微博搜索、網頁搜索對用戶信息需求滿足能力的對比分析
劉明珠 楊建林
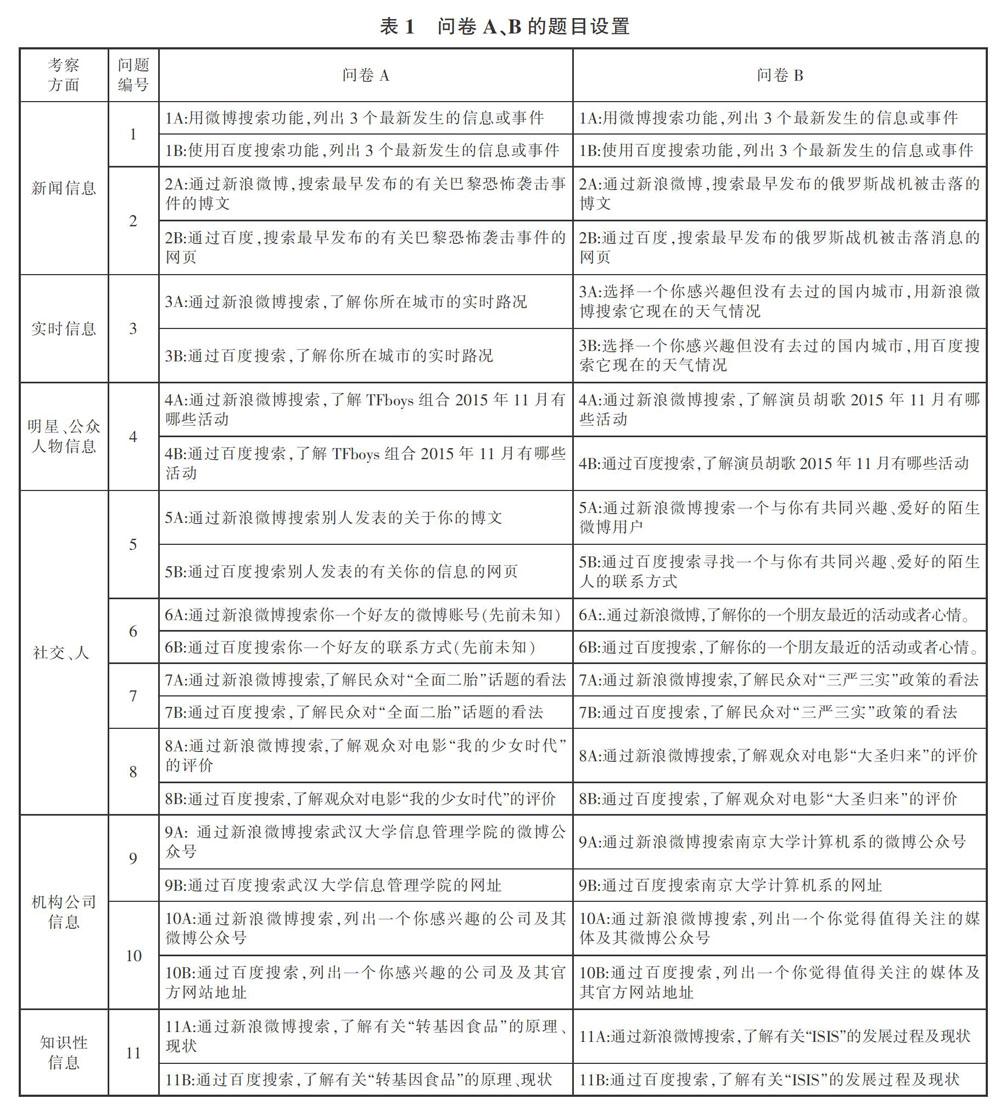


摘 要:文章通過對已有研究成果的分析總結,結合專家建議,將用戶進行微博搜索時的信息需求歸納為七類:新聞信息、實時信息、明星公眾人物信息、社交人際關系信息、公眾輿論信息、機構公司信息、知識性信息,并基于這七類信息需求設計調查問卷,考察了微博搜索對用戶信息需求的滿足能力,同時與網頁搜索進行對比研究,分析了兩種搜索方式在滿足用戶不同信息需求方面的能力差異,以及產生差異的原因。
關鍵詞:微博搜索;網頁搜索;信息需求;問卷調查
中圖分類號: G254.97 文獻標識碼: A DOI:10.11968/tsyqb.1003-6938.2016104
Abstract Based on the study of existing research results and expert suggestions, the information needs of users when searching in micro-blog are divided into 7 categories: news information, real time information, celebrity information, people information, public opinion, organization information and informative information. According to these categories, a questionnaire is designed to examine the ability of micro-blog search and web search in meeting users' information need. A comparative study is conducted to show the differences of two search engines' ability and the reasons behind the differences.
Key words micro-blog search;web search;information need;questionnaire survey
1 引言
隨著互聯網技術的發展,互聯網應用模式已經由傳統的“人-機”交互模式變為“社會化”交互模式[1]。在用戶生成海量內容的Web2.0時代,如何對信息資源進行再組織,使得用戶快速高效地搜索到所需信息或知識,已經成為業界學界廣泛關注的話題和研究領域。
傳統的網頁搜索引擎利用爬蟲軟件采集資源,而爬蟲軟件抓取信息的滯后性會影響搜索結果的質量,此外,許多用戶不再滿足于舊式的“人-機”搜索體驗,他們更期望利用在線社會網絡(Online Social Networks,OSN)進行溝通協作來獲得質量更高的智能化搜索結果[2]。于是,“社會化搜索”的理念應運而生。
Teevan J等[3]認為傳統搜索引擎建立了信息與信息之間的關系,在線社會網絡建立了人與人之間的關系,而社會化搜索則將信息與人關聯起來,重建了一種人與信息之間的映射。當前,實現社會化搜索的平臺與工具可以分為四類:一是專業的社會化搜索引擎,如谷歌的Social Searcher;……

