparative biochemistry and physiology part A,2007,147(2):475-483.
[50] CHISTOSERDOVA L.Modularity of methylotrophy,revisited[J].Environmental microbiology, 201 13(10):2603-2622.
[51] 付雪媛,劉豐海,姜城子,等.高效液相色譜-質譜聯(lián)用檢測水產(chǎn)品中氧化三甲胺[J].食品安全質量檢測學報,201 7(1):269-275.
[52] 蔡英華,舒緒剛,廖列文,等.氧化三甲胺在動物養(yǎng)殖中的應用研究進展[J].廣東飼料,2009,18(3):32-35.
[53] DEHAUT A,DUTHEN S,GRARD T,et al.Development of an SPME-GC-MS method for the specific quantification of dimethylamine and trimethylamine:Use of a new ratio for the freshness monitoring of cod fillets[J].Journal of the science of food and agriculture,201 96(11):3787-3794.
[54] NITISEWOJO P,HULTIN H O.Characteristics of TMAO degrading systems in Atlantic short finned squid(Illex illecebrosus)[J].Journal of food biochemistry,198 10(2):93-106.
[55] LUNDSTROM R C,CORREIA F F,WILHELM K A.Enzymatic dimethylamine and formaldehyde production in minced American plaice and blackback flounder mixed with a red hake TMAO-ase active fraction[J].Journal of food science,198 47(4):1305-1310.
[56] CHAREST R P,CHENOWETH M,DUNN A.Metabolism of trimethylamines in kelp bass(Paralabrax clathratus)and marine and freshwater pink salmon(Oncorhynchus gorbuscha)[J].Journal of comparative physiology B,1988,158(5):609-619.
[57] ANTHONI U,B RRESEN T,CHRISTOPHERSEN C,et al.Is trimethylamine oxide a reliable indicator for the marine origin of fish?[J].Comparative biochemistry and physiology B:Comparative biochemistry,1990,97(3):569-571.
[58] LI F,LIU H Y,XUE C H,et al.Simultaneous determination of dimethylamine,trimethylamine and trimethylamine-n-oxide in aquatic products extracts by ion chromatography with non-suppressed conductivity detection[J].Journal of chromatography A,2009,1216(31):5924-5926.
[59] BOCKUS A B,SEIBEL B A.Synthetic capacity does not predict elasmobranchs' ability to maintain trimethylamine oxide without a dietary contribution[J].Comparative biochemistry and physiology part A,2018,217:35-42.
[60] KELLY R H,YANCEY P H.High contents of trimethylamine oxide correlating with depth in deep-sea teleost fishes,skates,and decapod crustaceans[J].The biological bulletin,1999,196(1):18-25.
[61] 姜城子,崔潔,周苗苗,等.青島地區(qū)部分水產(chǎn)品中氧化三甲胺含量的測定[J].食品安全質量檢測學報,201 5(1):41-46.
[62] BEDFORD J J,HARPER J L,LEADER J P,et al.Betaine is the principal counteracting osmolyte in tissues of the elephant fish,Callorhincus millii(Elasmobranchii,Holocephali)[J].Comparative biochemistry and physiology part B,1998,119(3):521-526.
[63] TREBERG J R,DRIEDZIC W R.Elevated levels of trimethylamine oxide in deep-sea fish:Evidence for synthesis and intertissue physiological importance[J].The journal of experimental zoology,200 293(1):39-45.
[64] 陳帥,朱軍莉,勵建榮.非抑制離子色譜檢測海產(chǎn)品中氧化三甲胺、三甲胺和二甲胺[J].中國食品學報,201 13(4):163-171.
[65] MACLELLAN R J,TUNNAH L,BARNETT D,et al.Chaperone roles for TMAO and HSP70 during hyposmotic stress in the spiny dogfish shark(Squalus acanthias)[J].Journal of comparative physiology B,201 185(7):729-740.
[66] 林海生,秦小明,章超樺,等.中國沿海主要牡蠣養(yǎng)殖品種的營養(yǎng)品質和風味特征比較分析[J].南方水產(chǎn)科學,2019,15(2):110-120.
[67] DOWNING A B,WALLACE G T,YANCEY P H.Organic osmolytes of amphipods from littoral to hadal zones:Increases with depth in trimethylamine N-oxide,scyllo-inositol and other potential pressure counteractants[J].Deep sea research part I:Oceanographic research papers,2018,138:1-10.
[68] YANCEY P H,RHEA M D,KEMP K M,et al.Trimethylamine oxide,betaine and other osmolytes in deep-sea animals:Depth trends and effects on enzymes under hydrostatic pressure[J].Cellular and molecular biology,200 50(4):371-376.
[69] KELLER M D,KIENE R P,MATRAI P A,et al.Production of glycine betaine and dimethylsulfoniopropionate in marine phytoplankton.II.N-limited chemostat cultures[J].Marine biology,1999,135(2):249-257.
[70] SAMEROTTE A L,DRAZEN J C,BRAND G L,et al.Correlation of trimethylamine oxide and habitat depth within and among species of teleost fish:An analysis of causation[J].Physiological and biochemical zoology,2007,80(2):197-208.
[71] YANCEY P H,GERRINGER M E,DRAZEN J C,et al.Marine fish may be biochemically constrained from inhabiting the deepest ocean depths[J].Proceedings of the national academy of sciences of the United States of America,201 111(12):4461-4465.
[72] PILLANS R D,GOOD J P,ANDERSON W G,et al.Freshwater to seawater acclimation of juvenile bull sharks(Carcharhinus leucas):Plasma osmolytes and Na+/K+-ATPase activity in gill,rectal gland,kidney and intestine[J].Journal of comparative physiology B,200 175(1):37-44.
