健康教育干預對社區中老年頸椎病患者自我管理能力干預效應分析*
岑 川 馬海琴
?
健康教育干預對社區中老年頸椎病患者自我管理能力干預效應分析*
岑川馬海琴
上海市寶山區張廟街道長江路社區衛生服務中心(上海 200431)
摘要:目的評價健康教育對社區中老年頸椎病患者自我管理能力干預的效果。方法選取本社區門診經牽引治療后的頸椎病患者90例,隨機分為干預組和對照組各45例,對干預組進行系列有序系統的健康教育干預活動和隨訪督導,對照組只進行隨訪,評價兩組干預前后頸椎病相關基礎知識測試成績(總均分)、防治保健知識知曉率、預防措施執行率。結果干預后,干預組較對照組頸椎病相關基礎知識測試成績(總均分)、防治保健知識知曉率、預防措施執行率都有明顯提高,差異有統計學意義(P<0.05)。結論社區綜合健康教育干預可以提高患者對疾病的認知,以及患者疾病自我管理能力。
關鍵詞:神經根型頸椎病;自我管理;社區;健康教育
頸椎病是目前嚴重危害中老年患者的骨關節退行性變的社區常見病,壓迫周圍組織、韌帶、肌肉、神經而引起的相應的頸項部僵硬,上肢麻木,眩暈等臨床癥狀。臨床中分為頸型、神經根型、脊髓型、椎動脈型、食管壓迫型及混合型,以神經根型居多。有調查表明51~60歲中老年的患病率為33.8%,明顯高于其他年齡段[1],已嚴重影響病患的日常生活質量。我院開展社區中老年神經根型頸椎病患者系列有序健康教育,對疾病的認知及自我管理能力上取得較好效果,現報道如下。
1 資料與方法
1.1一般資料上海寶山區長江路社區服務中心門診及其服務點自2011年4月-2011年8月門診收治的居住張廟街道社區范圍,并根據《2010版頸椎病診治與康復指南》確診神經根型頸椎病診斷標準及排除標準,經牽引治療,療程結束后以療效評估臨床治愈和顯效者為入組患者共90例,按隨機法把入選患者分為干預組和對照組。干預組45例,其中男5例,女40例,年齡(62.31±6.92)歲,病程(13.11±7.23)年;對照組45例,其中男7例,女38例,年齡(60.67±6.90)歲,病程(11.47±7.14)年。兩組患者性別、年齡、病程、病情等一般資料差異無統計學意義(P>0.05),有可比性。
1.2方法
1.2.1問卷調查自行設計調查表,內容包括基本情況、個人生活習慣、頸椎病相關基礎知識測試、頸椎病防治知識知曉、頸椎病預防措施執行情況等。
1.2.2干預方法對干預組進行頸椎病專題健康教育,以沙龍講座形式每月組織患者集中進行, 1~2次頸椎病系列專題健康教育活動(責任醫師亦參加),為期1年。每次都進行基礎知識測試。健康教育內容包括頸椎病自我防治保健知識,防治保健操指導、健康生活方式指導等。責任醫師每月定期1次上門督導(癥情記錄、防治保健措施執行等)。對照組不采取任何健康干預措施,每月集中組織1次進行一般健康教育,責任醫師每月上門1次進行病情隨訪(癥情記錄),不進行任何督導。
1.3評估指標①頸椎病相關基礎知識測試成績(總均分):兩組患者共10次相同健康教育知識測試,每組每次干預前、后各1次的測試(初、復測)成績的總均分(滿分100分)。②防治保健知識知曉率:兩組進行防治保健知識知曉問卷調查,知曉率=實得分/滿分×100%。每3月進行一次評估。③預防措施執行率:兩組執行各項預防措施的人數占各組總人數的比率。每3月進行一次評估。
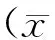
2 結果
2.1干預前后頸椎病相關基礎知識測試成績(總均分)兩組比較顯示:干預后,干預組相關基礎知識測試(含生理病理基礎知識、誘發因素及治療知識、日常不良生活習慣知識、日常防治保健知識)成績總均分高于對照組,差異有統計學意義(P<0.05)。兩組干預前比較,差異無統計學意義(P>0.05),見表1。
表1 兩組基礎知識測試成績(總均分)比較 ±s)
2.2干預前后防治保健知識知曉率(%)兩組比較顯示:干預前兩組防治保健知識知曉率比較,差異無統計學意義(P>0.05),干預后干預組較對照組提高幅度大,差異有統計學意義(χ2=12.359,P=0.000),見表2。
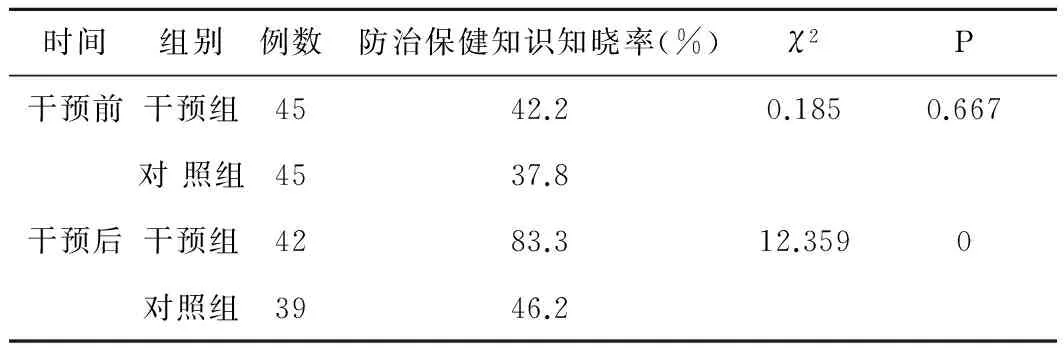
表2 兩組干預前后防治保健知識知曉率(%)比較 (例,%)
2.3干預前后預防措施執行率(%)兩組比較顯示:干預前,兩組預防措施(糾正不良體位姿勢、注意頸部肌肉休息、糾正睡眠體位、加強頸部受涼防護、頸椎保健操)執行率比較,差異無統計學意義(P>0.05)。干預后,干預組各項執行情況均優于對照組,差異有統計學意義(P<0.05),見表3。
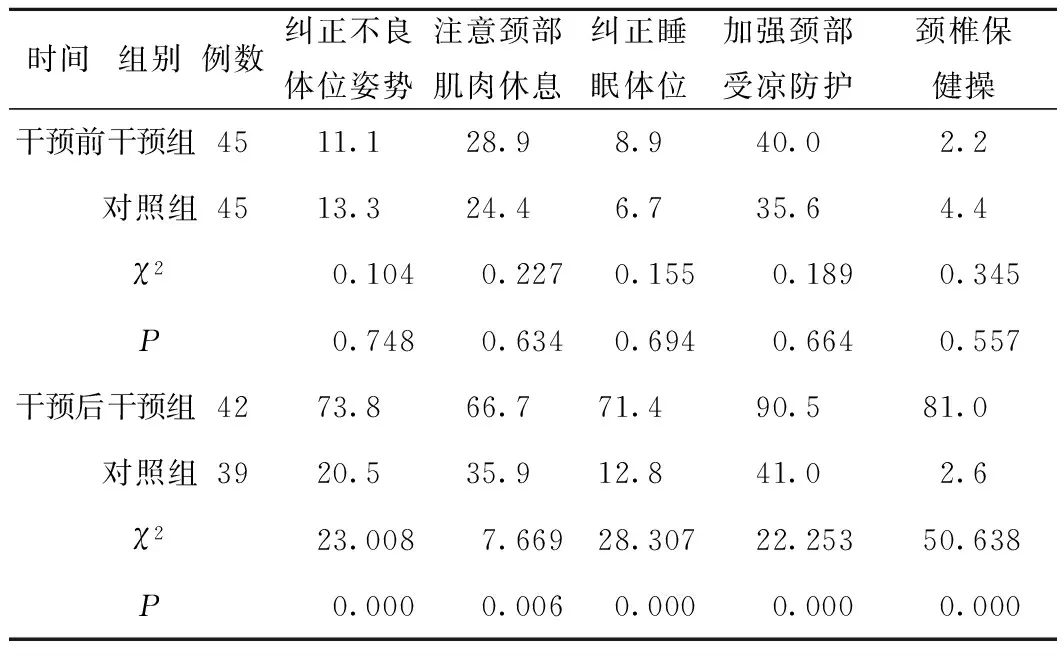
表3 兩組干預前后預防措施執行率(%)比較 (例,%)
3 討論
神經根型頸椎病是頸椎病臨床中最常見的一種。牽引治療是神經根型頸椎病的有效治療手段,但牽引療法治療神經根型頸椎病遠期療效上尚不能令人滿意[2]。我社區衛生服務中心通過歷時一年的時間以團隊形式開展系列有序的健康干預宣教活動,不僅讓社區中老年頸椎病患者了解掌握了正確的頸椎病防治保健知識,而且也大大提高了患者疾病自我管理的能力,糾正不良生活方式和行為,讓患者主動參與到頸椎病保健防護中。
