毗鄰顆粒鏈菌感染一例
呂漫?羅潔麗?張友平
【摘要】毗鄰顆粒鏈菌可引起包括心內膜、骨髓、關節等不同部位的感染,因缺少統一的藥物敏感度試驗結果使其治療變得困難。該文分析1例毗鄰顆粒鏈菌感染患者的病例資料。該例60歲男性患者入院后病情進展迅速,出現嚴重心力衰竭、膿毒血癥休克、MODS,經抗感染、腎臟替代治療、呼吸機輔助通氣等積極治療仍無效,于入ICU 60 h死亡,血培養回報結果為革蘭陽性球菌、毗鄰顆粒鏈菌,確診為毗鄰顆粒鏈菌敗血癥。文獻分析顯示,毗鄰顆粒鏈菌普遍對萬古霉素、左氧氟沙星、克林霉素,美羅培南敏感。該文提示,毗鄰顆粒鏈菌感染病情進展極為迅速,臨床醫師應加深對毗鄰顆粒鏈菌的認識,提高對相關感染所致敗血癥的警惕。
【關鍵詞】毗鄰顆粒鏈菌;感染;藥物敏感試驗;敗血癥;診斷
Granulicatella adiacens infection: a case report Lyu Man, Luo Jieli, Zhang Youping. Puren Hospital Affiliated to Wuhan University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430080, China
Corresponding author, Zhang Youping, E-mail: fongbaiyang@ 163. com
【Abstract】Granulicatella adiacens can cause infection in multiple sites, such as endocardium, bone marrow and joints, etc. Lack of standardized antimicrobial susceptibility test results increases the difficulty of treatment.? In this article, clinical data of 1 patient with Granulicatella adiacens infection were reported. The 60-year-old male patient developed rapidly after admission and suffered from severe heart failure, septic shock and MODS. After active treatment such as anti-infection, renal replacement therapy, ventilator-assisted ventilation and other organ support therapy, the patient was still not treated and died at 60 h after admission to ICU. Blood culture result was Gram-positive cocci. The patient was diagnosed with Granulicatella adiacens septicemia. Literature review revealed that Granulicatella adiacens was generally sensitive to vancomycin, levofloxacin, clindamycin and meropenem. This case prompts that the disease progression of Granulicatella adiacens infection is extremely rapid. Clinicians should deepen their understanding of Granulicatella adiacens septicemia and enhance their cautions against infection-related bacteremia.
【Key words】Granulicatella adiacens;Infection;Drug susceptibility test;Septicemia;Diagnosis