[73] SULIKOWSKI J A,TREBERG J R,HOWELL W H.Fluid regulation and physiological adjustments in the winter skate,Leucoraja ocellata,following exposure to reduced environmental salinities[J].Environmental biology of fishes,200 66(4):339-348.
[74] OGILVIE J M G,WARREN A A.The occurrence of trimethylamine oxide in fundulus heteroclitus[J].Canadian journal of zoology,1957,35(6):735-745.
[75] CHUNG S W C,CHAN B T P.Trimethylamine oxide,dimethylamine,trimethylamine and formaldehyde levels in main traded fish species in Hong Kong[J].Food additives & contaminants part B,2009,2(1):44-51.
[76] CLOWES L A,F(xiàn)RANCESCONI K A.Uptake and elimination of arsenobetaine by the mussel Mytilus edulis is related to salinity[J].Comparative biochemistry and physiology part C,200 137(1):35-42.
[77] BRICTKUX-GRGOIRE S,DUCHTEAU-BOSSON G,F(xiàn)LORKIN C J M.Constituants osmotiquement actifs des muscles adducteurs de mytilus edulis adaptée a l′eau de mer ou a l′eau saumatre[J].Archives of physiology and biochemistry,196 72(1):116-123.
[78] DELGADO-GAYTN M F,GMEZ-JIMNEZ S,GMEZ-ALEJO L A,et al.Effect of salinity on the synthesis and concentration of glycine betaine in osmoregulatory tissues from juvenile shrimps Litopenaeus vannamei[J].Comparative biochemistry and physiology part A:Molecular & integrative physiology,2019,240:110628.
[79] RAYMOND J A.Seasonal variations of trimethylamine oxide and urea in the blood of a cold-adapted marine teleost,the rainbow smelt[J].Fish physiology and biochemistry,199 13(1):13-22.
[80] GORDON M S,AMDUR B H,SCHOLANDER P F.Freezing resistance in some northern fishes[J].Biological bulletin,196 122(1):52-62.
[81] DEVRIES A L,WOHLSCHLAG D E.Freezing resistance in some Antarctic fishes[J].Science,1969,163(3871):1073-1075.
[82] HUGHES R B.Chemical studies on the herring(Clupea harengus).II.—The free amino-acids of herring flesh and their behaviour during post-mortem spoilage[J].Journal of the science of food and agriculture,1959,10(10):558-564.
[83] 李豐.水產(chǎn)品中氧化三甲胺、三甲胺、二甲胺檢測方法及魷魚絲中甲醛控制研究[D].保定:河北農(nóng)業(yè)大學,2010:22.
[84] BOCKUS A B,SEIBEL B A.Trimethylamine oxide accumulation as a function of depth in Hawaiian mid-water fishes[J].Deep-sea research part I,201 112:37-44.
[85] DACOSTA K A,VRBANAC J J,ZEISEL S H.The measurement of dimethylamine,trimethylamine,and trimethylamine N-oxide using capillary gas chromatography-mass spectrometry[J].Analytical biochemistry,1990,187(2):234-239.
[86] AGU'STSSON I,STR M A R.Biosynthesis and turnover of trimethylamine oxide in the teleost cod,Gadus morhua[J].The journal of biological chemistry,198 256(15):8045-8049.
[87] 黃國霞,賴春華,李軍生,等.6種水產(chǎn)動物中氧化三甲胺的提取與含量測定[J].食品科技,201 37(7):305-307.
[88] STIBOLLER M,RABER G,F(xiàn)RANCESCONI K A.Simultaneous determination of glycine betaine and arsenobetaine in biological samples by HPLC/ICPMS/ESMS and the application to some marine and freshwater fish samples[J].Microchemical journal,201 122:172-175.
[89] DE ZWART F J,SLOW S,PAYNE R J,et al.Glycine betaine and glycine betaine analogues in common foods[J].Food chemistry,200 83(2):197-204.
[90] 陳德慰,蘇鍵,顏棟美,等.廣西北部灣常見水產(chǎn)品中甜菜堿含量測定及呈味效果評價[J].現(xiàn)代食品科技,201 27(4):468-472.
[91] 丁源,邢家溧,承海,等.基于高效液相色譜法測定水產(chǎn)品中甘氨酸甜菜堿[J].食品工業(yè)科技,2019,40(15):184-187.
[92] FARABEGOLI F,ZIRONI E,GAZZOTTI T,et al.Isotope dilution LC-MS/MS method for glycine betaine in manila clam(Tapes philippinarum)[J].Food analytical methods,2019,12(6):1448-1455.
[93] 王士穩(wěn),梁萌青,林洪,等.海水和淡水養(yǎng)殖凡納濱對蝦呈味物質的比較分析[J].海洋水產(chǎn)研究,200 27(5):79-84.
[94] 金蕾,徐善良,邱成功,等.三疣梭子蟹肌肉組織中甜菜堿、糖原及無機鹽變化研究[J].生物學雜志,201 31(4):24-28.
[95] TIMM M,J RGENSEN B M.Simultaneous determination of ammonia,dimethylamine,trimethylamine and trimethylamine-n-oxide in fish extracts by capillary electrophoresis with indirect UV-detection[J].Food chemistry,200 76(4):509-518.
[96] BEDFORD J J,HARPER J L,LEADER J P,et al.Identification and measurement of methylamines in elasmobranch tissues using proton nuclear magnetic resonance(1H-NMR)spectroscopy[J].Journal of comparative physiology B,1998,168(2):123-131.

