中西醫辨證治療對慢性阻塞性肺疾病急性加重期患者氣道炎癥、氧化應激反應的影響
朱靜 徐維國

【摘要】 目的:探討疏風解毒膠囊對慢性阻塞性肺疾病急性加重期(AECOPD)的作用及其相關作用機制。方法:選取2018年5-8月本院收治的AECOPD患者90例,隨機分為常規治療組和疏風解毒膠囊組,每組45例。常規治療組給予常規治療,疏風解毒膠囊組在常規治療的基礎上給予疏風解毒膠囊,選取同期30例來本院體檢的健康者為對照組。比較各組血清中丙二醛(MDA)、一氧化氮(NO)含量及過氧化氫酶(CAT)、過氧化物歧化酶(SOD)、谷胱甘肽過氧化物酶(GSH)、總一氧化氮合酶(eNOS)活性;比較疏風解毒膠囊組和常規治療組治療前后呼出氣一氧化氮(FeNO)水平和肺功能水平。結果:三組MDA含量、CAT、SOD以及GSH活性比較,差異均有統計學意義(P<0.05)。疏風解毒膠囊組的MDA含量明顯高于對照組,CAT、SOD以及GSH活性均明顯低于對照組(P<0.05);常規治療組MDA含量顯著高于疏風解毒膠囊組,CAT、SOD以及GSH活性均明顯低于疏風解毒膠囊組(P<0.05)。三組NO含量和eNOS活性比較,差異均有統計學意義(P<0.05)。疏風解毒膠囊組NO含量和eNOS活性均顯著高于對照組(P<0.05);常規治療組NO含量和eNOS活性均顯著高于疏風解毒膠囊組(P<0.05)。治療前,常規治療組和疏風解毒膠囊組FeNO水平均高于對照組,差異均有統計學意義(P<0.05);治療后,常規治療組和疏風解毒膠囊組FeNO水平均明顯低于治療前,差異均有統計學意義(P<0.05)。治療后,兩組FEV1占預計值百分比、FEV1/FVC水平均高于治療前,且疏風解毒膠囊組均高于常規治療組,差異均有統計學意義(P<0.05)。結論:疏風解毒膠囊可顯著改善AECOPD引起的氧化應激反應,能有效抑制患者氣道炎癥和改善AECOPD患者的肺功能。
【關鍵詞】 慢性阻塞性肺疾病 疏風解毒膠囊 氣道炎癥 氧化應激反應
Effect of Syndrome Differentiation of Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine on Airway Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in Patients with Acute Exacerbation of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases/ZHU Jing, XU Weiguo. //Medical Innovation of China, 2020, 17(03): 008-012
[Abstract] Objective: To explore the effect of Shufeng Jiedu Capsule on acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (AECOPD) and its mechanism. Method: A total of 90 patients with AECOPD admitted to our hospital from May to August 2018 were selected. They were randomly divided into conventional treatment group and Shufeng Jiedu Capsule group, 45 cases in each group. The conventional treatment group was given conventional treatment, the Shufeng Jiedu Capsule group was given Shufeng Jiedu Capsule on the basis of conventional treatment. 