毗鄰顆粒鏈菌是一種營養變異鏈球菌(NVS)。毗鄰顆粒鏈菌感染則是一種少見的機會性感染,在國外早有相關的病例報道,而在國內僅有個別報道。臨床醫師對該病的認識和重視嚴重不足。本文擬結合近年確診的1例毗鄰顆粒鏈菌感染病例及國內外相關文獻綜合分析,為該病的治療提供藥物選擇依據。
病例資料
一、病史和體格檢查
患者男,60歲。因反復胸悶、氣喘半年余、再發加重伴少尿1 d于2017年5月14日從武漢科技大學附屬武漢市普仁醫院心內科轉入ICU。患者半年前無明顯誘因反復胸悶、氣喘,休息后可緩解,未予重視。入院前1 d癥狀加重,且感少尿,遂來求診。因入院后病情加重,轉入ICU治療。起病以來,患者神志清晰,精神差,體力下降,體質量變化不明顯。患者有高血壓病史1年(未服藥控制血壓),有頭孢類藥物過敏史。
入院體格檢查:體溫36.5 ℃,脈搏98次/分,血壓96/54 mm Hg(1 mm Hg = 0.133 kPa,升壓藥維持),呼吸36次/分。患者煩躁不安,呼吸急促,顏面冷汗,四肢冰冷,伴全身及四肢花斑樣改變,面罩給氧,SaO2 1.0,雙側瞳孔等大、等圓,直徑2 mm,對光反射存在,雙肺呼吸音粗,右下肺可聞及明顯干性啰音及少量濕性啰音。心界擴大,節律整齊,二尖瓣區可聞及收縮期Ⅳ/Ⅵ級雜音,腹軟,無壓痛反跳痛,肝脾肋下未捫及,墨菲征陰性,雙下肢輕度凹陷性水腫。生理反射存在,病理反射未引出。
在臨床表現上,毗鄰顆粒鏈菌感染患者多有基礎心臟疾病或是中性粒細胞減少性發熱,口腔黏膜炎癥和中性粒細胞減少患者可能更易發生毗鄰顆粒鏈菌感染[7]。無論何種NVS菌屬,均主要表現為典型的菌血癥、敗血癥或者感染性心內膜炎的表現。2001年Christensen等道了97例乏養球菌和顆粒鏈菌引起的感染,55例患者為鄰顆粒鏈菌感染,其中IE 25例、菌血癥或敗血癥10例;43例患者乏養球菌感染,其中IE、菌血癥或敗血癥28例。2003年Woo等報道了9例毗鄰顆粒鏈菌和缺陷乏養球菌感染者,9例均有基礎疾病,其中4例為心血管疾病,6例為顆粒鏈菌血培養陽性。此外有報道顆粒性鏈球菌可引起中樞神經系統、關節腔、骨髓、腹膜等的感染[8-11]。
美國心臟協會和英國抗菌化學治療學會推薦顆粒鏈菌和乏養球菌引起的IE在治療上可參考腸球菌性IE方案,即芐星青霉素或氨芐青霉素聯合慶大霉素;青霉素過敏者可單用萬古霉素6周。目前針對NVS的治療多數先給予經驗性抗菌藥物方案,再結合血培養藥物敏感度試驗(藥敏)結果及時調整。有學者使用氨芐青霉或頭孢曲松鈉聯合慶大霉素4 ~ 6周的治療方案[7] 。
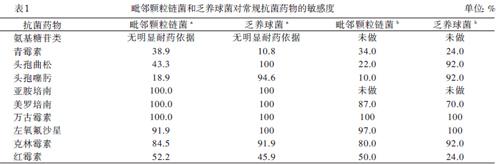
由于NVS的培養條件苛刻,目前尚無標準的藥敏結果可參考。早在2000年Marion等參照2000年國際臨床實驗室關于青霉素在鏈球菌上的敏感度標準,提出顆粒鏈菌和乏養球菌對克林霉素、利福平、左氧氟沙星與萬古霉素敏感,對慶大霉素也未見明顯的耐藥。現有的2項高質量的大樣本研究則更為詳細和深入地研究顆粒鏈菌和乏養球菌的藥敏結果差異后也得出類似結論:顆粒鏈菌和乏養球菌普遍對萬古霉素、左氧氟沙星、克林霉素、美羅培南敏感,其中顆粒鏈菌對常用抗菌藥物的敏感度低于乏養球菌,見表1 [12-13]。
盡管經過積極的治療,本文病例結局仍然不如人意,提示毗鄰顆粒鏈菌感染危害極大,臨床醫師需要提高對其的認識水平。另外,該病例也值得我們進一步思考。首先,文獻提示美羅培南對毗鄰顆粒鏈菌敏感,我們給予了同樣屬碳青霉烯類的比阿培南聯合替加環素抗菌方案。在短短的48 h抗生素治療中,患者的炎癥指標降鈣素原由8.92 μg/L 降到2.74 μg/L,降幅接近60%,提示抗感染治療有效,但患者病情仍持續進展導致死亡。究其原因,可能是患者在入院時已有嚴重的肝、腎、肺、腦等重要器官衰竭,已處于不可逆的終末期,雖然我們積極地給予了強力的抗感染及臟器功能支持等治療,但患者病情仍持續進展,后期出現DIC及頑固性代謝性酸中毒、高鉀血癥,最終死亡。其次,盡管比阿培南對該菌的有效性是較肯定的,但現有的國內外文獻中替加環素對該菌的敏感度尚無相關報道,該聯合治療方案對毗鄰顆粒鏈菌敗血癥的療效有待進一步研究明確。
總之,毗鄰顆粒鏈菌感染病情進展迅速,危害極重,提高對該病的認識與警惕對診斷和治療尤其重要。
參 考 文 獻
[1] 游文忠. 左心房黏液瘤并發感染性心內膜炎1例. 新醫學, 2010, 41(9): 622-623.
