以循證支持為基礎的綜合護理對慢阻肺合并2型糖尿病患者預后的影響
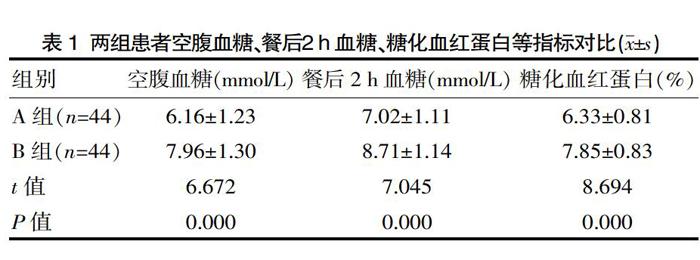
[摘要] 目的 探究以循證支持為基礎的綜合護理對慢阻肺合并2型糖尿病患者預后的影響。方法 選取該院2018年3月—2019年3月收治的慢阻肺合并2型糖尿病患者88例,采用雙盲法分為A組和B組,各44例。A組采用以循證支持為基礎的綜合護理,B組采用常規護理。護理2個月后觀察效果,包括并發癥發生率、呼吸功能評分及空腹血糖、餐后2 h血糖、糖化血紅蛋白等指標。結果 A組并發癥發生率2.27%,低于B組的22.73%,對比差異有統計學意義(P<0.05)。A組呼吸功能評分(0.32±0.05)分,低于B組(1.05±0.12)分,對比差異有統計學意義(P<0.05)。A組空腹血糖、餐后2 h血糖、糖化血紅蛋白等指標均低于B組,對比差異有統計學意義(P<0.05)。結論 以循證支持為基礎的綜合護理在慢阻肺合并2型糖尿病患者中具有顯著效果,可改善患者呼吸功能及血糖各指標,降低并發癥發生風險,值得臨床推廣。
[關鍵詞] 循證支持;綜合護理;慢阻肺合并2型糖尿病;并發癥;呼吸功能評分
[中圖分類號] R473.5? ? ? ? ? [文獻標識碼] A? ? ? ? ? [文章編號] 1672-4062(2020)02(a)-0163-02
Impact of Comprehensive Nursing Based on Evidence-based Support on the Prognosis of Patients with COPD Complicated with Type 2 Diabetes
ZHU Yan
Daqing Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital of Heilongjiang Province, Daqing, Heilongjiang Province, 163311 China
[Abstract] Objective To explore the effect of comprehensive nursing based on evidence-based support on the prognosis of patients with COPD complicated with type 2 diabetes. Methods 88 patients with COPD and type 2 diabetes treated in the hospital from March 2018 to March 2019 were selected and divided into group A and group B with 44 patients each by double-blind method. Group A used comprehensive nursing based on evidence-based support, and group B used routine nursing. The effects were observed after 2 months of nursing, including the incidence of complications, respiratory function scores and fasting blood glucose, 2 h postprandial blood glucose, glycated hemoglobin and other indicators. Results The incidence of complications in group A was 2.27%, which was lower than 22.73% in group B, and the comparison was statistically significant(P<0.05). The respiratory function score of group A (0.32±0.05)points was lower than that of group B (1.05±0.12)points, and the comparison was statistically significant difference(P<0.05). Fasting blood glucose, 2 h postprandial blood glucose, and glycated hemoglobin in group A were lower than those in group B, and the comparison was statistically significant difference(P<0.05). Conclusion Comprehensive nursing based on evidence-based support has significant effects in patients with COPD and type 2 diabetes, which can improve patients' respiratory function and blood glucose indexes, reduce the risk of complications, and is worthy of clinical promotion.
[Key words] Evidence-based support; Comprehensive nursing; COPD with type 2 diabetes; Complications; Respiratory function score
慢阻肺是臨床呼吸內科常見疾病,以氣流阻塞性特征為主要病理變化[1]。患病后,患者可出現咳嗽、氣喘及不同程度呼吸困難等臨床癥狀,如未能得到及時有效治療,便會持續對其呼吸道及肺功能造成損傷。目前臨床部分慢阻肺患者并發2型糖尿病,患者血糖持續處于較高水平,導致臨床治療難度增加;而由于糖尿病屬于終身性慢性代謝性疾病,患者極易受臨床癥狀影響和長期治療而出現不依從,導致治療效果下降[2]。該院圍繞2018年3月—2019年3月收治的88例慢阻肺合并2型糖尿病患者護理工作開展研究,整理報道如下。
1? 資料與方法
1.1? 一般資料
選取該院收治的慢阻肺合并2型糖尿病患者88例,采用雙盲法分為A組和B組,各44例。A組男25例,女19例,年齡52~86歲,平均年齡(69.3±1.4)歲,病程2~14年,平均病程(7.2±0.9)年;B組男24例,女20例,年齡51~86歲,平均年齡(69.4±1.3)歲,病程2-15年,平均病程(7.3±1.0)年;兩組一般資料可對比,差異無統計學意義(P>0.05)。