30 healthy patients who came to our hospital for physical examination during the same period were selected as the control group. The contents of malondialdehyde (MDA), nitric oxide (NO), catalase (CAT), superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione peroxidase (GSH) and total nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) in serum of each group were compared. The levels of exhaled nitric oxide (FeNO) and lung function were compared between the Shufeng Jiedu Capsule group and the conventional treatment group before and after treatment. Result: The MDA content, CAT, SOD and GSH activity in three groups were compared, the differences were statistically significant (P<0.05). The content of MDA in the Shufeng Jiedu Capsule group was significantly higher than that in the control group, the activity of CAT, SOD and GSH were significantly lower than those of the control group (P<0.05). MDA content in the conventional treatment group was significantly higher than that in the Shufeng Jiedu Capsule group, the activity of CAT, SOD and GSH were significantly lower than those of Shufeng Jiedu Capsule group (P<0.05). The NO content and eNOS activity in three groups were compared, the differences were statistically significant (P<0.05). NO content and eNOS activity in Shufeng Jiedu Capsule group were significantly higher than those in control group (P<0.05). NO content and eNOS activity in the conventional treatment group were significantly higher than those in the Shufeng Jiedu Capsule group (P<0.05). Before the treatment, FeNO levels in the conventional treatment group and the Shufeng Jiedu Capsule group were higher than those in the control group, the differences were statistically significant (P<0.05). After treatment, FeNO levels in the conventional treatment group and the Shufeng Jiedu Capsule group were significantly lower than those before treatment, the differences were statistically significant (P<0.05). After treatment, the predicted value of FEV1% pred and the level of FEV1/FVC in both groups were higher than those before treatment, and the levels of Shufeng Jiedu Capsule group were higher than those in the conventional treatment group, the differences were statistically significant (P<0.05). Conclusion: Shufeng Jiedu Capsule can significantly improve oxidative stress response caused by AECOPD, effectively inhibit airway inflammation and improve lung function in patients with AECOPD.
[Key words] Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease Shufeng Jiedu Capsule Airway inflammation Oxidative stress
First-authors address: Center Hospital of Mianyang, Mianyang 621000, China
doi:10.3969/j.issn.1674-4985.2020.03.003
慢性阻塞性肺疾病(COPD)是一種以持續氣流受限為特征的疾病,其氣流受限多呈進行性發展,該疾病的發生與氣道和肺組織對有害氣體或有害顆粒的異常慢性炎癥反應有關[1]。COPD病程長、患病率和死亡率逐年升高,因肺功能進行性減退,嚴重影響患者的勞動力和生活質量。COPD的病因可能是多種環境因素與機體自身因素長期相互作用的結果。其中COPD的急性加重(AECOPD)是導致COPD患者肺功能下降和死亡主要原因。研究發現,氣道炎癥反應和氧化應激反應參與了AECOPD的發生、發展過程。疏風解毒膠囊在抗氧化、抗炎作用等方面被證明是通過控制NF-κB的激活或影響組蛋白修飾[2],進而在肺上皮細胞炎癥基因表達方面發揮作用的[3-4]。本研究分為對照組、常規治療組及疏風解毒膠囊組(COPD常規治療+疏風解毒膠囊治療),觀察疏風解毒膠囊對AECOPD患者氧化應激水平及氣道炎癥的影響,并對相關機制進行探討。現報道如下。
1 資料與方法
1.1 一般資料 選取2018年5-8月本院收治的AECOPD患者90例。(1)納入標準:①患者均符合中華醫學會呼吸病學制定的《慢性阻塞性肺疾病診療指南》診斷標準;②肺功能Ⅲ級的COPD患者。(2)排除標準:①合并胸腔積液、肺栓塞、肺結核、心力衰竭、心律失常者;②對本研究所涉藥物既往有過敏史者。隨機分為常規治療組(COPD常規治療)及疏風解毒膠囊組(COPD常規治療+疏風解毒膠囊治療);每組45例。納入同期30例來本院體檢的健康體檢者為對照組;研究對象均知情同意且簽署知情同意書,該研究已經醫院倫理學委員會批準。
