羅哌卡因不同注藥速度對超聲聯(lián)合神經(jīng)刺激儀引導鎖骨上臂叢神經(jīng)阻滯術后鎮(zhèn)痛效果的影響
香效明 楊智學 林有梅 周小敏
摘要:目的 ?探討0.375%羅哌卡因不同注藥速度對超聲聯(lián)合神經(jīng)刺激儀引導鎖骨上臂叢神經(jīng)阻滯術后鎮(zhèn)痛效果的影響。方法 ?選擇我院2017年5月~2020年5月?lián)衿谛袉蝹壬现钦蹆裙潭ㄊ中g患者100例作為研究對象,隨機分為低速組(L組)和高速組(H組),各50例,兩組患者均采用超聲聯(lián)合神經(jīng)刺激儀引導鎖骨上臂叢神經(jīng)阻滯,注射0.375%羅哌卡因30 ml,L組注藥速度為20 ml/h,H組注藥速度為40 ml/h。比較兩組感覺阻滯起效時間、運動阻滯起效時間、感覺阻滯持續(xù)時間、運動阻滯持續(xù)時間、麻醉效果、術后2、4、6、12、24、48 h VAS評分;記錄兩組術后首次按壓鎮(zhèn)痛泵時間、術后48 h舒芬太尼使用量、鎮(zhèn)痛泵按壓總次數(shù)、鎮(zhèn)痛滿意度、臂叢神經(jīng)阻滯并發(fā)癥和鎮(zhèn)痛相關并發(fā)癥發(fā)生率。結果 ?H組感覺阻滯起效時間、運動阻滯起效時間短于L組(P<0.05),且H組感覺阻滯持續(xù)時間、運動阻滯持續(xù)時間長于L組(P<0.05);兩組麻醉效果比較,差異無統(tǒng)計學意義(P>0.05);H組術后12 h VAS評分低于L組(P<0.05),其余時間點兩組VAS評分比較,差異無統(tǒng)計學意義(P>0.05);H組術后48 h舒芬太尼使用量、鎮(zhèn)痛泵按壓總次數(shù)低于L組(P<0.05),術后首次按壓鎮(zhèn)痛泵時間長于L組(P<0.05);兩組患者鎮(zhèn)痛滿意度比較,差異無統(tǒng)計學意義(P>0.05);兩組均未發(fā)生臂叢神經(jīng)阻滯及鎮(zhèn)痛相關并發(fā)癥。結論 ?0.375%羅哌卡因注藥速度是影響雙重引導鎖骨上臂叢神經(jīng)阻滯術后鎮(zhèn)痛效果的因素之一,與20 ml/min注藥速度相比,40 ml/min注藥速度起效時間更短,維持時間更長,術后鎮(zhèn)痛效果更佳,持續(xù)時間更長,術后舒芬太尼用量少,且不會增加阻滯相關并發(fā)癥的發(fā)生率。
關鍵詞:羅哌卡因;注藥速度;超聲;神經(jīng)刺激儀引導;鎖骨上臂叢神經(jīng)阻滯;術后鎮(zhèn)痛
中圖分類號:R614 ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?文獻標識碼:A ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-1959.2020.18.021
文章編號:1006-1959(2020)18-0069-04
Effects of Different Injection Speeds of Ropivacaine on the Analgesic Effect of Supraclavicular
Brachial Plexus Block Guided by Ultrasound Combined with Neurostimulator
XIANG Xiao-ming,YANG Zhi-xue,LIN You-mei,ZHOU Xiao-min
(Department of Anesthesiology,Hengli Hospital,Dongguan 523460,Guangdong,China)
