營養(yǎng)支持對急性發(fā)作期COPD患者的效果觀察 ??
李雪婷

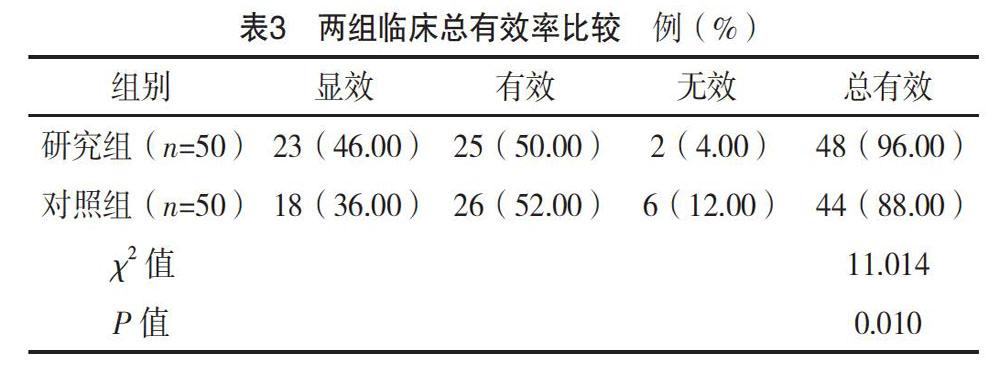
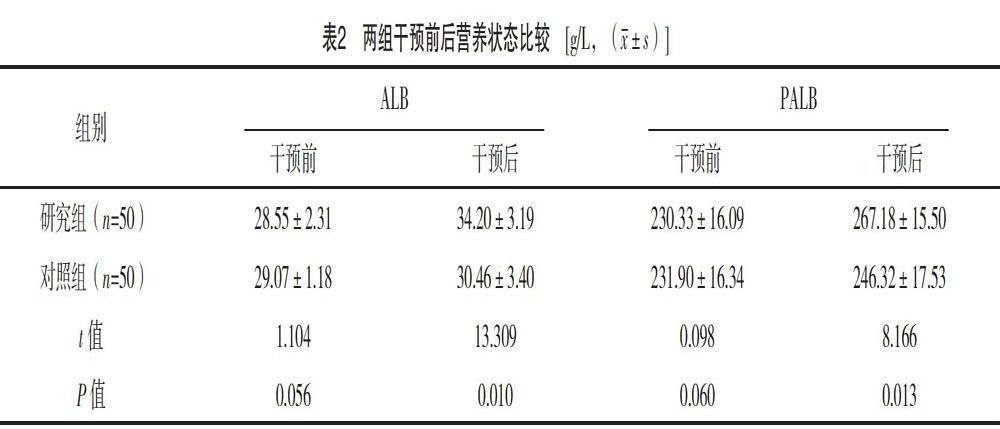
【摘要】 目的:探析營養(yǎng)支持對急性發(fā)作期慢性阻塞性肺疾病(COPD)患者的效果。方法:將筆者所在醫(yī)院呼吸內(nèi)科2019年4-10月收治的100例急性發(fā)作期COPD患者納入觀察中,基于隨機數(shù)字表法分成研究組和對照組,每組50例;兩組均給予專科對癥治療,對照組給予常規(guī)膳食,研究組同時行腸內(nèi)營養(yǎng)(EN),對比兩組臨床療效,并測定干預(yù)前后患者營養(yǎng)狀況。結(jié)果:研究組機械通氣時間、癥狀緩解時間均早于對照組,差異有統(tǒng)計學(xué)意義(P<0.05)。干預(yù)后,兩組ALB、PALB均有改善,但研究組均顯著高于對照組(P<0.05)。研究組臨床總有效率為96.00%,高于對照組的88.00%,差異有統(tǒng)計學(xué)意義(P<0.05)。結(jié)論:在急性發(fā)作期COPD治療中配合營養(yǎng)支持,可有效促進病情轉(zhuǎn)歸,改善患者機體營養(yǎng)狀態(tài),提升臨床效果,有著重要臨床價值。
【關(guān)鍵詞】 慢性阻塞性肺疾病 急性發(fā)作期 營養(yǎng)支持 免疫功能
[Abstract] Objective: To explore the effect of nutritional support on patients with COPD in acute attack stage. Method: A total of 100 patients with COPD in acute attack stage who admitted to respiratory department of our hospital from April to October 2019 were included in the observation. Based on the method of random number table, they were divided into the study group and the control group, 50 cases in each group. The two groups were given special symptomatic treatment, the control group was given conventional diet, the study group was given enteral nutrition (EN) at the same time. The clinical efficacy of the two groups was compared, and the nutritional status of patients before and after the intervention were determined. Result: The mechanical ventilation time and symptom relief time in the study group were earlier than those in the control group, the differences were statistically significant (P<0.05). After intervention, ALB and PALB of the two groups were improved, but those of the study group were significantly higher than those of the control group (P<0.05). The total clinical effective rate of the study group was 96.00%, which was higher than 88.00% of the control group (P<0.05). Conclusion: In the treatment of COPD in acute attack stage, nutritional support can effectively promote the outcome of the disease, improve the nutritional status of patients, and improve the clinical effect, which has important clinical value.
COPD是臨床呼吸內(nèi)科常見的一種慢性病癥,以持續(xù)性氣流受阻為病理特征,有著較高發(fā)病率,以中老年人為主要發(fā)病群體[1]。臨床表現(xiàn)為咳嗽、咳痰、胸悶等,在急性期會顯著加重,且反復(fù)發(fā)作,嚴(yán)重影響到患者身心健康,增加家庭經(jīng)濟負擔(dān)。營養(yǎng)缺乏是COPD患者常見的并發(fā)表現(xiàn),據(jù)報道,在COPD的發(fā)展中通常伴不同程度的營養(yǎng)不良,并發(fā)率在24%~71%[2]。COPD患者因長期缺氧、CO2潴留,同時機體處于高分解代謝狀態(tài),能量消耗會明顯增加,再加上長期攝入不足,會導(dǎo)致呼吸肌功能下降與機體免疫功能受損,在疾病急性加重期更為嚴(yán)重,對臨床療效和預(yù)后造成極大影響。基于此,在COPD急性加重期治療期間如何給予患者營養(yǎng)支持成為臨床研究熱點。本文對筆者所在醫(yī)院收治的100例急性發(fā)作期COPD患者的臨床干預(yù)進行研究,分析營養(yǎng)支持的臨床效果,現(xiàn)報告如下。
1 資料與方法
1.1 一般資料
將2019年4-10月在筆者所在醫(yī)院呼吸內(nèi)科住院治療的100例急性發(fā)作期COPD患者作為觀察對象,均經(jīng)癥狀、影像學(xué)、實驗室培養(yǎng)等檢查確診,符合文獻[3]《慢性阻塞性肺疾病診療指南》相關(guān)診斷標(biāo)準(zhǔn)。……