1.2 方法 常規治療組與疏風解毒膠囊組均給予COPD常規治療,包括保持低流量吸氧、保持呼吸道通暢、積極抗感染、解痙平喘、祛痰等綜合治療。疏風解毒膠囊組在上述治療基礎上給予疏風解毒膠囊(生產廠家:安徽濟人藥業有限公司,批準文號:國藥準字Z20090047,規格:0.52 g/粒),口服,4粒/次,3次/d,連續用藥7 d。
1.3 觀察指標及判定標準 (1)比較三組血清丙二醛(MDA)含量、過氧化氫酶(CAT)、過氧化物歧化酶(SOD)以及谷胱甘肽過氧化物酶(GSH)活性,檢測均采用ELISA法;(2)比較三組血清一氧化氮(NO)含量和總一氧化氮合酶(eNOS)活性,檢測均使用化學定量法;(3)比較三組呼出氣一氧化氮(FeNO)變化情況;(4)比較疏風解毒膠囊組和常規治療組治療前后肺功能情況,包括FEV1占預計值百分比及FEV1/FVC。
1.4 統計學處理 采用SPSS 19.0軟件對所得數據進行統計分析,計量資料用(x±s)表示,組間采用單因素方差分析,兩兩比較采用SNK-q檢驗;計數資料以率(%)表示,比較采用字2檢驗。以P<0.05為差異有統計學意義。
2 結果
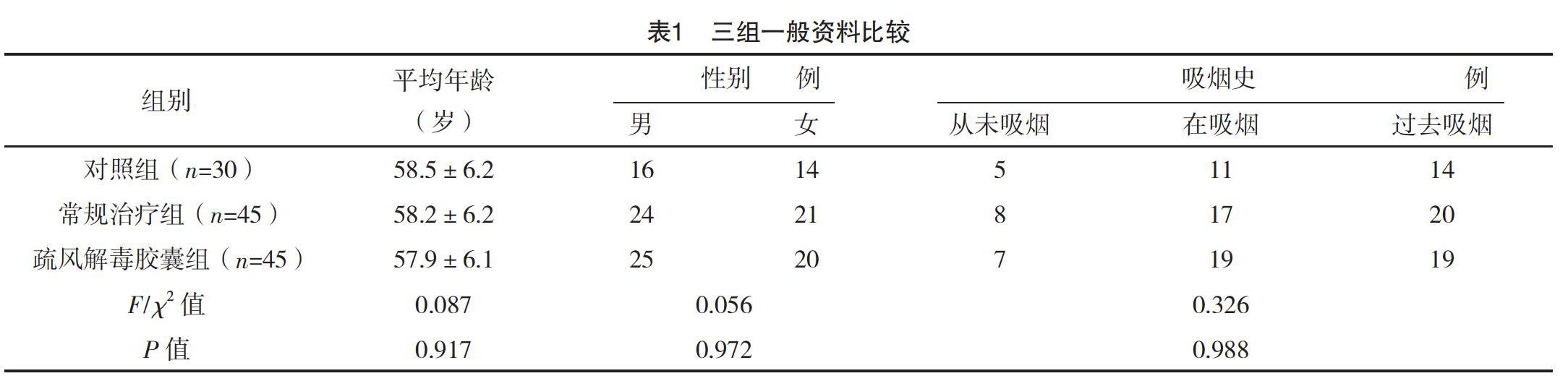
2.1 三組一般資料比較 三組性別、年齡、吸煙史比較,差異均無統計學意義(P>0.05),具有可比性,見表1。
2.2 三組MDA含量、CAT、SOD以及GSH活性比較 三組MDA含量、CAT、SOD以及GSH活性比較,差異均有統計學意義(P<0.05)。疏風解毒膠囊組的MDA含量明顯高于對照組(t=9.278,P=0.001);疏風解毒膠囊組的CAT、SOD以及GSH活性均明顯低于對照組(t=10.055、14.196、22.535,P=0.001、0.001、0.001);常規治療組MDA含量顯著高于疏風解毒膠囊組(t=25.641,P=0.001);常規治療組的CAT、SOD以及GSH活性均明顯低于疏風解毒膠囊組(t=29.012、25.188、20.102,P=0.001、0.001、0.001)。見表2。
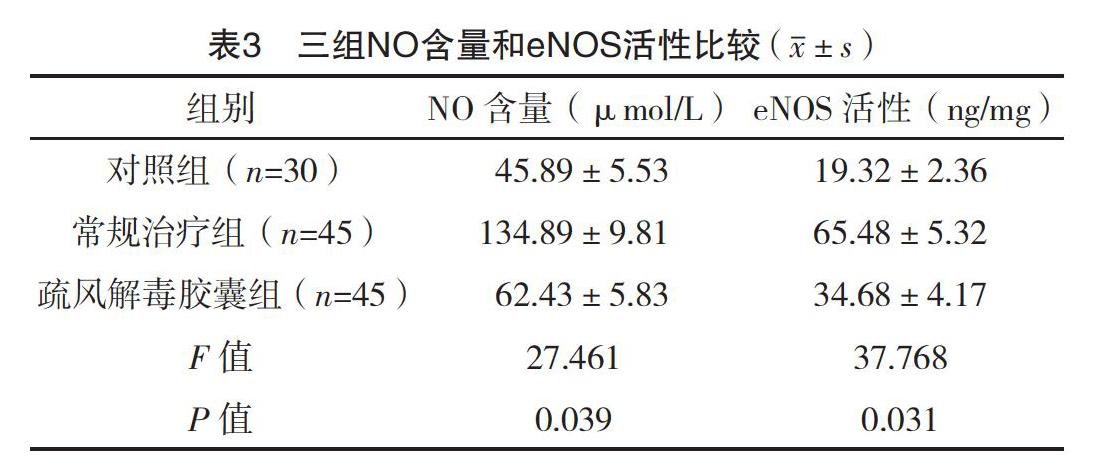
2.3 三組NO含量和eNOS活性比較 三組NO含量和eNOS活性比較,差異均有統計學意義(P<0.05)。疏風解毒膠囊組NO含量和eNOS活性均顯著高于對照組(t=12.284、18.291,P=0.001、0.001);常規治療組NO含量和eNOS活性顯著高于疏風解毒膠囊組(t=42.595、30.566,P=0.001、0.001)。見表3。
2.4 三組FeNO變化情況比較 治療前,常規治療組和疏風解毒膠囊組FeNO水平均高于對照組,差異均有統計學意義(t=8.269、7.079,P=0.001、0.001);治療后,常規治療組和疏風解毒膠囊組FeNO水平均明顯于低治療前,差異均有統計學意義(t=5.343、6.752,P=0.001、0.001)。見表4。
2.5 兩組治療前后肺功能比較 治療前,兩組FEV1占預計值百分比、FEV1/FVC水平比較,差異均無統計學意義(P>0.05);治療后,兩組FEV1占預計值百分比、FEV1/FVC水平均高于治療前,且疏風解毒膠囊組均高于常規治療組,差異均有統計學意義(P<0.05)。見表5。
3 討論