Abstract:Objective ?To explore the effect of different injection speeds of 0.375% ropivacaine on the analgesic effect of supraclavicular brachial plexus block guided by ultrasound combined with neurostimulator.Methods ?100 patients with elective internal fixation of unilateral upper limb fractures in our hospital from May 2017 to May 2020 were selected as the research objects. They were randomly divided into low-speed group (L group) and high-speed group (H group), with 50 cases in each. Both groups of patients were guided by ultrasound combined with nerve stimulator to guide supraclavicular brachial plexus nerve block, and injected 0.375% ropivacaine 30 ml, the injection rate of group L was 20 ml/h, and the injection rate of group H was 40 ml/h. Compare the onset time of sensory block, the onset time of motor block, the duration of sensory block, the duration of motor block, the effect of anesthesia, and the VAS scores at 2, 4, 6, 12, 24, and 48 h after operation between the two groups; The time of first pressing the analgesic pump after operation, the amount of sufentanil used 48 h after the operation, the total number of analgesic pump pressings, the satisfaction degree of analgesia, the complications of brachial plexus block and the incidence of analgesia-related complications in the two groups. Results ?The onset time of sensory block and motor block in group H was shorter than that in group L (P<0.05), and the duration of sensory block and motor block in group H was longer than that in group L (P<0.05); There was no statistically significant difference in the effect of anesthesia (P>0.05); the VAS score of the H group was lower than that of the L group at 12 h after the operation (P<0.05), and there was no significant difference in the VAS score between the two groups at other time points (P>0.05); 48 h after surgery, the amount of sufentanil