不同劑量左氧氟沙星治療淋病合并非淋菌性尿道炎的臨床效果
陳玉梅 王元豐 譚艷 王崗 李庭恒
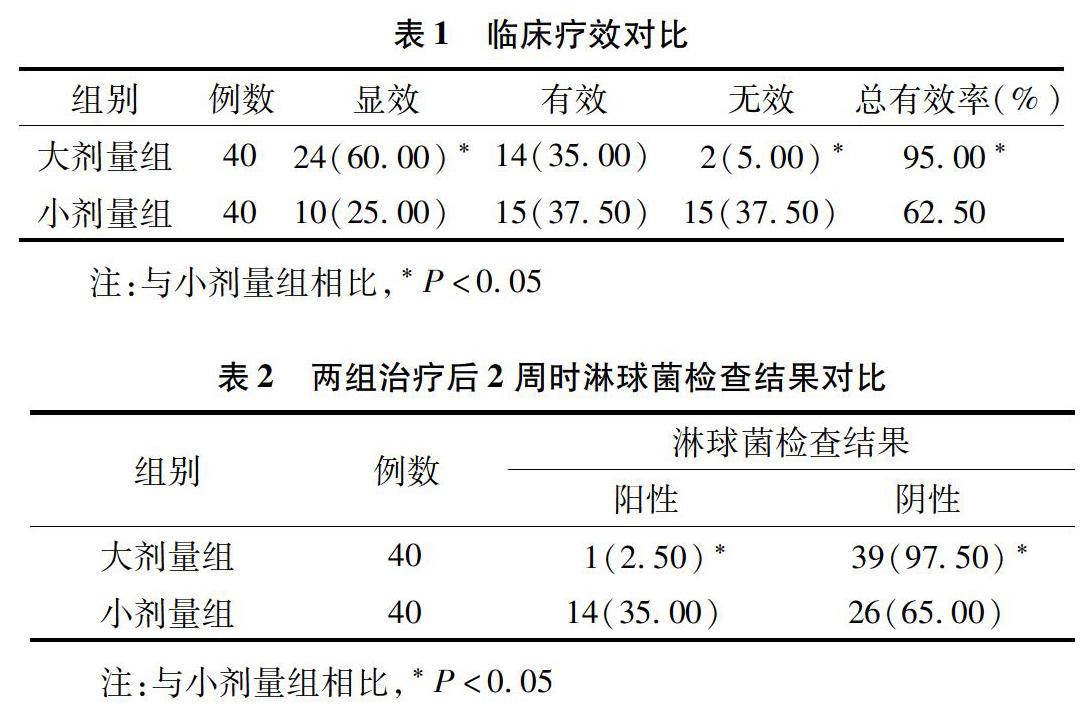
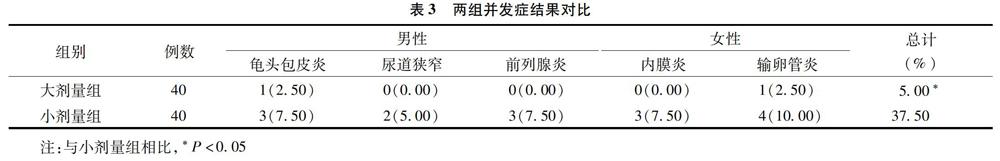
【摘要】目的:對淋病合并非淋菌性尿道炎患者給予不同劑量左氧氟沙星實施治療的效果進行分析探究。方法:選取在我院接受治療的80例淋病合并非淋菌性尿道炎患者作為本次研究對象,根據(jù)隨機數(shù)字表法將其平均分為大劑量組與小劑量組兩組,分別給予0.5g/次、0.1g/次左氧氟沙星治療,對比分析兩組臨床療效、治療后2周淋球菌篩查結果以及并發(fā)癥情況。結果:兩組患者均未見不良反應,大劑量組總有效率為95.00%,小劑量組為62.50%,兩組相比試驗組明顯較高,差異有統(tǒng)計學意義(χ2=15.7404,P=0.00038)。大劑量組研究對象的淋球菌檢測陽性率(2.50%)與小劑量組淋球菌檢測陽性率(35.00%)相比明顯較低,差異有統(tǒng)計學意義(χ2=13.8667,P=0.0002)。大劑量組研究對象的并發(fā)癥發(fā)生率(5.00%)與對照組(37.50%)相比明顯較低,差異有統(tǒng)計學意義(χ2=10.7563,P=0.00104)。結論:對淋病伴非淋菌性尿道炎患者采用大劑量左氧氟沙星治療的效果顯著,復查結果較好,藥物抗菌性較強,并發(fā)癥較少發(fā)生,具有較高的安全性,值得推廣。
【關鍵詞】不同劑量;左氧氟沙星;淋病;非淋菌性尿道炎;臨床效果
【Abstract】Objectives: To analyze the treatment efficacy of different levofloxacin dosages in the treatment of gonorrhea and non-gonococcal urethritis. Methods: Eighty patients with gonorrhea and non-gonococcal urethritis were randomly divided into two groups. Patients in high dose group and low dose group were respectively treated with 0.5 g and 0.1 g levofloxacin. Clinical efficacy, Neisseria gonorrhoeae screening results 2 weeks after treatment and complications were compared in the two groups. Results: No adverse reactions were found in the two groups. The overall response rate in high dose group (95.00%) was significantly higher than that in low dose group (62.50%) (χ2=15.7404, P=0.00038). Neisseria gonorrhoeae positive rate (2.50%) in high dose group was obviously lower than that in low dose group (35.00%), with statistically significant difference (χ2=13.8667, P=0.0002). The incidence of complications in high dose group (5.00%) was obviously lower than that in control group (37.50%), with statistically significant difference (χ2= 10.7563, P=0.00104). Conclusion: High-dose levofloxacin is effective in treating gonorrhea and non-gonococcal urethritis, with good recheck outcome, strong antibacterial property, fewer complications and high security, which is worth popularizing.
【Key words】Different dosages; Levofloxacin; Gonorrhea; Non-gonococcal urethritis; Clinical efficacy
【中圖分類號】R759.2【文獻標志碼】A
近幾年來,臨床上淋病的發(fā)病人數(shù)不斷增多,該疾病主要是由淋病雙球菌引起的,通常情況下通過性途徑傳播,患者在患病后,男性一般表現(xiàn)為尿痛、尿頻、尿道口膿性分泌物,女性患者則表現(xiàn)為尿痛、陰道內(nèi)分泌物呈膿性,且分泌量較大,嚴重威脅患者的生命與生活質(zhì)量[1]。非淋菌性尿道炎是由衣原體、支原體等細菌引起的疾病,亦通過性途徑傳播[2]。……