COPD在發病機制方面主要包括炎癥機制、氧化應激機制、蛋白酶-抗蛋白酶失衡等機制。其中,氧化應激反應及氣道炎癥是AECOPD發生發展的重要機制,也是當今研究的熱點內容。氧化應激是體內氧化與抗氧化機制平衡被打破,氧化作用大于抗氧化作用,其結果是中性粒細胞炎性浸潤,導致蛋白酶分泌增加,從而產生一系列的氧化中間產物。氧化應激是煙草煙霧導致呼吸道損傷的重要因素之一,其作用機制為通過過量活性氧簇(reactive oxygen species, ROS)的累積誘導細胞發生氧化應激反應,進而導致細胞損傷和凋亡[5-7]。脂質氧化的最終產物是MDA,其表達水平越高,體內氧自由基的產生和釋放水平也越高,細胞受自由基攻擊的程度也就越劇烈。肺組織本身為了保護細胞防御氧化損傷,含有豐富的抗氧化系統。SOD作為細胞內主要的自由基清除劑和抗氧化酶,可有效對抗氧自由基對機體的損害,SOD水平越高,內源性氧自由基清除系統功能就越強[8-10]。CAT作為一種酶類清除劑,存在于細胞的過氧化物體內,是過氧化物酶體的標志酶。CAT可將H2O2分解為分子氧和水,通過這樣的方式清除掉體內的H2O2,從而使細胞免于遭受H2O2的毒害,是生物防御體系的關鍵酶之一。GSH可催化H2O2分解,是機體內的一種重要的抗氧化酶,其水平越高,那么機體清除氧自由基的能力就越強[11]。
疏風解毒膠囊原名“祛毒散”,主要由甘草、連翹、敗醬草、虎杖、隔山消、馬鞭草六味藥物組成,用于治療扁桃體炎、傷風、腮腺炎、白喉等病。現代藥理學研究表明疏風解毒膠囊具有控制炎癥、抗病毒及抗細菌等功能作用,還具有免疫調節功能,具備治療COPD的理論基礎[12-13]。文獻[14-16]
發現疏風解毒膠囊降低對肺、心臟和肝臟的損傷是通過抑制腫瘤壞死因子-α(TNF-α)、白介素-1β(IL-1β)等細胞因子的表達來實現的,對INF-γ具有雙向表達作用。呂偉偉等[17]發現通過抑制MAPK/NF-κB Signaling通路,下調NF-κB mRNA的表達,最終抑制LPS誘導的炎癥反應,減輕LPS誘導的肺損傷反應。從本試驗中可以看到,AECOPD患者MDA含量明顯提高,而SOD、CAT和GSH活性明顯受到抑制,經過疏風解毒治療
1周,發現其可顯著逆轉COPD引起的氧化應激反應。另外,過氧亞硝酸鹽可介導肺組織損傷,而超氧化物和NO反應可生成過氧亞硝酸鹽,在受損的血管內eNOS的含量往往是增加的,作為調控血管功能的關鍵因子,可產生收縮血管的超氧化物以及NO,因此被視為氧化應激反應的標志物之一[18]。從本試驗結果中可以看出,疏風解毒膠囊組NO含量和eNOS活性均顯著高于對照組(P<0.05);常規治療組NO含量和eNOS活性均顯著高于疏風解毒膠囊組(P<0.05)。說明疏風解毒膠囊能顯著抑制NO含量以及eNOS活性,急性加重期患者是可以獲益的。
現階段,肺功能檢查仍是診斷COPD的金標準,在吸入支氣管擴張劑后,第1秒用力呼氣容積/用力肺活量(FEV1/FVC)<0.70表示存在持續氣流受限。呼出氣NO是檢測氣道炎癥主要手段之一[19]。FeNO檢測是一項具有快速、精確、無創、簡便、安全且能有效量化氣道炎癥的檢測手段,最早是Gustafsson等[20]通過化學發光法發現的,目前已廣泛用于支氣管哮喘和AECOPD期的輔助診斷。本研究顯示疏風解毒治療組較常規治療組能有效改善COPD患者的肺功能(P<0.05);治療后,兩組FeNO均較治療前明顯降低,且疏風解毒膠囊組低于常規治療組,差異均有統計學意義(P<0.05)。證實了疏風解毒膠囊能有效抑制患者氣道炎癥。
本研究證實疏風解毒膠囊可顯著改善AECOPD引起的氧化應激反應,能有效抑制患者氣道炎癥和改善AECOPD患者的肺功能情況。通過逐步完善的藥理學及分子學研究,為疏風解毒膠囊臨床應用提供了可靠依據,也為中醫辨證將疏風解毒膠囊用于呼吸系統等疾病提供了理論支持。
參考文獻
[1]葛均波,徐永健.內科學[M].8版.北京:人民衛生出版社,2013:16-18.
[2] Rahman I,Adcock I M.Oxidative stress and redox regulation of lung inflammation in COPD[J].Eur Respir J,2006,28(1):219-242.
