健康教育及盆底肌訓練對產后盆底功能障礙的影響
黃健 丁巖 程明軍
(復旦大學附屬婦產科醫院婦科,上海 200011)
?
·論著·
健康教育及盆底肌訓練對產后盆底功能障礙的影響
黃健丁巖程明軍
(復旦大學附屬婦產科醫院婦科,上海200011)
摘要目的:探討健康教育和盆底肌訓練對產后盆底功能障礙的防治效果。方法: 選擇復旦大學附屬婦產科醫院2015年1月—3月產后42 d來復診的足月單胎初產婦312例,根據孕期及產褥期是否接受健康教育及盆底肌訓練分為訓練組和對照組,訓練組64例,對照組248例。測定盆底肌肌力,進行盆腔器官脫垂定量(pelvic organ prolapse quantitation,POP-Q)評分和尿墊試驗及性生活質量問卷調查等,產后6個月復查。結果: 訓練組產后6個月盆底肌肌力、盆腔臟器脫垂發生率、性生活質量與對照組比較差異均有統計學意義(P<0.05),兩組尿墊試驗陽性率差異無統計學意義;產后42 d各項檢測結果差異均無統計學意義。結論: 孕期及產褥期開展健康教育及盆底肌訓練有助于防治產后盆底功能障礙的發生。
關鍵詞盆底功能障礙;健康教育;盆底肌訓練
Effect of Health Education and Pelvic Muscle Training on Postpartum Pelvic Floor Dysfunction
HUANGJianDINGYanCHENGMingjun
DepartmentofGynecology,ObstetricsandGynecologyHospitalofFudanUniversity,Shanghai200011,China
AbstractObjective: To investigate the preventive and therapeutic effect of health education and pelvic muscle training on postpartum pelvic floor dysfunction. Methods: A total of 312 full-term single-fetus primiparas, who came to Obstetrics and Gynecology Hospital of Fudan University for further consultation 42 days after delivery, were enrolled from Jan. 2015 to Mar. 2015. And they were divided into exercise group and control group according to whether they had received health education and pelvic floor muscle exercise during pregnancy and puerperium.There were 64 cases in exercise group and 248 cases in control group. The pelvic floor muscle strength testing, pelvic organ prolapse quantitation(POP-Q) score, urine pad test, and questionnaire of sexual life quality were conducted. And they were conducted again six months after delivery. Results: Six months after delivery, the pelvic floor muscle strength, occurrence rate of pelvic organ prolapse and sexual quality of life in exercise group were all significantly better than those in control group (P<0.05),however there was no significant difference regarding the positive rate of urine pad test.There was no significant difference regarding all those measures 42 days after delivery. Conclusions: Health education and pelvic muscle training is conducive to prevent and treat postpartum pelvic floor dysfunction.
Key WordsPelvic floor dysfunction;Health education;Pelvic muscle training