used and the total number of compressions of the analgesic pump in the H group were lower than those in the L group (P<0.05), and the first compression of the analgesic pump after surgery was longer than that of the L group (P<0.05); There was no significant difference in satisfaction with analgesia between the two groups (P>0.05); there was no brachial plexus block and analgesia-related complications in the two groups.Conclusion ?The injection rate of 0.375% ropivacaine was one of the factors affecting the postoperative analgesic effect of dual-guided supraclavicular brachial plexus block. Compared with the injection rate of 20 ml/min, the injection rate of 40 ml/min was effective time was shorter, the maintenance time was longer, the postoperative analgesia effect was better, the duration was longer, the postoperative sufentanil dosage was less, and the incidence of block-related complications would not increase.
Key words:Ropivacaine;Injection speed;Ultrasound;Guidance by nerve stimulator;Supraclavicular brachial plexus block;Postoperative analgesia
臂叢神經(jīng)阻滯是上肢手術麻醉常用方法,根據(jù)解剖學特征和注藥靶點可分為肌間溝臂叢神經(jīng)阻滯、鎖骨上臂叢神經(jīng)阻滯、鎖骨下臂叢神經(jīng)阻滯、腋路臂叢神經(jīng)阻滯等多種入路[1-3]。鎖骨上臂叢神經(jīng)阻滯俗稱上肢手術的“蛛網(wǎng)膜下腔阻滯”,這種入路對臂叢神經(jīng)各分支均能有效阻滯,適用于所有上肢手術[4-6]。影響神經(jīng)阻滯效果最主要的因素是局麻藥濃度和劑量,但注藥速度、注藥方式等可能也是影響阻滯效果的因素,目前國內外對注藥速度對麻醉效果研究主要集中在椎管內麻醉,國內外鮮見有公開報道探究局麻藥注射速度對鎖骨上臂叢神經(jīng)阻滯鎮(zhèn)痛效果的影響,本研究擬探討0.375%羅哌卡因不同注藥速度對超聲聯(lián)合神經(jīng)刺激儀引導鎖骨上臂叢神經(jīng)阻滯術后鎮(zhèn)痛效果的影響,現(xiàn)報道如下。
1資料與方法
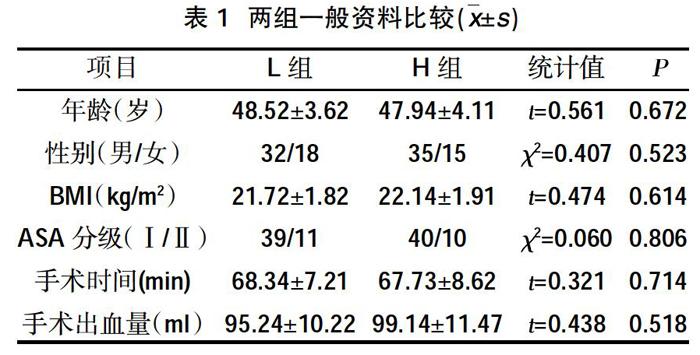