[3] Lehtonen S T,Ohlmeier S,Kaarteenaho-Wiik R,et al.Does the oxidative stress in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease cause thioredoxin/peroxiredoxin oxidation?[J].Antioxid Redox Signal,2008,10(4):813-819.
[4] Wood Z A,Schr?der E,Robin Harris J,et al.Structure, mechanism and regulation of peroxiredoxins[J].Trends Biochem Sci,2003,28(1):32-40.
[5] Avila P C,Kropotov A V,Krutilina R,et al.Peroxiredoxin V contributes to antioxidant defense of lung epithelial cells[J].Lung,2008,186(2):103-114.
[6] Lehtonen S T,Markkanen P M,Peltoniemi M,et al.Variable overoxidation of peroxiredoxins in human lung cells in severe oxidative stress[J].Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol,2005,288(5):997-1001.
[7] Kim H S,Kang S W,Rhee S G,et al.Rat lung peroxiredoxins Ⅰ and Ⅱ are differentially regulated during development and by hyperoxia[J].Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol,2001,280(6):1212-1217.
[8] Kim H S,Manevich Y,Feinstein S I,et al.Induction of 1-cys peroxiredoxin expression by oxidative stress in lung epithelial cells[J].Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol,2003,285(2):363-369.
[9] Serikov V B,Leutenegger C,Krutilina R,et al.Cigarette smoke extract inhibits expression of peroxiredoxin V and increases airway epithelial permeability[J].Inhal Toxicol,2006,18(1):79-92.
[10] Yao H,Edirisinghe I,Rajendrasozhan S,et al.Cigarette smoke-mediated inflammatory and oxidative responses are strain-dependent in mice[J].Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol,2008,294(6):1174-1186.
[11] Jones F S,Meech R,Edelman D B,et al.Prx1 controls vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and tenascin-C expression and is upregulated with Prx2 in pulmonary vascular disease[J].Circ Res,2001,89(2):131-138.
[12] Kode A,Rajendrasozhan S,Caito S,et al.Resveratrol induces glutathione synthesis by activation of Nrf2 and protects against cigarette smoke-mediated oxidative stress in human lung epithelial cells[J].Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol,2008,294(3):L478-488.
[13] Wang Y,Feinstein S I,Manevich Y,et al.Peroxiredoxin 6 gene-targeted mice show increased lung injury with paraquat-induced oxidative stress[J].Antioxid Redox Signal,2006,8(1-2):229-237.
[14]薛明明,高靜琰,陳東旭,等.疏風解毒膠囊對D-氨基半乳糖/脂多糖誘導大鼠急性肝損傷保護作用[J].中草藥,2015,46(9):1348-1353.
[15]張亞平,陶振剛,宋振舉,等.疏風解毒膠囊對小鼠病毒性心肌炎模型的影響[J].中草藥,2016,47(1):110-113.
[16] Wang Y,Feinstein S I,Fisher A B.Peroxiredoxin 6 as an antioxidant enzyme: protection of lung alveolar epithelial type II cells from H2O2-induced oxidative stress[J].J Cell Biochem,2008,104(4):1274-1285.
[17]呂偉偉,朱童娜,邱歡,等.疏風解毒膠囊抗病毒及抗菌的體外藥效學實驗研究[J].中藥新藥與臨床藥理,2013,24(3):234-238.
[18] Tao Z,Gao J,Zhang G,et al.Shufeng Jiedu Capsule protect against acute lung injury by suppressing the MAPK/NF-κB pathway[J].Biosci Trends,2014,8(1):45-51.
[19]文富強.慢性阻塞性肺疾病炎癥反應的復雜性及治療新選擇[J].中華結核和呼吸雜志,2012,35(4):246-248.
[20] Gustafsson L E,Leone A M,Persson M G,et al.Endogenous nitric oxide is present in the exhaled air of rabbits, guinea pigs and humans[J].Biochem Biophys Res Commun,1991,181(2):852-857.
(收稿日期:2019-06-28) (本文編輯:姬思雨)

