肺彌散功能檢查在支氣管哮喘與慢性阻塞性肺疾病鑒別診斷中的意義
蔡蕾
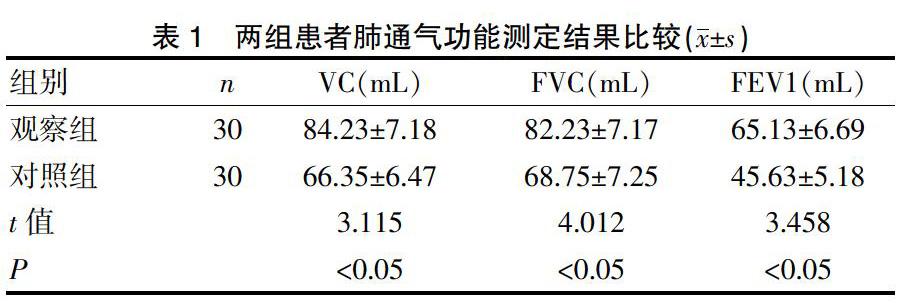
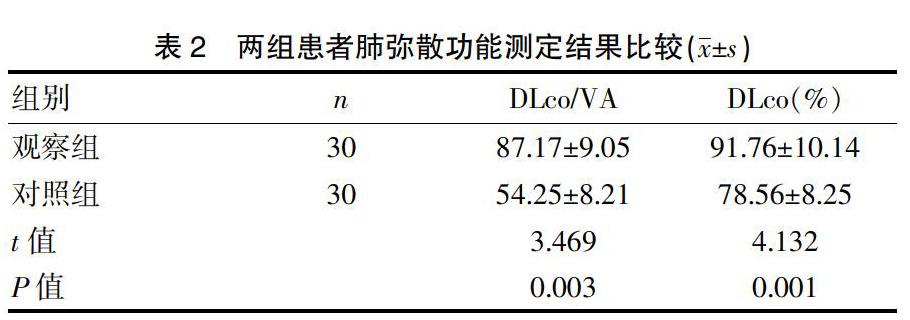
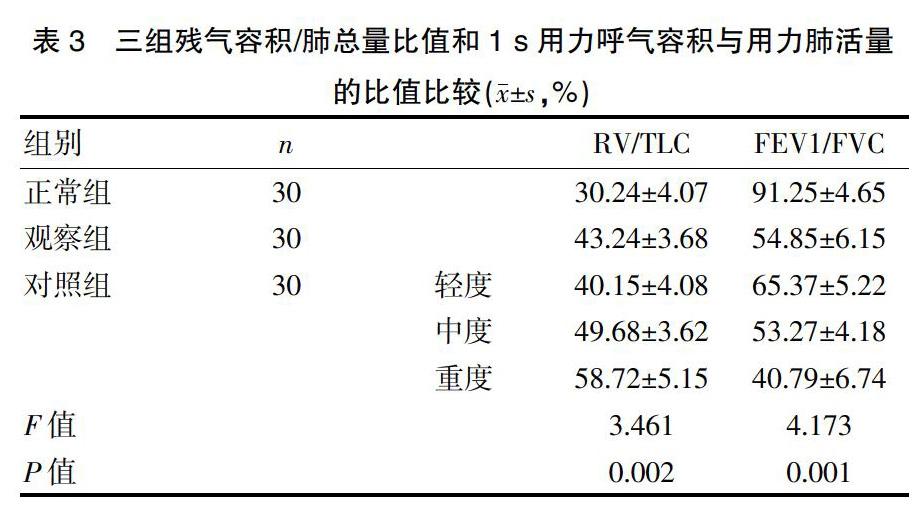
[摘要] 目的 探討肺彌散功能檢查在支氣管哮喘與慢性阻塞性肺疾病鑒別診斷中的意義。 方法 選取我院2017年5月~2019年8月收治的60例患者,采取抽簽分組方式分為兩組,觀察組(n=30)為支氣管哮喘患者,對照組(n=30)為慢性阻塞性肺疾病患者,另選30例正常人作為正常組,對比觀察組和對照組肺通氣功能的測定結果,觀察組與對照組的肺彌散功能測定結果,正常組、觀察組及對照組的殘氣容積/肺總量比值(RV/TLC)和1 s用力呼氣容積與用力肺活量的比值(FEV1/FVC)。 結果 觀察組的肺活量、用力肺活量、1 s用力呼氣容積數值均高于對照組(P<0.05);觀察組的肺彌散率和一口氣彌散量高于對照組(P<0.05);觀察組與對照組的1 s用力呼氣容積與用力肺活量的比值低于正常組,且對照組隨著疾病的加重,其比值越小;觀察組與對照組的殘氣容積/肺總量比值高于正常組,且對照組隨著疾病的加重,其比值越大,差異有統計學意義(P<0.05)。 結論 肺彌散功能檢查有助于支氣管哮喘及慢性阻塞性肺疾病的鑒別和診斷,可區分支氣管哮喘及慢性阻塞性肺疾病,對早期疾病、病變部位的判斷以及評估病情嚴重程度等多方面具有重要的意義,值得推廣應用。
[關鍵詞] 肺彌散功能檢查;支氣管哮喘;慢性阻塞性肺疾病;肺通氣測定
[中圖分類號] R563.9? ? ? ? ? [文獻標識碼] A? ? ? ? ? [文章編號] 1673-9701(2020)08-0012-03
Significance of pulmonary diffusion function examination in differential diagnosis of bronchial asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
CAI Lei
Function Examination Section, Jiujiang No.1 People's Hospital in Jiangxi Province, Jiujiang? ?332000,China
[Abstract] Objective To explore the significance of pulmonary diffusion function examination in the differential diagnosis of bronchial asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Methods Sixty patients admitted to our hospital from May 2017 to August 2019 were selected and divided into two groups by drawing lots. The observation group(n=30) consisted of patients with bronchial asthma, the control group(n=30) consisted of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and another 30 normal people were selected. The determination results of pulmonary vital copacity, pulmonary diffusion function between the observation group and the control group, and the ratios of residual gas volume/total lung volume(RV/TLC) and forced vital capacity and forced expiratory