吡蟲啉在生菜中的吸收遷移及轉化行為
劉倩宇 李遠播 董豐收 劉新剛 徐軍 吳小虎 鄭永權 劉穎超





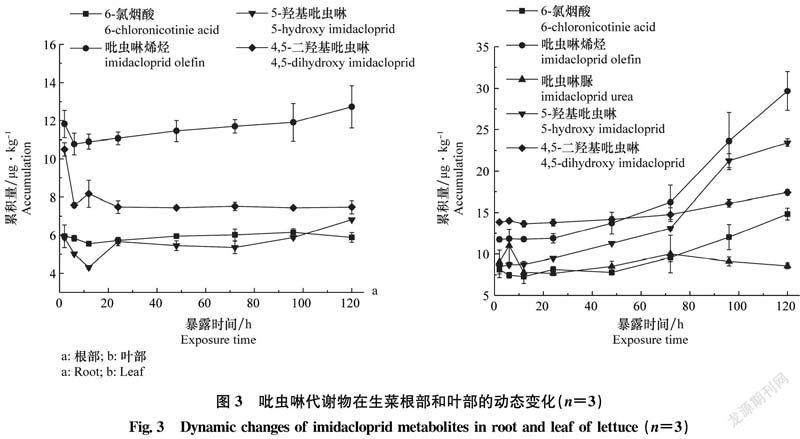
摘要 為了探究吡蟲啉在植物中的吸收轉運規律,本研究選擇生菜為研究對象,將其在含有1 mg/kg吡蟲啉的水培液中持續暴露120 h,利用超高效液相色譜三重四極桿質譜檢測吡蟲啉及其5種代謝物在生菜不同部位動態吸收變化和轉運分布規律。結果表明,吡蟲啉在葉部富集程度明顯高于根部,當達到吸收穩定狀態時,吡蟲啉在葉部富集程度約為根部的6倍。吡蟲啉在生菜中的吸收和代謝是同步進行的,代謝物在生菜葉部的富集程度排序為:吡蟲啉烯烴>5-羥基吡蟲啉>4,5-二羥基吡蟲啉>6-氯煙酸>吡蟲啉脲,代謝物在葉部富集高于根部。結果表明吡蟲啉從根部向地上部遷移能力較強,根部施用吡蟲啉可有效防治葉部害蟲。本研究為吡蟲啉的科學使用,保障農產品的質量安全提供了必要的數據支持。
關鍵詞 吡蟲啉; 生菜; 吸收; 轉化
中圖分類號: X592
文獻標識碼: A
DOI: 10.16688/j.zwbh.2021070
Abstract In order to explore the uptake and translocation of imidacloprid in plants, lettuce was exposed to 1 mg/kg of imidacloprid in hydroponic solution for 120 h. The uptake and translocation of imidacloprid and its five metabolites in lettuce were determined by ultra-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (UPLC-MS/MS). The results showed that the accumulation of imidacloprid in leaves was significantly higher than that in roots. When reaching uptake quasi-equilibrium, the accumulation of imidacloprid in leaves was about six times of that in roots. The uptake and metabolism of imidacloprid in lettuce co-occurred, and the concentrations of metabolites in leaves ranked from high to low as followed: imidacloprid-olefin, 5-hydroxy-imidacloprid,4,5-dihydroxy-imidacloprid, 6-chloronicotinic acid, and imidacloprid-urea. The concentration of metabolites in leaves was higher than that in roots. These results suggested that imidacloprid had a better translocation ability from roots to the aboveground, and thus application in roots could effectively prevent and control leaf insect pests. This research provided essential data to support the scientific use of imidacloprid and ensure the quality and safety of agricultural products.
Key words imidacloprid; lettuce; uptake; transformation
吡蟲啉是拜耳公司生產的首個氯代煙堿殺蟲劑,通過作用于昆蟲的乙酰膽堿受體,擾亂神經活動達到殺蟲效果,具有觸殺和胃毒雙重作用[1]。作為全球首個商品化的新煙堿殺蟲劑,自1991年投放市場以來,已在120多個國家登記使用[23]。因其具有高水溶性和優良的內吸傳導性,除噴霧施用外,吡蟲啉也常用于種子及土壤處理[45]。與葉面施藥不同的是,吡蟲啉施用于土壤并被植物吸收,會代謝成具有殺蟲活性的化合物,且代謝完全取決于植物種類和時間[67]。……