事實表明,社區開展頸椎病健康教育干預活動是普及社區頸椎病防治知識、提高患者疾病自我管理主動性有效的方法。
參考文獻
[1]楊新文,朱遠熔,汪志良.上海市徐匯區頸椎病患者情況調查分析[J]. 中國康復,2011,26(2):101-102.
[2]董一諭,顏景芳.神經根型頸椎病的康復護理研究[J].護士進修雜志,2005,6(20):553-554.
*基金項目:上海寶山區區科委基金項目(No.10-E-43)
doi:10.3969/j.issn.1003-8914.2016.01.070
文章編號:1003-8914(2016)-01-0133-02
收稿日期:(本文校對:方宗君2014-12-25)
Analysis on the Intervention Effect of the Health Education on the Self Management Ability of Elderly Patients with Cervical Spondylosis in Community
CEN ChuanMA Haiqing
(Baoshan District Zhangmiao Subdistrict Changjiang Road Community Health Service Center, Shanghai 200431, China)
Abstract:ObjectiveTo evaluate the intervention effect of the health education on the self management ability of elderly patients with cervical spondylosis in community. MethodsNinety cases patients with cervical spondylosis treated by traction were selected in the Out-patient Department of the community health service center, and they were randomly divided into intervention group with 45 cases and control group with 45 cases. The intervention group was given a series of orderly systematic health education intervention activities and following-up supervision. The control group was only given following-up evaluation. Before and after the study, the basic knowledge of cervical spondylosis test score, the rate of the awareness of the prevention and health knowledge and the execution rate of the preventive measures were evaluated. ResultsAfter intervention, the basic knowledge of cervical spondylosis test score, the rate of the awareness of the prevention and health knowledge and the execution rate of the preventive measures of the intervention group were increased obviously, and the difference between two groups had the statistical significance (P<0.05). ConclusionThe community comprehensive health education intervention for cervical spondylosis can improve the patient’s awareness of the disease and the self management ability.
Key words:Cervical spondylosis of nerve root type; Self management; Community; Health education