[2] 梁峰,沈珠軍,方全,胡大一. 2015年歐洲心臟病學會關于感染性心內膜炎指南的解讀.中華臨床醫師雜志(電子版),2017,11(6):975-983.
[3] Hase R, Otsuka Y, Yoshida K, Hosokawa N. Profile of infective endocarditis at a tertiary-care hospital in Japan over a 14-year period: characteristics, outcome and predictors for in-hospital mortality. Int J Infect Dis,2015,33:62-66.
[4] Téllez A, Ambrosioni J, Llopis J, Pericàs JM, Falces C, Almela M, Garcia de la Mària C, Hernandez-Meneses M, Vidal B, Sandoval E, Quintana E, Fuster D, Tolosana JM, Marco F, Moreno A, Miro JM; Hospital Clínic Infective Endocarditis Investigators. Epidemiology, clinical features, and outcome of infective endocarditis due to Abiotrophia species and Gran-ulicatella species: report of 76 cases, 2000-2015. Clin Infect Dis,2018,66(1):104-111.
[5] Akiyama T, Miyamoto H, Fukuda K, Sano N, Katagiri N, Shobuike T, Kukita A, Yamashita Y, Taniguchi H, Goto M. Development of a novel PCR method to comprehensively analyze salivary bacterial flora and its application to patients with odontogenic infections. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod,2010,109(5):669-676.
[6] Ratcliffe P, Fang H, Thidholm E, Bor?ng S, Westling K, ?zenci V. Comparison of MALDI-TOF MS and VITEK 2 system for laboratory diagnosis of Granulicatella and Abiotrophia species causing invasive infections. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis,2013,77(3):216-219.
[7] Vandana KE, Mukhopadhyay C, Rau NR, Ajith V, Rajath P. Native valve endocarditis and femoral embolism due to Granulicatella adiacens: a rare case report. Braz J Infect Dis,2010,14(6):634-636.
[8] Elfessi Z, Liu E, Dukarevich Y, Caniff K, Marquez K, Shabbir Z. Sepsis induced bacterial peritonitis caused by Granulicatella adiacens. Am J Emerg Med,2019,pii: S0735-6757(19)30577-7.
[9] Patil SM, Arora N, Nilsson P, Yasar SJ, Dandachi D, Salzer WL. Native valve infective endocarditis with osteomyelitis and brain abscess caused by Granulicatella adiacens with literature review. Case Rep Infect Dis,2019,2019:4962392.
[10] Pingili C, Sterns J, Jose P. First case of prosthetic knee infection with Granulicatella adiacens in the United States. IDCases,2017,10:63-64.
[11] York J, Fisahn C, Chapman J. Vertebral osteomyelitis due to Granulicatella adiacens, a nutritionally variant streptococci. Cureus,2016,8(9):e808.
[12] Alberti MO, Hindler JA, Humphries RM. Antimicrobial susce-ptibilities of abiotrophia defectiva, Granulicatella adiacens, and granulicatella elegans. Antimicrob Agents Chemother,2015,60(3):1411-1420.
[13] Mushtaq A, Greenwood-Quaintance KE, Cole NC, Kohner PC, Ihde SM, Strand GJ, Harper LW, Virk A, Patel R. Differential antimicrobial susceptibilities of Granulicatella adiacens and abi-otrophia defectiva. Antimicrob Agents Chemother,2016,60(8):5036-5039.
(收稿日期:2019-09-18)
(本文編輯:林燕薇)