volume in 1 second(FEV1/FVC) among the normal group, the observation group and the control group were compared. Results The vital capacity, forced vital capacity and forced expiratory volume in 1 second in the observation group were all higher than those in the control group(P<0.05). The lung dispersion rate and one-breath dispersion were higher in the observation group than those in the control group(P<0.05). The ratios of forced expiratory volume in 1 second to forced vital capacity in the observation group and the control group were lower than that in the normal group, and with the aggravation of the disease, the ratio in the control group became smaller. The ratios of residual gas volume/total lung volume in the observation group and the control group were higher than that in the normal group, and with the aggravation of disease, the ratio grew larger in the control group, with statistically significant differences(P<0.05). Conclusion The pulmonary diffusion function examination contributes to the identification and diagnosis of bronchial asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, which can be used to distinguish between the two diseases. It is of great significance for the judgment of the early stage of disease and the lesion site, the evaluation of the severity of disease and many other aspects, which is worthy of promotion and application.
[Key words] Pulmonary diffusion function examination; Bronchial asthma; Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; Pulmonary determination of ventilation
支氣管哮喘是由多種細胞和細胞組分參與的氣道慢性炎癥為特征的異質性疾病,具有反復發作的喘息、氣促、胸悶和咳嗽等癥狀[1]。支氣管哮喘長期發作會引發肺源性心臟病,并嚴重影響呼吸系統和心血管系統功能。慢性阻塞性肺疾病的特點是不可逆的氣流受限,其主要臨床表現為慢性咳嗽、咳痰或呼吸困難等[2]。慢性阻塞性肺疾病不僅損害患者呼吸功能,還影響其循環系統功能,甚至危及其生命安全。臨床研究表明[3-4]:支氣管哮喘和慢性阻塞性肺疾病兩者均是常見且多發的呼吸系統疾病。結合患者的臨床資料及影像學檢查結果,通過肺彌散功能檢查及肺通氣功能檢查的情況,有利于區分支氣管疾病及慢性阻塞性肺疾病。……