女性盆底功能障礙性疾病(pelvic floor dysfunction,PFD)是由于各種原因導致的盆腔臟器位置及功能異常的一組疾病,主要包括盆底器官脫垂、壓力性尿失禁等,發生率高達19.7%[1],嚴重影響婦女的身心健康和生活質量。PFD的誘發因素包括妊娠、分娩損傷、長期腹壓增加、肥胖、藥物等,其中妊娠和分娩是導致PFD的主要高危因素[2]。因此,在孕期及產褥期進行早期干預治療對預防PFD的發生及提高生活質量具有重要意義。
1資料與方法
1.1一般資料選擇復旦大學附屬婦產科醫院2015年1月—3月產后42 d來復診的初產婦312例,年齡25~35歲,足月單胎,經陰道分娩,無產科合并癥,無泌尿生殖系統疾病。根據孕期及產褥期是否接受過健康教育及盆底肌訓練分為訓練組和對照組,訓練組64例,對照組248例。訓練組和對照組年齡、孕產次、孕周、新生兒出生體質量、產前體質量指數比較,差異均無統計學意義(P>0.05)。
1.2方法產后42 d進行盆底肌肌力測定、盆腔器官脫垂定量(pelvic organ prolapse quantitation,POP-Q)評分、尿墊試驗及性生活質量問卷調查,產后6個月復查。
1.2.1人工法和機器法檢測盆底肌肌力(1)人工法:將中指和食指放在產婦陰道后穹隆并后退1.5 cm,使手指與陰道肌肉接觸,根據Ortiz標準評估盆底肌肌力(分0~5級)。(2)機器法:使用法國神經肌肉刺激治療儀(PHENIX USB4),將壓力探頭放入陰道內,評估盆底Ⅰ/Ⅱ類肌纖維的肌力。產婦盆底肌肌力的綜合評分為:80%儀器評分+20%指檢評分。
1.2.2性生活質量問卷調查采用盆腔器官脫垂及尿失禁性生活質量問卷(pelvic organ prolapse-urinary incontinence sexual questionnaire,PISQ-12)[3]調查產婦產后性生活質量。
1.2.3盆腔臟器脫垂由同一位盆底康復師按照國際統一的POP-Q分度法進行分度。
1.2.4壓力性尿失禁在產婦有明顯尿意、無急迫感時,讓其用最大力屏氣和咳嗽,觀察有無尿液流出,并做尿墊試驗和尿失禁問卷,根據結果做出壓力性尿失禁的診斷。
1.3統計學處理采用SPSS 13.0軟件進行統計學分析,計數資料組間比較采用χ2檢驗,計量資料組間比較采用t檢驗。以P<0.05為差異有統計學意義。
2結果
2.1健康教育及盆底肌訓練對產后盆底肌肌力及性生活質量的影響訓練組產后42 d盆底肌肌力、性生活質量與對照組比較差異均無統計學意義,產后6個月盆底肌肌力、性生活質量與對照組比較差異均有統計學意義(P<0.05),見表1。
2.2健康教育及盆底肌訓練對產后盆底臟器脫垂的影響訓練組產后42 d POP-Q Ⅰ、Ⅱ度臟器脫垂率與對照組比較,差異均無統計學意義;訓練組產后6個月POP-Q Ⅰ、Ⅱ度臟器脫垂率與對照組比較差異均有統計學意義(P<0.05),見表2。
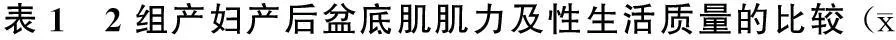
±s)
注:與對照組比較,*P<0.05
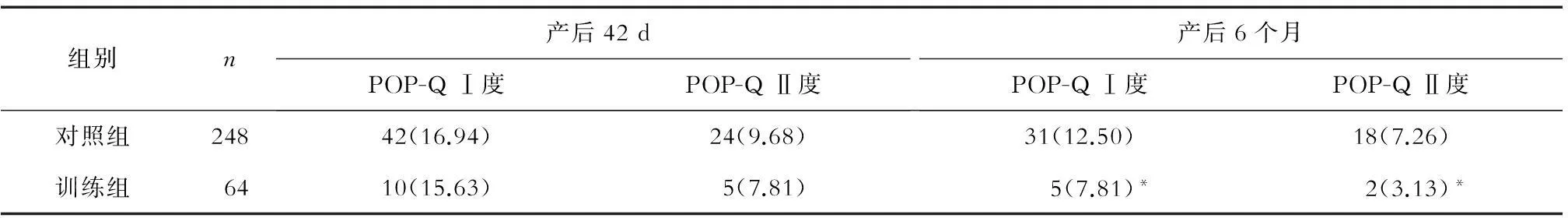
表2 2組產婦產后盆腔臟器脫垂發生率的比較 (n,%)
注:與對照組比較,*P<0.05
2.3健康教育及盆底肌訓練對產后尿失禁的影響訓練組尿墊試驗陽性率為4.68%(3/64),對照組為5.24%(13/248),差異無統計學意義。
3討論
妊娠和分娩可能對盆底肌肉造成不同程度的損傷,從而影響產后性生活質量,引起產后尿失禁、盆腔器官脫垂等癥狀[4-7],是女性PFD的主要危險因素[8]。盆底肌訓練(Kegel訓練)指有意識地對以肛提肌為主的盆底肌肉進行自主性收縮、加強控尿能力及盆底肌肉力量,是PFD最常用的非手術治療方法[9]。產后早期就進行盆底肌訓練,對提高產后性生活質量,預防和治療產后尿失禁、盆腔器官脫垂有重要意義[10-13]。
本研究中產后42 d問卷調查結果顯示,僅有20.51%(64/312)產婦了解孕前、產后盆底相關知識并進行盆底肌訓練,說明孕婦學校、醫生的宣傳力度不夠或者不夠重視;訓練組產婦經過健康教育及盆底肌訓練后,其產后6個月盆底肌肌力、盆底臟器脫垂及性生活質量與對照組比較均有明顯改善(P<0.05),與文獻報道相符,但在產后42 d時效果不明顯,說明長期的盆底肌訓練才會有效。另外,健康教育及盆底肌訓練對尿失禁療效不理想,可能與本研究樣本量不夠大有關。因此,如果能夠在孕期及產褥期盡早對孕產婦進行健康教育和指導盆底肌訓練,并長期堅持,則可以降低PFD的發生。
參考文獻
[ 1 ]Walker GJ,Gunasekera P.Pelvic organ prolapse and incontinence in developing countries:review of prevalence and risk factors[J].Int Urogynecol J,2011,22(2):127-135.
[ 2 ]Shek KL,Dieta HP.Intrapartum risk factors for levator trauma[J].BJOG,2010,117(12):1485-1492.