1.1一般資料 ?選擇2017年5月~2020年5月在東莞市橫瀝醫(yī)院擇期行單側上肢骨折內固定手術患者100例作為研究對象,男55例,女45例,年齡18~65歲,美國麻醉醫(yī)師協(xié)會ASA分級Ⅰ~Ⅱ級,體重指數(shù)(BMI)18~24 kg/m2。納入標準:①術前診斷為“單側上肢骨折”,擬行骨折復位內固定手術;②無嚴重心血管系統(tǒng)或呼吸系統(tǒng)疾病,能夠耐受鎖骨上臂叢神經(jīng)阻滯。排除標準:①存在明顯中樞神經(jīng)系統(tǒng)或外周神經(jīng)系統(tǒng)疾病;明顯心肺疾病;②肝腎疾病,腎功能不全或肝功能不全、凝血功能異常;③內分泌系統(tǒng)疾病、糖尿病者;④存在精神異常或意識障礙,難以配合完成各項指標評估;⑤羅哌卡因過敏者;⑥鎖骨上臂叢神經(jīng)阻滯禁忌癥者,穿刺部位感染者;⑦安裝心臟起搏器者;⑧近期服用鎮(zhèn)靜鎮(zhèn)痛藥、抗凝藥物者;⑨妊娠期婦女。本研究經(jīng)過我院倫理委員會審批確認,所有入組患者及家屬均知情并簽署同意書。采用計算機系統(tǒng)產(chǎn)生隨機數(shù)字法將患者分為低速組(L組)和高速組(H組),各50例。兩組患者年齡、性別、BMI、ASA分級、手術時間、手術出血量比較無統(tǒng)計學意義(P>0.05),有可比性,見表1。
1.2方法 ?兩組患者均進行常規(guī)禁食8 h,禁飲2 h,不使用麻醉前用藥。進入手術間后常規(guī)監(jiān)測無創(chuàng)血壓(NIBP)、心率(HR)、呼吸頻率(RR)、脈搏血氧飽和度(SpO2),開放下肢靜脈通路,輸注轉化糖電解質溶液500 ml。兩組患者在行鎖骨上臂叢神經(jīng)阻滯前20 min持續(xù)靜脈輸注右美托咪定(江蘇揚子江醫(yī)藥公司,國藥準字號H20183219,規(guī)格:2 ml∶0.2 mg)0.5 μg/kg,15 min輸注完畢,隨后行鎖骨上臂叢神經(jīng)阻滯阻滯。超聲聯(lián)合神經(jīng)刺激儀引導鎖骨上臂叢神經(jīng)阻滯:采用索諾聲M-Turbo便攜式多功能超聲儀及配套的HFL38x高頻線陣探頭和德國貝朗神經(jīng)刺激儀Stimuplex HNS12及配套的50 mm D型神經(jīng)刺激針。神經(jīng)刺激儀初始刺激電流設置為1.0 mA,頻率為1 Hz,患者取仰臥位,頭轉向對側,將超聲探頭以鎖骨中點為中心放置在鎖骨上窩處,探頭長軸與鎖骨平行,首先在超聲圖像上尋找鎖骨下動脈、第一肋、胸膜,在鎖骨下動脈外上方的橢圓形如蜂窩狀或篩孔狀的不均勻回聲則為鎖骨上臂叢神經(jīng)阻滯。常規(guī)消毒鋪巾,采用平面內穿刺技術由探頭外側進針,實時觀察穿刺針尖行進軌跡,保持全針在超聲圖像上清晰顯影,待針尖到達目標神經(jīng)附近,上肢任意肌肉出現(xiàn)節(jié)律性收縮,此時調整刺激電流為0.3 mA,若相應肌肉仍出現(xiàn)節(jié)律性收縮,說明針尖位置良好,此時牢固固定針尖,使用相應速度注射0.375%羅哌卡因(江蘇恒瑞醫(yī)藥公司,國藥準字號H20060137,規(guī)格:10 ml∶100 mg)30 ml,使用電子輸注泵設置輸注速度,L組注藥速度為20 ml/h,H組注藥速度為40 ml/h,兩組患者神經(jīng)阻滯操作均由一位不參與觀察指標評估的有經(jīng)驗的麻醉醫(yī)生完成,術后由另外一位不參與手術麻醉管理的有經(jīng)驗的麻醉醫(yī)生進行隨訪評估記錄各指標。兩組患者阻滯后30 min仍未測得相應區(qū)域出現(xiàn)感覺阻滯則視為神經(jīng)阻滯失敗,退出本研究。
兩組患者術后均采用靜脈自控鎮(zhèn)痛(PCIA),舒芬太尼100 μg(宜昌人福藥業(yè)公司,國藥準字號H20054172,規(guī)格:1 ml:50 μg)加入生理鹽水稀釋至100 ml,輸注速度為2 ml/h,PCA量為2 ml,鎖定時間30 min。
1.3觀察指標 ?比較兩組患者感覺阻滯起效時間、運動阻滯起效時間、感覺阻滯持續(xù)時間、運動阻滯持續(xù)時間;記錄兩組患者麻醉效果,術中完全無痛則為優(yōu);術中微痛,需要輔助小劑量鎮(zhèn)靜鎮(zhèn)痛藥則為良;術中疼痛劇烈,需要使用大劑量鎮(zhèn)靜鎮(zhèn)痛藥或變更為全身麻醉;記錄兩組患者術后2、4、6、12、24、48 h的疼痛VAS評分(0分為無痛,10分為難以忍受的劇痛);記錄兩組患者術后首次按壓鎮(zhèn)痛泵時間、術后48 h舒芬太尼使用總量、鎮(zhèn)痛泵按壓總次數(shù)和鎮(zhèn)痛滿意度(0分為非常不滿意,10分為非常滿意);記錄兩組患者臂叢神經(jīng)阻滯并發(fā)癥和鎮(zhèn)痛相關并發(fā)癥發(fā)生率。