[ 3 ]Rogers RG,Kammerer-Doak D,Villarreal A,et al.A new instrument to measure sexual function in women with urinary incontinence or pelvic organ prolapse[J].Am J Obstet Gynecol,2001,184(4):552-558.
[ 4 ]Resende AP,Petricelli CD,Bernardes BT,et al.Electromyographic evaluation of pelvic floor muscle in pregnant and nonpregnant women[J].Int Urogynecol J,2012,23(8):1041-1045.
[ 5 ]Botelho S,Riccetto C,Herrmann V,et al.Impact of delivery mode on electromyographic activity of pelvic floor:comparative prospective study[J].Neurourol Urodyn,2010,29(7):1258-1261.
[ 6 ]Chan SS,Cheung RY,Yiu AK,et al.Pevalence of levator ani muscle injury in Chinese women after first delivery[J].Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol,2012,39(6):704-709.
[ 7 ]Dieta HP,Bond V,Shek KL.Does childbirth alter the reflex pelvic floor response to coughing?[J].Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol,2012,39(5):569-573.
[ 8 ]Rodríguez-Mias NL,Martínez-Franco E,Aguado J,et al.Pelvic organ prolapse and stress urinary incontinence, do they share the same risk factors?[J].Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol,2015,190:52-57.
[ 9 ]Cavkaytar S,Kokanali MK,Topcu HO,et al.Effect of home-based Kegel exercises on quality of life in women with stress and mixed urinary incontinence[J].J Obstet Gynaecol,2015,35(4):407-410.
[10]Batista BL,Franco MM,Naldoni LM,et al.Biofeedback and the electromyographic activity of pelvic floor muscles in pregnant women[J].Rev Bras Fisioter,2011,15(5):386-392.
[11]Boyle R,Hay-Smith EJ,Cody JD,et al.Pelvic floor muscle training for prevention and treatment of urinary and faecal incontinence in antenatal and postnatal women:a short version Cochrane review[J].Neurourol Urodyn,2014,33(3):269-276.
[12]M?rkved S,B? K.Effect of pelvic floor muscle training during pregnancy and after childbirth on prevention and treatment of urinary incontinence:a systematic review[J].Br J Sports Med,2014,48(4):299-310.
[13]朱蘭,郎景和.女性盆底功能障礙性疾病的防治策略[J].中華婦產科雜志,2007,42(12):793-794.
中圖分類號R711.5
文獻標志碼A
通訊作者程明軍,E-mail:chengmingjun04@163.com
基金項目:上海市衛生和計劃生育委員會青年科研項目(編號:20124Y054);上海市科學技術委員會西醫引導類項目(編號:124119a5501);上海市申康醫院管理集團新興前沿項目(編號:SHDC12013120)