1.4統(tǒng)計學分析 ?實驗數(shù)據(jù)采用SPSS 20.0軟件進行統(tǒng)計學處理,計量資料進行正態(tài)性檢驗,符合正態(tài)分布的計量資料以(x±s)表示,組間比較采用獨立樣本t檢驗;計數(shù)資料以(%)表示,組間比較采用?字2檢驗。P<0.05為差異有統(tǒng)計學意義。
2結果
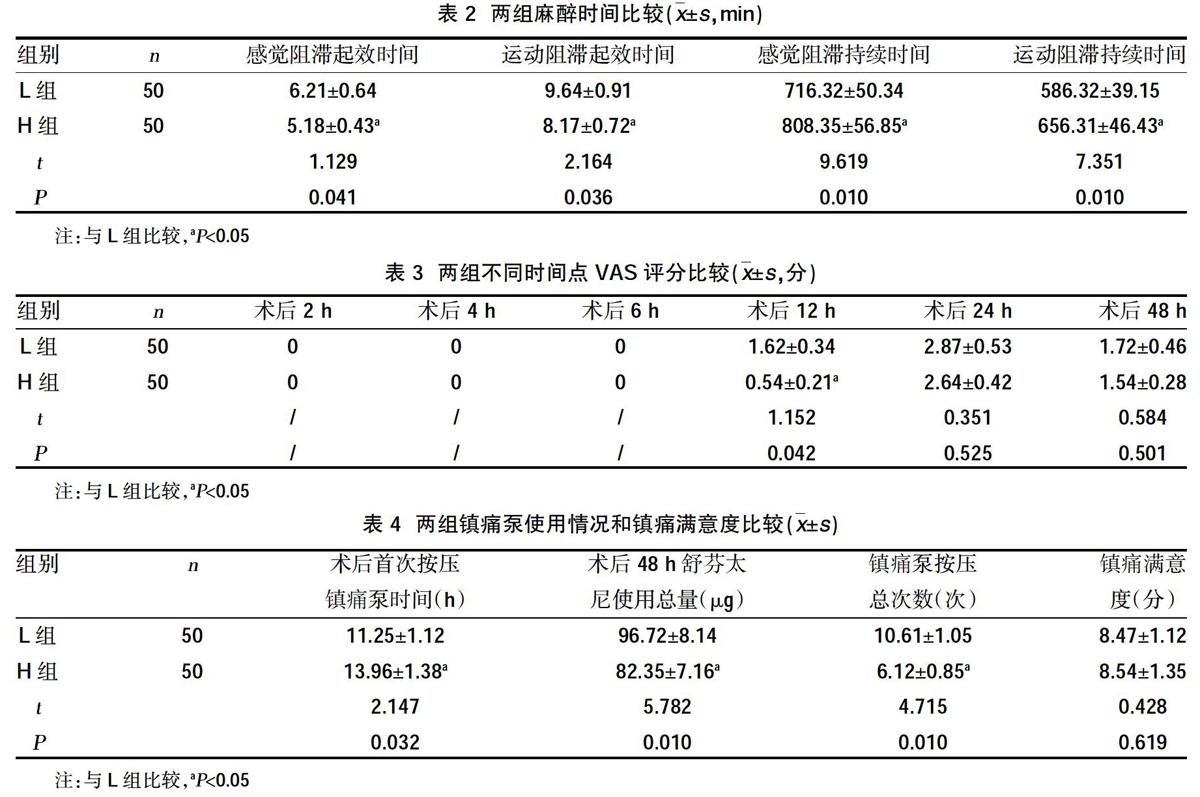
2.1兩組麻醉時間比較 ?H組感覺阻滯起效時間、運動阻滯起效時間短于L組,差異有統(tǒng)計學意義(P<0.05);H組感覺阻滯持續(xù)時間、運動阻滯持續(xù)時間長于L組,差異有統(tǒng)計學意義(P<0.05),見表2。
2.2兩組不同時間點VAS評分比較 ?H組術后12 h VAS評分低于L組,差異有統(tǒng)計學意義(P<0.05);其余時間點兩組VAS評分比較,差異無統(tǒng)計學意義(P>0.05),見表3。
2.3兩組鎮(zhèn)痛泵使用情況和鎮(zhèn)痛滿意度比較 ?H組術后48 h舒芬太尼使用總量、鎮(zhèn)痛泵按壓次數(shù)低于L組,差異有統(tǒng)計學意義(P<0.05);H組術后首次按壓鎮(zhèn)痛泵時間長于L組,差異有統(tǒng)計學意義(P<0.05);兩組患者鎮(zhèn)痛滿意度評分比較,差異無統(tǒng)計學意義(P>0.05),見表4。
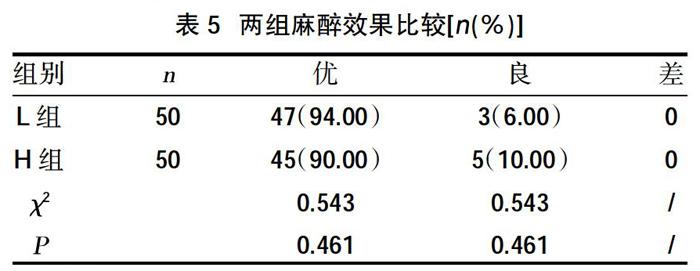
2.4兩組麻醉效果比較 ?兩組患者麻醉效果比較,差異無統(tǒng)計學意義(P>0.05),見表5。
2.5兩組并發(fā)癥發(fā)生率比較 ?兩組患者均未發(fā)生臂叢神經(jīng)阻滯并發(fā)癥和鎮(zhèn)痛相關并發(fā)癥。
3討論
鎖骨上臂叢神經(jīng)阻滯對各大分支阻滯效果較好,被廣泛應用于上肢各種手術麻醉鎮(zhèn)痛,俗稱上肢手術的“蛛網(wǎng)膜下腔阻滯”。 傳統(tǒng)鎖骨上臂叢神經(jīng)阻滯阻滯僅靠解剖定位并結合異感法完成,但這種方法成功率較低且阻滯不全概率較高,穿刺操作時容易進針過深損傷胸膜導致氣胸,近年來隨著超聲和神經(jīng)刺激儀在臨床上的廣泛應用,超聲聯(lián)合神經(jīng)刺激儀雙重引導大大提高阻滯成功率,利用超聲的影像學方法能清晰顯示鎖骨上臂叢神經(jīng)及周邊重要解剖結構如胸膜和鎖骨下動脈,穿刺過程穿刺針尖全稱顯現(xiàn),能避免病人出現(xiàn)異感不適及損傷臂叢神經(jīng),并結合神經(jīng)刺激儀的電生理方法,優(yōu)化針尖與神經(jīng)距離,在保證穿刺成功率及阻滯效果的前提下縮短阻滯起效時間并最大程度減少局麻藥的使用[1-3]。
近年來超聲和神經(jīng)刺激儀被廣泛應用于臂叢神經(jīng)阻滯阻滯,極大提高阻滯成功率,縮短阻滯操作時間。使用超聲能夠清晰顯現(xiàn)臂叢神經(jīng)及周圍重要解剖結構,在穿刺過程實時引導能夠避免針尖誤傷神經(jīng)或血管,不需要病人異感來判斷針尖是否到位,在昏迷病人應用非常有優(yōu)勢,單獨使用超聲在極度肥胖或頸部粗短患者的應用,由于超聲設備性能受限或操作者熟練程度等因素受限,超聲圖像偶爾會顯影不清,操作難度增加,因此對于這類患者可以采用超聲聯(lián)合神經(jīng)刺激儀雙重引導,通過神經(jīng)刺激儀給予電流刺激引發(fā)臂叢神經(jīng)支配的上肢肌肉運動,確定穿刺針尖到達目標神經(jīng)附近,能夠最大程度提高阻滯成功率、降低并發(fā)癥發(fā)生率,同時還能減少局麻藥用量且縮短阻滯時間[7,8]。本研究設計所有患者采用雙重引導鎖骨上臂叢神經(jīng)阻滯,影像學結合電生理方法,優(yōu)化穿刺路徑及方法。影響神經(jīng)阻滯效果的因素較多,局麻藥的濃度、容量、穿刺針尖離目標神經(jīng)的位置、注藥速度、注藥模式、局麻藥的種類、佐劑等,濃度過低或容量不足會導致阻滯起效緩慢或阻滯不全,因此保證神經(jīng)阻滯達到滿意效果需要合適的濃度和劑量。近年來臨床上在鎖骨上臂叢神經(jīng)阻滯的研究多集中在探討佐劑或藥物對阻滯效果的影響[9],在注藥速度對阻滯效果影響的研究較少,目前國內外鮮見公開報道,本研究設計不同注藥速度作為干預因素,探討雙重引導鎖骨上臂叢神經(jīng)阻滯時高速或低速注射0.375%羅哌卡因對術后鎮(zhèn)痛效果的影響。本研究結果顯示,H組感覺阻滯起效時間、運動阻滯起效時間均較L組縮短,感覺阻滯維持時間、運動阻滯維持時間均較L組延長,且術后12 h疼痛(VAS)評分較L組降低,H組術后48 h舒芬太尼使用總量、鎮(zhèn)痛泵按壓次數(shù)較L組減少,首次按壓鎮(zhèn)痛泵時間較L組延長,提示實施鎖骨上臂叢神經(jīng)阻滯阻滯時40 ml/h注藥速度能縮短阻滯起效時間,延長羅哌卡因作用時間,提供更長時間良好術后鎮(zhèn)痛,減少阿片類藥物應用,可能與注藥速度快羅哌卡因擴散迅速且擴散范圍廣泛相關。快速注射局麻藥需要考慮局麻藥短時間內迅速吸收增加局麻藥毒性反應和高壓注射神經(jīng)損傷的風險,本研究中兩組患者均未發(fā)生阻滯相關并發(fā)癥,提示40 ml/h或20 ml/h比較安全。
綜上所述,0.375%羅哌卡因注藥速度是影響雙重引導鎖骨上臂叢神經(jīng)阻滯術后鎮(zhèn)痛效果的因素之一,與20 ml/min注藥速度相比,40 ml/min注藥速度起效時間更短,維持時間更長,術后鎮(zhèn)痛效果更佳及持續(xù)時間更長,術后舒芬太尼用量少,但不增加阻滯相關并發(fā)癥發(fā)生率。
參考文獻:
[1]李慧莉,馬丹旭,王云.不同濃度羅哌卡因對老年患者肌間溝臂叢神經(jīng)阻滯后膈肌運動功能的影響[J].國際麻醉學與復蘇雜志,2020,41(3):255-259.
[2]殷琴琴,許強,陳有園,等.兩種容量羅哌卡因用于超聲引導下肌間溝臂叢神經(jīng)阻滯對膈肌麻痹的影響[J].臨床麻醉學雜志,2019,35(12):1170-1173.
[3]李靜,趙玲,向富森,等.0.5%羅哌卡因用于超聲引導下肋鎖間隙臂叢神經(jīng)阻滯的半數(shù)有效容量[J].臨床麻醉學雜志,2019,35(8):762-764.
[4]鮑秀霞,黃娟娟,豐浩榮,等.相同濃度不同容量羅哌卡因超聲引導鎖骨上臂叢神經(jīng)阻滯對膈肌麻痹的影響[J].臨床麻醉學雜志,2017,33(8):768-771.
[5]謝平,查本俊,吳志云,等.超聲引導下鎖骨上臂叢神經(jīng)阻滯對左旋布比卡因ED50的影響[J].臨床麻醉學雜志,2017,33(2):184-185.
[6]傅志海,吳雅松,王小虎,等.連續(xù)鎖骨上臂叢神經(jīng)阻滯用于上肢術后鎮(zhèn)痛的效果[J].臨床麻醉學雜志,2012,28(8):819-820.
[7]王煥彬,田文華,廖婷.超聲聯(lián)合神經(jīng)刺激儀引導下臂叢神經(jīng)阻滯在老年2型糖尿病患者上肢手術中的應用效果[J].中國實用醫(yī)藥,2020,15(9):79-81.
[8]程晴晴,李元海,夏曉瓊,等.超聲聯(lián)合神經(jīng)刺激儀臂叢神經(jīng)干精準阻滯在肥胖患者上肢手術中的應用[J].醫(yī)學信息,2019,32(19):94-96.
[9]雒小平,陳民為,陳燕峰,等.右美托咪定對肌間溝臂叢神經(jīng)阻滯患者血流動力學的影響[J].浙江創(chuàng)傷外科,2020,25(2):356-357.
收稿日期:2020-06-22;修回日期:2020-06-30
編輯/成森

